Manure as fertilizer for potatoes: when is it better to apply, in autumn or spring
Manure is one of the most popular and valuable fertilizers, but not many people know how to use it correctly. In order for nutrients to benefit potato plantings, it is important to use specially prepared organic matter and observe the measure in dressing... Read below what types of manure are, which manure is better and how to use it for feeding potatoes.
The content of the article
Manure and dung as fertilizer for potatoes

The chemical composition of manure and its properties depend on the type of animal, the feed used, the bedding material and the method storage.
From the point of view of origin, there are:
- Small livestock manure (sheep, lamb, goat) contains few substances useful for plants, therefore it is least in demand. It is mainly used on heavy loams and clay soils.
- Pig manure decomposes in the ground longer than other species, cannot create high temperatures. The reason is the mixed nutrition of pigs - both plant feed and animal products.
- Horse dung - the most valuable due to its rich composition: it contains a lot of potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus. The porous structure decomposes well, releasing a large amount of heat - the temperature rises to 70 ° C. This allows the use of horse manure for heating greenhouses and open beds. It also stimulates the activity of soil microorganisms, increasing the humus content, loosens heavy soils, and helps the soil retain moisture.
- Cow dung, despite its popularity, it has low nutritional characteristics, therefore, on marginal soils, it is applied in large quantities or in combination with other fertilizers. Cow manure decomposes more slowly than horse manure and emits less heat (no more than + 32 ... + 34 ° С at a depth of 1 m).
The quality of the manure also depends on the litter material. The best material is straw and hay, whose fiber increases the looseness and moisture content of the soil.
Among the litter, the most valuable are:
- Chicken manure richest in nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium and potassium. It also has a high concentration of cobalt, boron, zinc, sulfur, magnesium.
- Rabbit able to replace potassium salt, superphosphate and ammonium sulfate. Softens dense soil, warms it up and makes it friable, saturated.
According to the degree of decomposition, the following types of manure and dung are distinguished:
- Fresh contains weed seeds, spores of harmful fungi and helminth eggs. It is undesirable as a fertilizer in its pure form, since it can inhibit plants, stunt growth and even lead to death. It is most often used for the preparation of slurry - a fermented aqueous solution for root top dressing.
- Semi-mature differs from fresh in dark brown color and loose structure. Used by under the autumn digging (from 500 g to 5 kg per 1 sq. m).
- Well rotted is an almost black mass with a viscous, smearing structure. It is lighter than fresh or semi-decomposed, so its consumption increases. Contains less nutrients.
- Granulated retains all the useful properties of fresh fertilizer, does not have an unpleasant odor. Such manure is free of chlorine and pathogenic flora, its pH is balanced. It is used both dry for digging and as a liquid top dressing.
Beneficial features
The benefits of manure as fertilizer include:
- rich set of biological substances;
- easily digestible form of potassium, phosphorus, boron, nitrogen and other elements;
- uniform and long-term positive impact on the soil;
- the presence of active microflora and an increase in the intensity of humus formation;
- acceleration of the decomposition of harmful chemicals (insecticides, pesticides, fungicides) and neutralization of excess salts formed by mineral fertilizers;
- the ability to use as a mulching material.
How to apply
There are several rules for using manure as fertilizer:
- Fresh and semi-rotten manure is applied to the soil in the fall after harvesting harvest, used in diluted form for root dressing or scattered between rows so that it disintegrates in the rain.
- In autumn plowing, composted organic fertilizers, including humus, are used.
- In spring and autumn, manure is buried to a depth of 25-30 cm so that it is not washed away by rains. And in winter they are scattered over the snow, then when the water melts, it will saturate the soil with fertilizer.
Humus as fertilizer
Humus is the last stage of manure decomposition... It is similar to earth in both appearance and smell. Despite the fact that the concentration of nutrients in humus decreases several times, it is considered the best fertilizer and is used for preparing soil mixtures and mulching.
Properties
Humus improves the quality of the soil, making it lighter, more water and breathable. When applied in autumn, it populates the substrate with useful microflora and promotes the appearance of earthworms.
Plants grown on humus receive nutrients in the most accessible form, which enhances photosynthesis and increases resistance to disease.
How to cook

To prepare a compost heap, you need:
- Build a fence with one open wall or dig a hole.
- Put straw, sawdust or peat on the bottom.
- Lay fresh and semi-rotten manure, plant tops in layers. For humus, you can use a mixture of feces from various animals, including pigs.
- Moisten each layer with warm water or slurry.
- Cover the top with a waterproof material, after making holes in it for air.
It is important to maintain the optimum discussion temperature at + 30 ° C. If the "burning" is too active, the compost heap is covered with earth, blocking the air supply.
During the heat, humus can dry out, so during the summer it is shoveled several times and, if necessary, moistened. The use of microbiological preparations such as "Shining-3" and "Baikal" accelerates fermentation.
Reference. You can regulate the chemical composition of humus by adding certain plants to the compost. For example, the weed white sweet clover, perennial lupine, seradella, whip of peas and beans are rich in nitrogen. A large amount of phosphorus contains the green mass of mustard, dandelion, rape, valerian and sorrel. The source of potassium is the tops of nightshade (tomatoes, eggplants, peppers), pumpkin (cucumbers, zucchini, squash), Jerusalem artichoke, as well as nettles, comfrey, chamomile, yarrow, apples and pears. Raspberry shoots will help to enrich compost with iron.
The time required for humus to form depends on the composition of the compost heap and the conditions:
- peat-manure compost takes 4-5 months;
- manure with straw and EM preparations - 1-2 months;
- compost only from manure - 1.5-2 years.
Application features
When should humus be introduced into the ground? It can be used for autumn or spring digging, poured directly into the holes during potato planting or used as mulch when hilling grown bushes.
When is it better to apply manure under potatoes - in autumn or spring
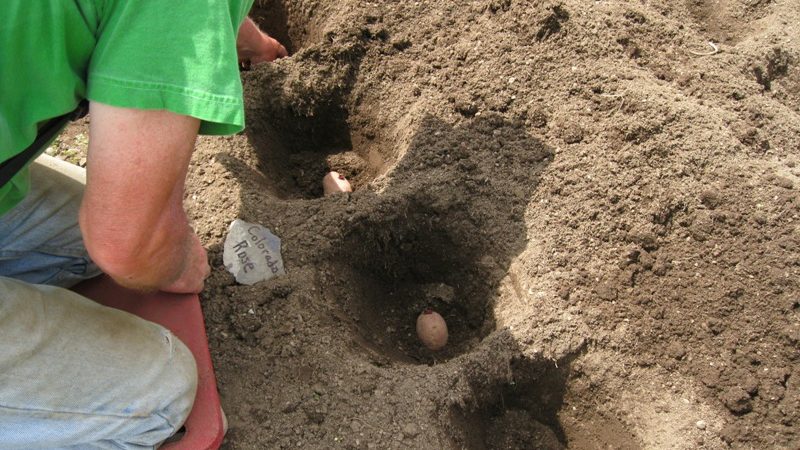

Fresh and semi-rotted manure is brought into the ground only in autumn, so that it can ferment during the winter months. In spring, fresh planting can "burn" plantings due to its high urea content.
In the spring, rotted manure is used, observing certain norms for the introduction of organic matter:
- on depleted soils or with a break of 3-5 years - 5 kg per 1 sq. m;
- in other cases - from 500 g to 1 kg per 1 sq. m.
From light sandy and sandy loamy soils, organic matter is quickly washed out, therefore it is recommended to fertilize them in the spring, and loamy soils - in the fall.
Rules for applying manure for potatoes
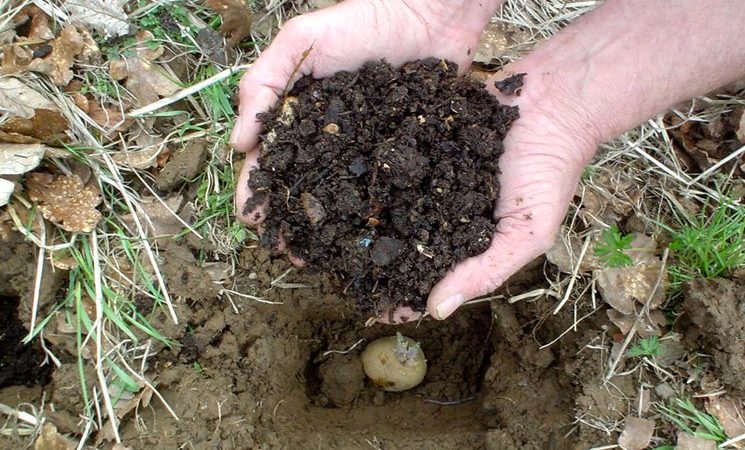

In autumn or spring, rotted manure is scattered over the entire area allocated for planting. It is important to dig up the soil with a shovel or plow the soil on the same day, since the naked fertilizer dries quickly, losing value.
Attention! Digging technique: so that the top, fertilized, layer of soil is below, the earth is captured with a shovel and turned over in the air. The dug row forms a trench after itself, into which a new portion of manure is introduced.
Organic fertilizers in the form of humus can be applied directly to the hole during planting. This will save fertilizer because the tubers will be fed directly from the substrate. The application rate in this case is 150-200 g per bush. The addition of 1 st. l. wood ash. A significant drawback of the method is the laboriousness and the risk of developing scab.
When the bushes reach a height of 8-10 cm, you can start feeding. To do this, manure is diluted with water: fresh - in a ratio of 1:10, semi-rotten - 1: 8. A good result is obtained by a combination of organic matter with a small portion of superphosphate. Fertilizer is applied under the root system during the first hilling, trying not to touch the tops.
During the budding period of potatoes, it is undesirable to use manure. The formation of tubers is stimulated by potassium and phosphorus fertilizing, and nitrogen contributes to the growth of green mass.
How much fertilizer should be applied during the flowering phase of plants? Can be supported with a mixture of organic matter and mineral fertilizers:
- 10 liters of water;
- 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate;
- 1 tbsp. slurry.
Such a solution is insisted for two days, and then water the soil under the potatoes at the rate of 500 ml per bush.
Tips & Tricks

Almost every garden owner has his own secret of working with organic fertilizers. The most proven ones are:
- You can improve the characteristics of cow dung by mixing 2 parts of mullein with 1 part of sawdust. This speeds up decomposition and raises the temperature of the discussion. A mixture of cow and horse manure with dry loosening materials is also effective: moss peat, sawdust, fire (stiff flax and hemp stalks).
- Horse manure is used together with straw, last year's foliage, peat and cut grass. The combination with sawdust gives low quality characteristics.
- Chicken droppings as a fertilizer has a prolonged effect, so it is enough to apply it once every 2-3 years.
- Granular manure is considered the most sterile and convenient for use. It is used according to the instructions on the package.
Conclusion
Although organic matter has undeniable advantages over mineral fertilizers, its improper use can seriously harm plants and even lead to their death.
Fresh manure should be used with extreme caution, since a high concentration of nutrients leads to mineral imbalances, and weed seeds and insect larvae undigested by animals only worsen the composition of the soil. The most preferred are semi-rotten manure and humus.