What are the diseases of onions and how to deal with them
Onions are a popular agricultural crop in Russia. In one form or another, the vegetable is present in the recipes of almost all first and second courses. Surprisingly, onions contain more natural sugars than apples and pears. During heat treatment, the bitterness inherent in onions disappears, and the vegetable acquires a sweetish taste. However, growing a much needed and useful culture on your own is not easy. Onion beds infest diseases that reduce yields or even kill plants.
The article will tell you about fungal and viral diseases of onions, methods of control and prevention. You will learn what to do if a gray bloom or black spots appear on the onion and how to get rid of onion diseases during storage.
The content of the article
How to understand that the onion is sick
Diseases and pests of onions, batun onions, as well as other species and botanical varieties of plants are the main reason for the decrease in yield and storage losses.
The culture is susceptible to diseases of fungal, bacterial and viral origin... The development of the disease is often associated with a violation crop rotation rules and agricultural techniques of plant cultivation.
Botanically, the onion belongs to the lily family. Like other members of this family, onion plants need protection from harmful microorganisms and insects that carry diseases.
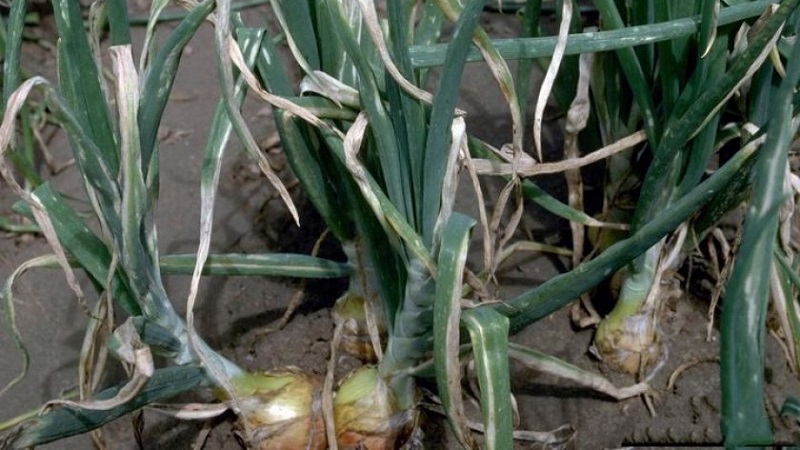

Signs and symptoms
Diseases develop both on the aerial parts of the plant and inside the bulbs. Fighting them is mandatory, otherwise there is a great risk of losing the harvest.
The development of the disease is indicated the following signs:
- yellowing, wilting and deformation of the feather;
- the appearance of spots and mold on onions;
- changes in the structure of tissues of leaves and bulbs;
- black dots on the bow.
Types of diseases
There are two main groups of diseases Luke:
- fungal;
- viral;
- bacterial.
Fungal diseases of the feather
Onion feather is prone to infection:
- peronosporosis;
- alternaria;
- rust.
Peronosporosis
Peronosporosis, or downy mildew, - a common fungal disease that affects all onion varieties... In the spring, infected seedlings cannot be distinguished from healthy ones. But after 20-30 days, the plants begin to wither.
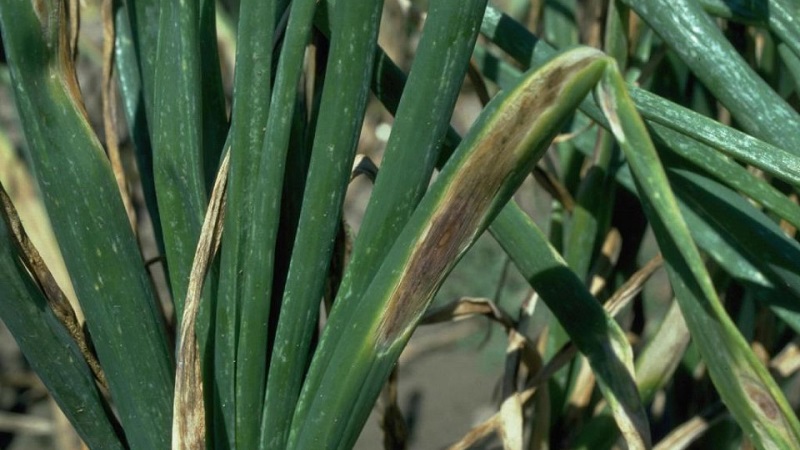

The first signs of infection appear on the tips of the feathers.... They turn yellow and change shape. Then the leaves are covered with yellow spots. In rainy weather, a gray-purple bloom forms. Gradually, the fungus spreads throughout the plant, affecting the bulb.
Caution. Shading, low beds, cloudy weather lead to the active development of the fungus. The dense planting contributes to the rapid spread of harmful spores.
Disease progresses actively at high humidity air and moderate temperature (+ 15-20 ° С). Under unfavorable conditions, the fungus does not die, but only stops development.
Poor-quality planting material is the source of infection. and violation of the rules of crop rotation. Sevok, affected by the fungus, retains its spores until the next sowing season. The pathogen overwinters on seeds and plant debris in the soil.
Alternaria
Fungal disease common in all onion-growing areas... Most dangerous in warm humid climates. It develops quickly, the first symptoms of Alternaria appear within a couple of days after infection.

First, feathers develop watery spots with a white center... Gradually increasing, they darken and become brownish-burgundy. The edges of the spots are surrounded by yellow stripes.
Attention. The causative agent of Alternaria often infects weakened, old plants with peronosporosis. In this case, the feather of the onion turns black and dies off.
Gradually, the disease also affects the bulbs. The tissues acquire a watery structure, then darken, a brown coating appears between the scales.
The fungus hibernates in plant debris, on diseased bulbs and seeds... During the growing season, spores are spread by wind.
Rust
The causative agent is the fungus Puccinia porri Wint, which loves a humid warm environment... The disease is recognized by small orange-yellow swollen spots, which then turn into black dots.
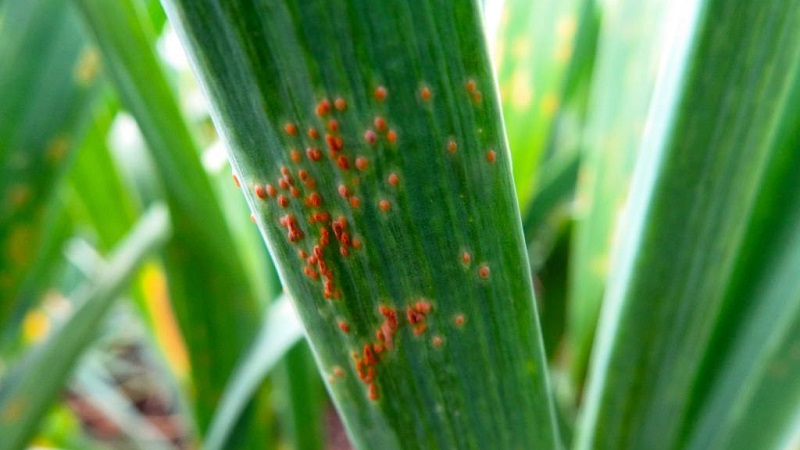

From onion beds, the pathogen moves to currants and other shrubs... Among the reasons for the appearance are called early or thickened planting, an abundance of weeds and excessive watering.
Need to know. The fungus settles only on wet onion feathers. In the period of prolonged rains, spores germinate quickly.
Fungal diseases of bulbs
Bulbs infect the following diseases fungal origin:
- neck rot;
- fusarium rot of the bottom;
- green moldy rot;
- aspergillosis.
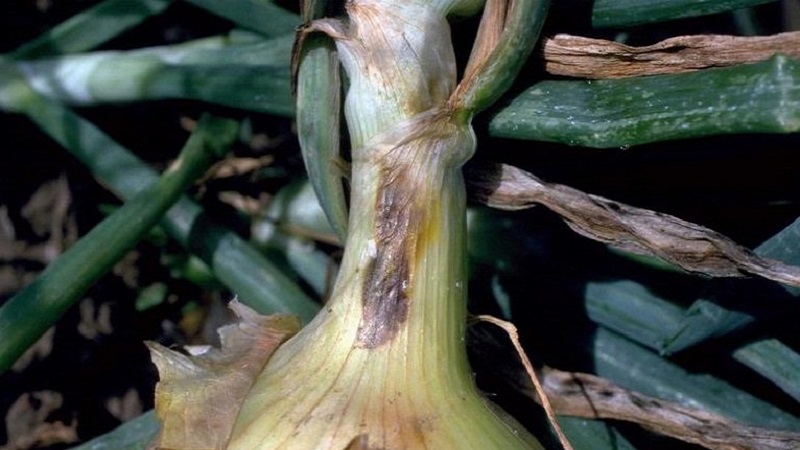
Cervical rot
The development of the disease is caused by a fungus that develops in the decaying remains of plants.... The disease is recognized by the yellowing of the onion neck. Gradually the entire bulb turns yellow to the bottom.
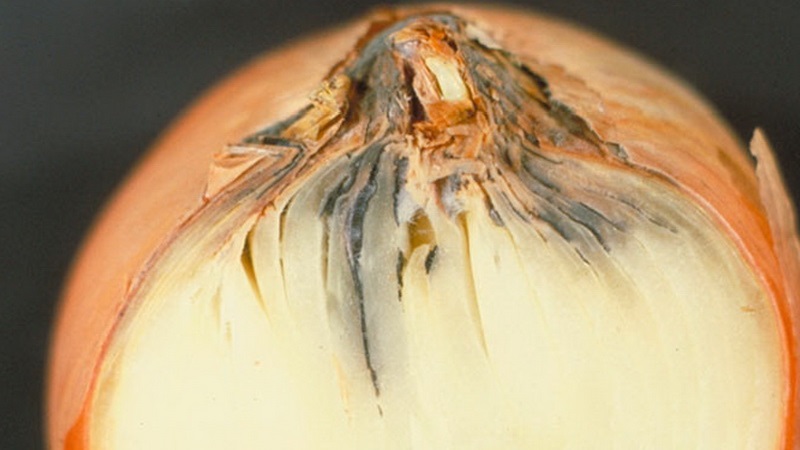

The harvested crop is distinguished by an unpleasant odor and friability of scales... When the head is cut, dark areas are visible at the base, on the sides and on the neck. A photo of onion neck rot is shown below.
Fusarium rot of the bottom
The causative agent is in the soil... First, it affects the tips of the feathers, then leads to their death along the entire length. Gradually spreads further and provokes rotting of the bulb. The tissues become softer and more watery, the bottom rot appears.
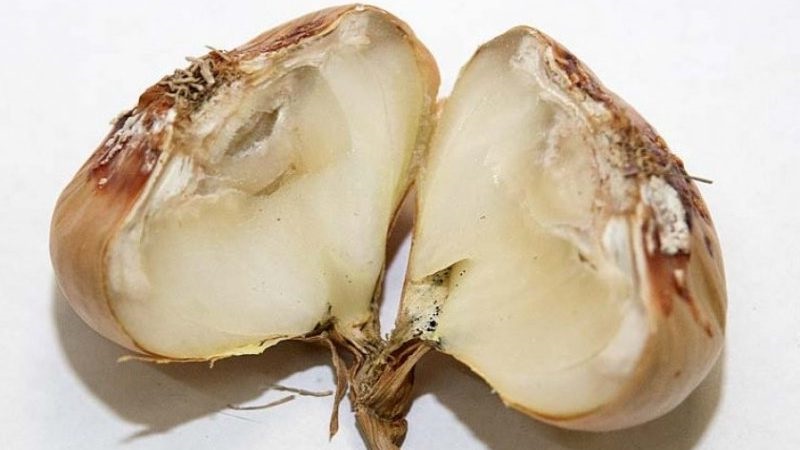
Leads to the onset of the disease excess moisture in the soil, untimely harvesting, contaminated planting material.
It can be useful:
How to grow onions in a plastic bottle
Green mold rot
The fungus infects the vegetable during storage... It is expressed by drying of the shells of the bulbs and the appearance of green mold on the bottom and side parts. The disease manifests itself after 2-3 months of storage.
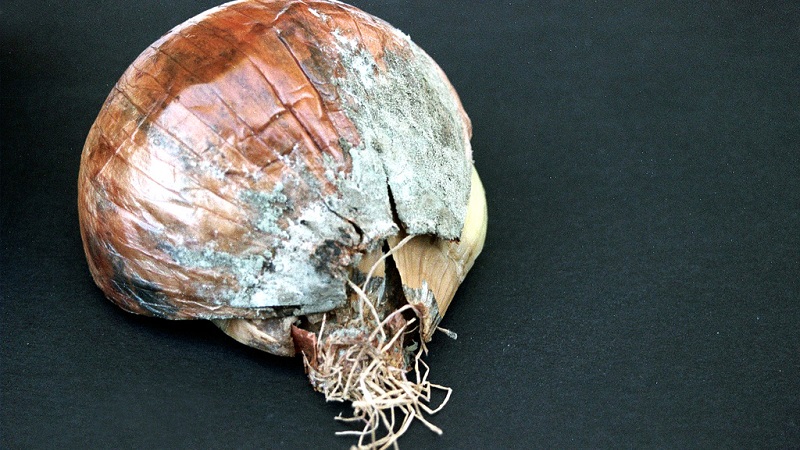
Among the causes of green mold rot are mechanical damage during harvesting, high temperature (from + 3 ° C) and excess moisture (over 60%) in the storage.
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis, or black moldy rot, - the main problem when storing and transporting onions... During the growing season, it is difficult to notice the symptoms of the disease. It is manifested by discoloration of the neck - it is in this place that the pathogen enters the bulb.
Black fungus spores found under dry scales in the absence of external signs of the disease... They acquire a watery texture. After a while, the mycelium of the fungus grows, black spores appear on it.
Important. Aspergillosis is often accompanied by a secondary infection that causes wet bulb rot.
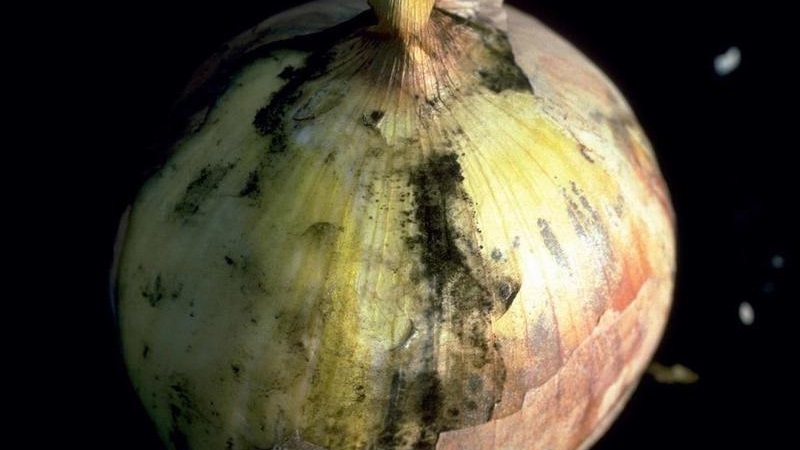

The disease progresses intensively in unripe and undried onion heads... Elevated storage temperatures and lack of ventilation contribute to the development of the disease. The pathogen persists in diseased bulbs and plant debris.
Viral diseases
In addition to diseases of fungal origin, onions are susceptible to viral infections, for example, mosaics and yellow dwarfism.
Mosaic
The green onion mosaic affects both the bulb and the feather. Recognize the disease by light yellow spots and light green longitudinal lines on the stems. The feather edge curls and dries up. At the same time, the development of the bulb slows down or stops altogether.
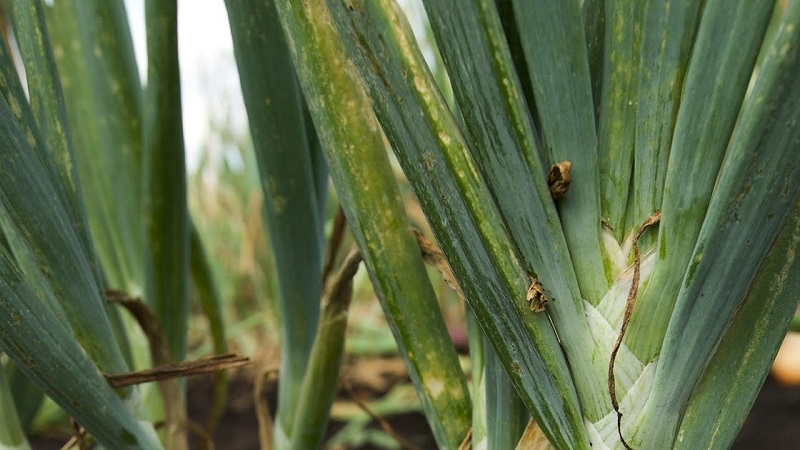

Among the causes of defeat, there are late planting, thickening of plants, lack of control of aphids - a carrier of infection.
Read also:
Yellow dwarfism
Yellow dwarfism, or yellow striping, - a viral disease that affects perennial onions, shallots. Leek it is immune to this virus.
Symptoms of defeat - yellow stripes on feathers and leaf deformation. The greens curl and lie down, the growth of the bulbs slows down.
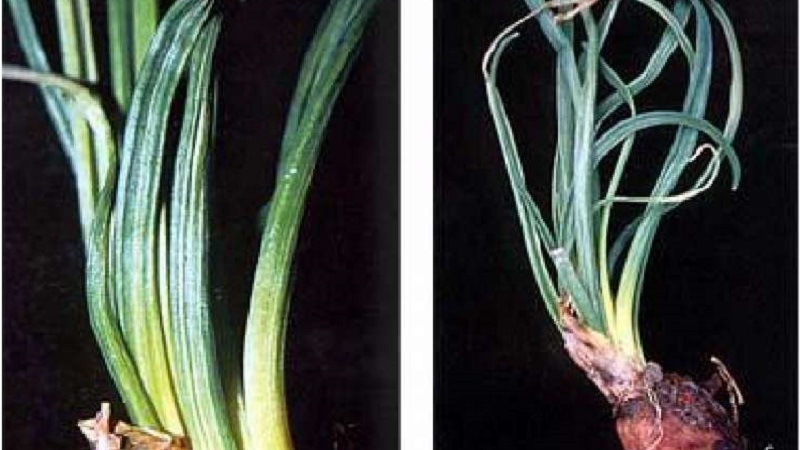

Virus spreads with planting material... Also transmitted by the parasitic plant dodder and some aphid species.
Bacterial diseases
Planting of onions is affected by diseases of bacterial origin, in particular, wet bacterial and black rot.
Wet bacterial rot and black rot
Caused by bacteria damaging harvested crops... Infection of plants in the soil is possible. The husk becomes moist, the inner tissues of the bulb acquire a loose structure, sticky to the touch. When pressed, moisture is released with an unpleasant odor.
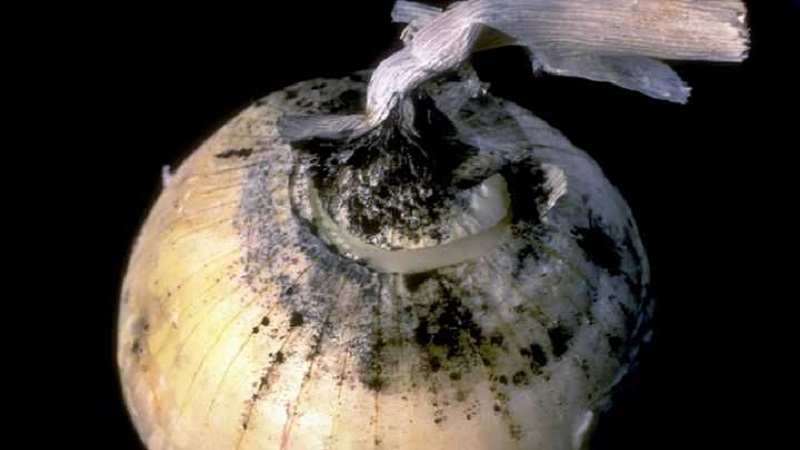
Reasons for defeat - high soil moisture, contaminated soil, violation of storage conditions, damage to the crop by insect pests.
Control methods
The fight against disease begins when the first signs of damage are detected... Otherwise, there is a risk of complete loss of crops and spread of infection to other crops.
Folk
The advantage of folk methods of struggle over chemical - their safety for humans. The processed plantings are suitable for human consumption.
Among the folk remedies, spraying is distinguished.
The most effective remedies:
- Wood ash... The solution is prepared at the rate of 50 g per 10 l of water. Both the aboveground parts of plants and the surface of the earth are cultivated. Spraying is carried out once a week.
 Sour whey... The treatment is effective for fungal infections. Lactic acid bacteria destroy the fungus without harming the onion plantings. To prepare the solution, use serum from any fermented milk product (cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir). The whey is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10 and mixed. The plantings are sprayed once a week.
Sour whey... The treatment is effective for fungal infections. Lactic acid bacteria destroy the fungus without harming the onion plantings. To prepare the solution, use serum from any fermented milk product (cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir). The whey is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10 and mixed. The plantings are sprayed once a week.- Infusion of garlic... Effective for rot, rust, scab, leaf spot. Garlic heads are crushed, diluted with water in a 1: 1 ratio and placed in a dark, warm place for 10 days. For spraying, use 20 ml of solution per 10 liters of water.
- Infusion of plants, for example, horsetail, nettle, wormwood. 1 kg of fresh green is poured into 10 liters of water. The mixture is infused for two weeks, stirring occasionally. As soon as fermentation stops, the infusion is ready for use. For spraying, it is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.
Chemical
If folk remedies did not have the desired effect, then move on to more effective chemicals.
Attention! Onions grown for feathers are not treated with chemicals.
Of the chemicals used:
- disinfection of the garden bed before planting with a solution of copper sulfate (25-30 g / 10 l of water);
- spraying seedlings with a solution of Bordeaux liquid;
- treatment with 0.04% solution of zineb or 0.5% solution of copper oxychloride (once during the period of growth of greenery).

From biological products, effective use "Glyokladina", "Fitosporina-M", "Alirina", "Gamaira". These funds are used 3-4 times during the growing season. The dosage and method of administration are indicated on the package.
Prevention measures
Regular use of preventive measures will protect plantings from the development of diseases. These include adherence to planting rules, cultivation technology, harvesting and storage of seed material.
Pre-planting treatment of the site and seeds
The processing of the site and seed material consists in carrying out the following activities:
- Removal of organic residues from the soil surface. This applies to bulbs with roots and aerial parts of the plant. If there are signs of infection, they are burned.
- Digging the soil in the fall. This helps her to freeze thoroughly in winter and reduces the number of pathogens.
- Warming up the seedlings before planting at + 40 ° C for 8-24 hours.
- Soaking of inoculum in a solution of the biological product "Trichodermin".
Other tricks
Effective and preventive measures:
- Compliance with the rules of crop rotation. Onions are planted in the same place only after 3-4 years. The best predecessors are unrelated plants (cucumbers, pumpkin, cabbage).
- Planting nigella, perennial onions and other varieties separately from each other.
- Periodic inspection of plants for infected specimens.
- Thinning of dense plantings, removing weeds.
- Watering in the morning.
- Compliance with storage conditions - in a dark cool place.

Recommendations and advice from experienced gardeners
Practicing the advice of experienced gardeners, you will save onions from diseases:
- For sowing onions, zoned varieties that are resistant to rot are chosen.
- The beds are weeded regularly to keep the rows of onions well ventilated.
- For sowing, a healthy seed is selected without the slightest signs of infection.
- Onions are planted on fertile, well-loosened, breathable soils. On heavy clay and acidic crops grows poorly.
- To scare off pests that carry infections, use tobacco dust, makhorka and its infusion, plant ash.
- Dill and marigolds, planted around the perimeter and in the aisles, protect the onion from pests and diseases.
- Onions are regularly watered only until early July, then watering is minimized or stopped altogether. Excessive moisture provokes the development of fungal diseases and rot.
- The bulbs are harvested in dry weather, avoiding mechanical damage to the heads.
- Before storage, the crop is dried in a dry, well-ventilated, warm place.
- During storage, the bulbs are regularly sorted out, removing rotten specimens.
Conclusion
Diseases and treatment of onions, including batun and onion, are far from an idle question for gardeners. In order to prevent infection of onion beds with infections, observe crop rotation, water wisely, treat the area before sowing, and avoid thickening of the plantings.
The quality of the seed is important, since many diseases are transmitted through it.
The material was not chosen very well. everything is piled in a heap: photo. disease and treatment. No consistency: Illness, photos, preventive measures and control.
Thank you, we will take note and consider for the future
the material is clearly copied not informative (((
Victor, all materials on our portal pass through strict anti-plagiarism, copying is excluded. Please specify what kind of information you lacked in this article?