Instructions for the correct cultivation of horseradish on your own plot
Horseradish is a frost-hardy and hardy plant that grows in almost every area and is often used in cooking. Despite its unpretentiousness, there are a number of nuances that you need to know to get a plentiful and high-quality harvest. We will tell you in detail about planting and caring for horseradish in the open field, we will share how to grow it so that it does not occupy the entire garden.
The content of the article
Choosing a horseradish variety for growing
The best horseradish varietiessuitable for growing in Russia: Accord, Picadrom, Wasabi, Atlant, Mid-season, Tolpukhovsky, Valkovsky, Latvian, Suzdal, Malinsky and Variegata.
Choosing a variety, start from the desired taste and the available growing conditions. Those who prefer a milder taste choose Katrana or Malinsky, lovers of spicy horseradish - Suzdalsky, Tolpukhovsky or Valkovsky.
Horseradish, bred by domestic breeders, is unpretentious in care, but the cultivation of exotic Wasabi requires attention and effort. Most often it is grown in hotbeds and greenhouses, which allows you to adjust the temperature and humidity.
They also focus on the climatic conditions of the region. For cultivation in southern regions with a mild and warm climate, Katran and Tolpukhovsky are suitable, for planting in the middle zone and the North-West region of Russia - Latvian. The Atlant variety is not afraid of frost and temperature contrast between cold winters and hot summers, therefore it is successfully grown in Siberia and the Far East.
Horseradish growing methods
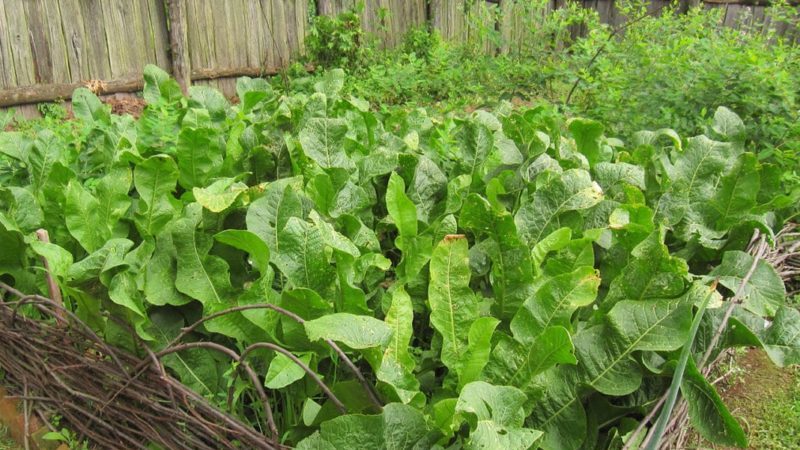

There are several ways to plant horseradish on your own plot. The most popular of them are in the open field and in containers.
In the ground
When growing horseradish in the open field, they form high or raised beds. To do this, make a ridge of the earth with a shovel so that the bed is located above the soil level.
Cuttings with prepared roots (lateral roots and buds are cut off, left at the ends) are planted in the ground at a distance of 30-40 cm from each other at an angle of 30 °, deepening by 10 cm and sprinkling the top with a layer of soil 3-4 cm thick.
Reference. This planting makes it easier to dig up long roots and protects the plants from flooding in high rainfall.
In a container
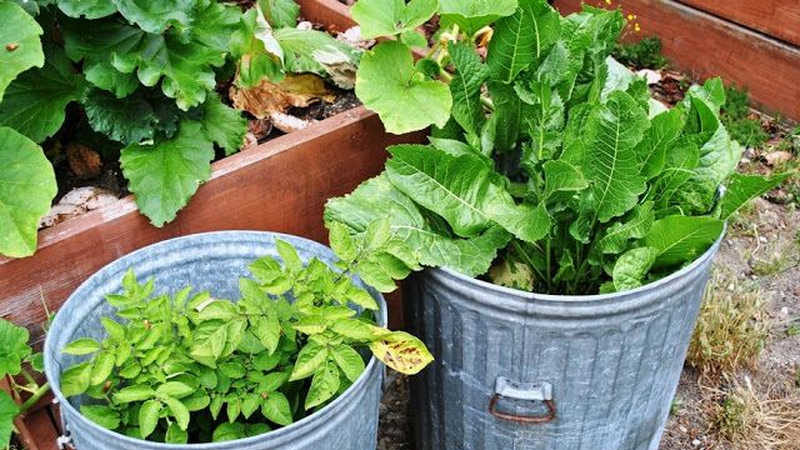

For planting and growing horseradish in a container, select a suitable container (barrel or bucket), fill it with a mixture of soil and humus, bury it in the ground so that only 2-3 cm high sides remain on the surface and several horseradish rhizomes are planted in it. The frequency and method of watering and fertilizing does not change.
To harvest, the container is pulled out of the ground and turned over on its side. At the same time, horseradish roots are not damaged, and it is not difficult to clean them of the earth.
Landing dates

Due to the endurance and resistance of horseradish to adverse conditions, planting is permissible almost at any time of the year:
- in the second half of April, when the soil warms up to at least + 5 ° C to a depth of 10 cm;
- in summer - provided there is no drought and air humidity of at least 70%;
- in autumn, 2 weeks before frost - in central Russia it is the 2nd decade of September - mid-October.
Podzimny planting is carried out in late October - early November, after clearing the soil from weeds and plant debris and digging it up.In this case, the cuttings are buried 3-4 cm in order to protect them from frost.
Training
For planting horseradish, choose a well-lit place or partial shade with fertile, moisture and breathable soil. The best option is black soil, loam, sandy loam, or drained and organic-enriched peatlands. The best predecessors are tomatoes, potatoes and other vegetables.
The plot in the country is prepared in advance (for spring planting - in the fall): the soil is cleaned of weeds, organic fertilizers are applied and dug up. Immediately before planting horseradish, re-digging is carried out, a mixture of equal parts of superphosphate, potassium and ammonium nitrate (30 g per 1 sq. M) is introduced. An additional bucket of peat and sand and 10 kg of manure per 1 square meter are added to the clay soil. m, in acidic soil - ash at the rate of 400-500 g per 1 sq. m.
Reference. In heavy clay soil, horseradish roots become bitter, tough and ligneous, in sandy soil - tasteless.
Containers (metal buckets or barrels) for growing horseradish are pre-washed and treated with a solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection.
Horseradish is most often grown from cuttings. 2 weeks before planting, they are cut so that the lower cut runs diagonally, and the upper cut across. Leave in a warm place and cover with a damp cloth or a layer of peat for germination. After that, the buds that have appeared in the middle part are removed in order to exclude excessive branching. The buds at the bottom and at the top of the cuttings are left: roots will grow from the lower ones, and a leaf rosette from the upper ones.
How to plant horseradish correctly
Prepared cuttings are planted in the ground at an inclination of 30-45 ° with an oblique cut downward, deepening by at least 10 cm, and sprinkle the upper part with a layer of earth 4-5 cm thick.The distance between plants should be 30-40 cm, between rows - 70 cm.
After planting, the soil is compacted and watered. This promotes the early rooting of the cuttings.
Further care

Despite the unpretentiousness of horseradish, it still needs basic care: watering, fertilizing and loosening the soil.
Watering and fertilizing
At the first time after planting, horseradish is watered once every 7-10 days, consuming 2-3 liters of water per 1 sq. m, after rooting - only in dry weather at the rate of 3-4 liters of water per 1 sq. m.
The plant does not require fertilization. Monthly feeding with a solution of complex fertilizers (50 g per 10 l of water) is permissible.
Thinning, weeding and loosening
Thinning is carried out immediately after the appearance of the first shoots, removing all weak shoots. Weed the soil as needed, preventing the growth of weeds.
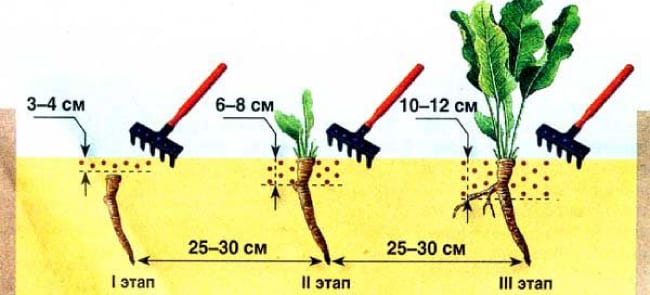
The earth is loosened 3 times over the summer:
- a week after landing at a depth of 3-4 cm;
- after sprouting 6-8 cm deep;
- after 12-14 days to a depth of 10-12 cm.
The soil is loosened carefully, at a distance from the plants, so as not to damage the root system.
Protection against diseases and pests

Diseases and pests that can affect horseradish are described in the table.
| Pest / disease | Signs | Treatment / prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Wavy flea | Females lay eggs on the surface of the soil, eat leaves, leaving holes in them. | The earth is loosened, the plantings are sprayed with insecticidal preparations, for example, "Foksim" or "Aktellik". |
| Cabbage moth | On the underside of the leaf plates, pest eggs can be seen, the larvae gnaw the leaves. | It is possible to completely eliminate the attack of pests when planting horseradish early, before the appearance of butterflies. To get rid of insects, they use insecticidal preparations ("Karbofos", "Actellik"). |
| Cabbage bug | Yellowing and death of leaves. | The foliage is treated with soapy water, the plantings are powdered with a mixture of wood ash and tobacco dust, and they are sprayed with chamomile broth or infusion of onion husks. |
| Babanukha (horseradish leaf beetle) | Pests gnaw the leaves of plants. | In the case of a small number of insects, they are harvested by hand; in case of serious damage, the plants are treated with a decoction of yarrow, wormwood or chamomile. |
| White rot | Rhizomes are covered with white bloom. | The soil is dug deeply, lime is added to it, horseradish is treated with copper-containing fungicides: "Ordan", "Previkur", "Acrobat MC". |
| Belle | A plaque appears on the leaves, reminiscent of white oil paint, gradually the foliage dries up. | Affected plants are removed, plantings are treated with "Ordan" or "Previkur". |
| Ascochitosis | Brown-yellow spots appear on the plants. | Horseradish is treated with Bordeaux liquid. |
Collection, storage and processing of crops

The rhizomes are harvested at the end of October at least 2-3 years after planting, digging them out of the ground and clearing them of small roots and soil. The leaves are cut earlier so that the stems are no more than 10 cm long - they protect the roots from damage.
Fresh, no part of horseradish can be stored for a long time. The leaves are folded in a bag and kept in the refrigerator for 10 days. It is important not to wash them before storing them. Freshly dug roots are stored in the same way (after a while they become soft, but retain their taste until spring) or put in wooden boxes, sprinkled with sand and put into a cellar with a temperature of 0 ... + 3 ° C.
The harvested crop is processed and made from horseradish a spicy seasoning, which, after rolling into jars, is suitable for eating for six months.
Another way to keep horseradish as long as possible is to make a dry powder out of it. To do this, the roots are washed, peeled and cut into pieces, then laid out in a thin layer on a baking sheet, dried for an hour in an oven with an open door at a temperature of + 100 ° C and grinded in a coffee grinder. Store the powder in paper bags. To obtain the finished product, take it for 15 minutes. pour hot water.
How horseradish reproduces
For seed propagation, sowing is carried out in early spring, when the soil warms up to + 5 ° C, or in late autumn, 2 weeks before frost. The seeds are buried 2.5-3 cm, 7-10 cm apart, keeping 90 cm between rows.
Horseradish rarely gives seeds, so it is most often propagated vegetatively:
- By cuttings. Planting material is harvested in the fall, by cutting off branches 20-30 cm long and at least 1 cm in diameter from the main root of 1-year-old plants. Thin stems with an apical bud are also used as cuttings. The prepared planting material is tied and stored in a cellar or basement, covered with sand or sawdust.
- Apical buds. The buds at the ends of the main or lateral shoot are cut along with pieces of rhizome, rooted in a fertile substrate, and then seated in separate containers, periodically removing excess leaf rosettes, leaving a maximum of two.
How to prevent overgrowth
Horseradish reproduces vegetatively and without much care, therefore, the roots left in the ground after harvesting over several years greatly grow and complicate crop rotation, turning from a garden crop into a weed.
To avoid this, they timely thin out the horseradish roots with a pitchfork or remove excess horseradish from the garden, covering the area with roofing material or a similar opaque material - a lack of light provokes the death of plants.
You can eliminate the growth of horseradish by limiting the space for its cultivation. To do this, it is planted in wooden boxes, buckets, barrels or "sleeves" made of polymer film.
It is interesting:
Uses of horseradish leaves and their health and beauty benefits
Conclusion
Growing horseradish in your garden is easy. The culture requires virtually no maintenance, it is enough to choose a suitable planting site. Often, gardeners have another problem: horseradish grows too much and litters the site, oppressing other crops. You can fight this by growing the plant in a container specially designated for this. Knowing the rules of horseradish cultivation, you can get a rich harvest for many years.