Effective pest control: how to get rid of a wireworm in a potato patch
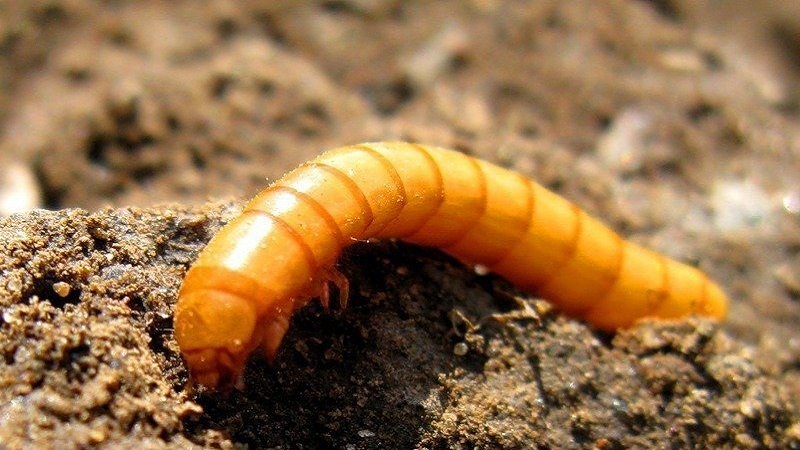
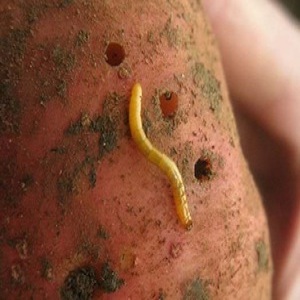
The body of the wireworm has a hard, wire-like shell, hence the name of this insect. The worms of yellow or orange color are the larvae of the click beetle, the appearance of which on the site indicates that it is time to be alarmed so as not to be left without a potato crop.
How to get rid of a wireworm in a potato area, which techniques, folk remedies and chemicals are more effective, you will learn from our article.
The content of the article
What a wireworm looks like and how is it dangerous for potatoes
Wireworms are click beetle larvae that live in the ground for 3 to 5 years, after which they turn into adults. Beetles come in a variety of colors: dark brown and black. They differ from other beetles in their ability to roll over from their backs onto their legs, while emitting a characteristic click. It is thanks to this feature that they got their name.
 The most common clickers are the dark striped and steppe beetle.... During the day, they hide under foliage, topsoil, boards, etc. Insects live in areas with moist and acidic soil, covered with weeds, and winter in the soil.
The most common clickers are the dark striped and steppe beetle.... During the day, they hide under foliage, topsoil, boards, etc. Insects live in areas with moist and acidic soil, covered with weeds, and winter in the soil.
Females lay 200 eggs each from June to July, from which white larvae with a delicate cover emerge. During this period, the wireworm is most vulnerable and often becomes the prey of ground beetles, chickens, and turkeys.
After a few molts, the outer shell of the larvae changes color from white to yellow or orange, becomes denser. Such larvae become a treat for rooks and starlings.
Wireworms live in the topsoil (no deeper than 5 cm), and with a decrease in air temperature or drought they go 50-60 cm deep. The larvae often concentrate in the area of the rhizome of weeds.
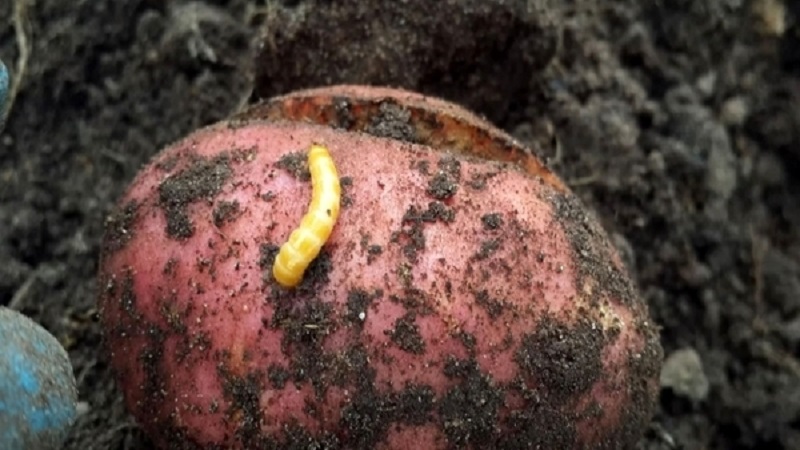
The pest's favorite food is potatoes, corn, carrots, beets, wheat, barley... In drought, the wireworm eats potato tubers and roots especially zealously, because they contain large reserves of valuable moisture.
Reference. The greatest threat to the crop is carried by larvae of 2-4 years. They reach a length of 2-3 cm and resemble worms with clear segments on the body.
Signs of a pest on the site
The appearance of a pest on the site is indicated by such signs:
- through holes in tubers;
- small dark depressions on the peel;
- single sluggish bushes among healthy plants (the larvae move in a vertical direction, making their way into the depth of 1-2 m, however, they do not move further from the root system than 20 cm, therefore, detached bushes and very rarely whole beds are usually attacked);
- in the process of collecting young potatoes, individual specimens of wireworm appear on the surface of the soil;
- the appearance of click beetles on the site.

Control methods
Pest control is carried out comprehensivelyusing agrotechnical techniques, chemicals, herbal infusions and traps.
Other pests and diseases of potatoes:
Chemicals
Treating potato plantings with chemicals - an extreme measure... Fungicides are toxic to the environment and require strict adherence to instructions. The table contains the most effective drugs.
| Name / active ingredient | Consumption rate | Protection period and frequency of processing |
| "Barguzin" (diazinon) | 150 g per 100 sq. m | 40 days, once when planting potatoes |
| "Pochin" (diazinon) | 30 g per 10 sq. m | 40 days, once when planting potatoes |
| "Provotox" (diazinon) | 40 g per 10 sq. m | Has no waiting period, acts instantly. Deposit 1 time at landing |
| "Medvetox" (diazinon) | 3 g per 1 sq. m | 60 days, 1 time landing |
| "Zemlin" (diazinon) | 30 g per 10 sq. m | 60 days, 1 time landing |
| "Taboo" (imidacloprid) | 0.08-0.1 g / l (10 l solution per 1 ton of tubers) | Pre-planting seed treatment, waiting period - 60 days |
| "Prestige" (imidacloprid, pencycuron) | 0.7-1 g / l (10 l solution per 1 ton of tubers) | Preplant seed treatment, waiting period - 60 days |
| "Force" (tefluthrin) | 10-15 g per 10 sq. m | Spread into soil when planting, no waiting period |
| Aktara (thiamethoxam) | 0.3-0.6 g per 10 l | Spraying holes when planting, has no waiting period |
Biological preparations
Biological products have a gentle effect on ecosystems and the environment... Their effect on wireworms is based on microscopic pathogenic fungi.
 Preparations "Entocid" or "Metarizin" contain mycelium and spores of the fungus Metarhizium anisopliae... When it gets into the ground, the fungus is in an active state and is waiting for its "finest hour".
Preparations "Entocid" or "Metarizin" contain mycelium and spores of the fungus Metarhizium anisopliae... When it gets into the ground, the fungus is in an active state and is waiting for its "finest hour".
After the wireworm enters the body, the fungus begins to break down its adipose tissue, the digestive system, the respiratory system, and the nervous system.
The spores of the fungus germinate after 12 hours. The larvae die in 40-120 hours. In the future, the fungus uses the body of the pest for further development. Regular use of the product helps to significantly reduce the wireworm population.
The table shows how to use biological products.
| Application method | Norm | Processing method |
| Soil application | 100 g per 100 sq. m | Mix 100 g of the product with 2 kg of river sand or soil and distribute evenly over the site (in spring or autumn before soil treatment). |
| Tuber processing 3 days before planting | 50 g for 3 liters of water | Soak the tubers in the prepared solution for 30 minutes and leave in a dark place. |
Another modern biological agent against wireworm - "Nemabakt", contains a predatory nematode. Penetrating into the body of the larva, the nematode infects it with a deadly bacterium. The drug is safe for plants and earthworms.
For solution preparation Fill a bucket with water, place a mosquito net on top so that the edges hang down. Empty the package of the drug. The water temperature should match the ground temperature. Leave the liquid to sit for an hour. Remove the mesh and water the soil in the morning or evening, cloudy or rainy weather. Water the area again after an hour. Consumption - 1 bucket of 10 liters per 100 sq. m.
Traditional methods
Herbal-based folk remedies are safe for the environment. In practice, gardeners use such improvised means to get rid of the wireworm:
 lay out ground eggshells on the beds;
lay out ground eggshells on the beds;- the holes are etched when planting with infusion of nettle and dandelion (0.5 kg of grass per 10 liters of water);
- the tubers are treated with an infusion of wormwood and celandine (300 g of grass per 10 l of water);
- watering the beds with infusion of coltsfoot (200 g per 10 l);
- in areas where walnuts grow, fresh leaves are placed in the holes;
- ash, onion husks, moss are poured into the pits and a pinch of salt is added;
- spill the holes with a solution of birch tar (200 ml per 10 liters of water);
- roll each potato in mustard powder before embedding in the ground;
- spill the depressions under the seed with a strong solution of potassium permanganate (2 g per 10 l).
Lures and traps
Making baits and traps is troublesome, but the result will certainly please:
- Rotten tubers are soaked in any insecticide for 24 hours and buried in the ground, in places of maximum concentration of larvae. After two days, the bait is collected, into which the pest has crawled, and disposed of away from the site.
- Pieces of carrots and potatoes are placed in a 500 ml jar, the container is driven into the ground, leaving the neck at the soil level. Larvae and beetles will fall into the trap.
- Vegetable "shashlik" is made from pieces of carrots, beets and potatoes by stringing them on a thick wire, and before planting the potatoes, they are buried in the ground to a depth of 10 cm.
- 1.5-2 weeks before planting potatoes, the plot is sown with corn, oats, barley and wheat, then they are dug up together with the larvae that "like" to settle in the roots of these crops.Before sowing, the seeds are treated with a solution of any insecticide.

Agrotechnical techniques
Agrotechnical methods are used to scare away adults and larvae.:
- The site is sown with siderates. The wireworm does not like mustard, rapeseed, spinach, rape, buckwheat, sweet clover. Decayed plants release essential oils that repel larvae.
- Peas, beans and beans are planted near cartel beds to repel the pest and enrich the soil with nitrogen.
- It is believed that the wireworm does not tolerate the smell of dahlias. Neighborhoods with them do not withstand and weeds.
- Reduce soil acidity. In the spring, when digging and loosening, lime, ash, chalk, dolomite flour are introduced.
- The soil is fertilized with ammonium nitrate or ammonium sulfate (20–30 g per sq. M).
- The plot is mulched with needles. The smell of pine or spruce needles repels the pest.
- Black beans are planted next to the potatoes to repel insects.
Read also:
Features of the fight against wireworm in spring and autumn
Agrotechnical techniques for combating wireworms in spring and autumn are not much different. All actions are aimed at stabilizing the level of soil acidity (larvae do not "like" neutral soil), increasing fertility and harvesting weeds.

Late in the fall, when digging a site, a soil deoxidation procedure is carried out... This creates favorable conditions for the growth and development of potatoes, allows you to get rid of the wireworms that have left for the winter.
Addition rates:
- dolomite flour - 400 g per sq. m;
- slaked lime (in acidic soil - 500 g per sq. m, medium acidic - 300 g per sq. m);
- chalk - 300 per sq. m;
- wood or peat ash - 400 g per sq. m.
In the spring, work is carried out to eliminate click beetles... During the day they hide in shady and humid places. Manure heaps or cut grass are used as baits. After 4-5 days, the bait is removed from the site and thrown into the fire. A similar procedure is carried out in the fall, but the grass is left to lie until the onset of cold weather.
Prevention
Compliance with preventive measures can significantly reduce the wireworm population... It will be possible to completely remove the pest after 2-3 years of hard work.
Prevention rules:
- Compliance with crop rotation... It is not recommended to plant potatoes in the same place from year to year. This is especially true for infected areas. The best precursors for potatoes are alfalfa, canola, legumes, onions, garlic, wheat, rye, and oats.
 Timely harvesting of tops (two weeks before digging) and tubers. After drying, the potatoes are removed to storage.
Timely harvesting of tops (two weeks before digging) and tubers. After drying, the potatoes are removed to storage.- Disinfection of tubers before boarding.
- Reducing soil acidity... Horsetail, plantain and sorrel grow on strongly acidic soil. These are a kind of indicator plants.
- Attracting the enemies of the wireworm and the click beetle: starlings, crows, blackbirds, turtle doves, rooks, wagtails, tits, ladybirds, ground beetles.
- Weeding... The wireworm uses burdocks and wheatgrass as a hiding place.
- On uncultivated plots it is better not to plant potatoes. After digging the soil, it is recommended to wait at least a year and sow the site with green manure, tomatoes, eggplant, peppers, beans, zucchini, cucumbers.
- Planting potatoes in compliance a certain interval - no thicker than after 30-40 cm. With a thickened planting, the plants acutely feel the deficit of sunlight and air. In such conditions, an ideal environment is created for the development of wireworms.
Advice and feedback from experienced gardeners
At various thematic forums, gardeners share recommendations and effective recipes for the destruction of a wireworm on the site.
Ivan, Lobnya: “Every gardener is probably familiar with a worm that eats potatoes. Agrotechnical techniques help me to fight the pest. Before planting potatoes in the spring, I sow the field with rapeseed.The wireworm does not like him and leaves the site. I advise you not to bring land to the site from unfamiliar places. It probably contains larvae, and all your work to cleanse the soil from the pest will go down the drain. ".

Maria, Smolensk: “What is a wireworm, all summer residents know. These are the larvae of the click beetle. They are very dense and difficult to crush. If you don't want to share the crop with a pest, pay attention to modern insecticides. I use Provotox for mass distribution. I try to comply with the norms of manure application. Remember that the soil can be fertilized only with rotted manure, avoiding an overabundance. This makes the soil too acidic. ".
Denis, Stavropol: “It is very unpleasant to find a worm on a potato. Many fall into despair because they know how difficult it is to get rid of it. I want to share one effective way that I learned about several years ago. First of all, I took care of normalizing the acidity of the soil, added dolomite flour. Then, when planting potatoes, ash and onion skins were added to each hole. I planted marigolds near the beds. The juice of these flowers is poisonous for the wireworm. ".
Conclusion
Fighting a wireworm in the garden is not an easy task, but a feasible one. It will be possible to destroy the "enemy" in the shortest possible time if: observe the crop rotation, sow green manure, process the tubers before planting, deacidify the soil by liming, it is normal to introduce chicken manure or cow dung into the soil, remove weeds, tops on time, and harvest.
Agrotechnical techniques are recommended to be used in combination with heavy artillery - fungicides (Medvetox, Prestige, Aktara, Barguzin) and biological products (Entocid, Metarizin, Nemabakt). With a small area of damage, plant solutions, walnut leaves, and onion husks are effective.