How to pinch cucumbers in a greenhouse correctly: rules of care from planting to harvest
The formation of cucumber bushes is an important agrotechnical measure, the meaning of which is the selective removal of plant parts. If this procedure is neglected, the yield of the crop decreases, the quality of the fruits suffers, and their ripening begins later. Consider the rules for pinching cucumbers and caring for them in the greenhouse from planting to harvest.
The content of the article
What is pinching and what is required for
The term "pinch" means to remove, cut off with your fingers or garden tools the growth point - the apical bud.
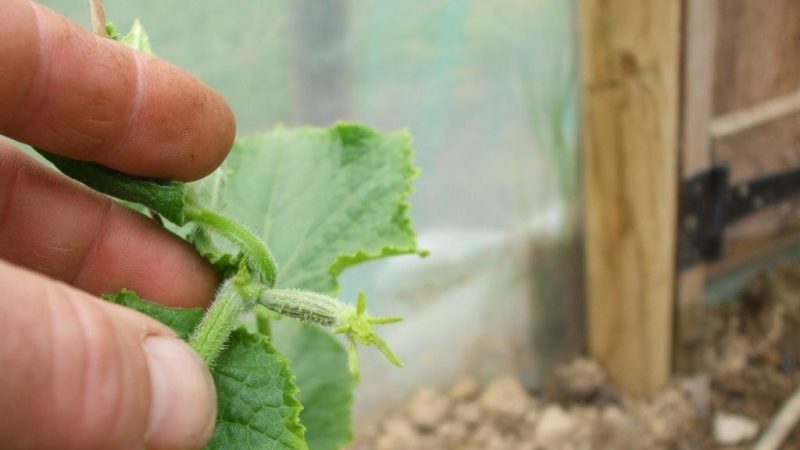

Pinching is carried out to prevent the following factors:
- strong thickening of the bush, which leads to a lack of lighting;
- poor ventilation of plants;
- a large number of barren flowers;
- the spread of pests and diseases.
The procedure promotes the development of the root system, and this is one of the main factors affecting the size and number of ripening fruits.
What other stages of cucumber care exist
In addition to pinching, cucumbers are organized with the correct irrigation regime - at least 5 liters of water per 1 m2, preferably in the morning, before the onset of heat. After moistening, the soil is loosened, giving the roots access to oxygen. During the season, 3-4 fertilizing of plants is done, using both organic and artificial fertilizers.
The air temperature in the greenhouse is maintained at + 18… + 30 ° C. The optimum humidity is at least 80%; drafts are not allowed with mandatory daily ventilation. The bushes are formed and tied on time using vertical or horizontal supports.
Benefits of pinching cucumbers in the greenhouse
Already during tying to the support of the seedlings, the first manipulations are carried out to form bushes. Pinching plants in the greenhouse affects the formation of ovaries, helping cucumbers to release more female flowers than male barren flowers.
Strongly overgrown bushes do not allow the fruits to grow large enough, affect the taste - even young greens begin to taste bitter if the plant gives up its juices to the bulk of the leaf mass.
Reference!When forming bushes, do not remove too many leaves - this can affect the rate of photosynthesis. The approximate number of leaves required for rapid ripening of the crop is calculated as follows: 1 leaf per 1 ovary.
When to pinch bushes
2 weeks after planting the seedlings in the greenhouse, they begin to fix the bushes to the supports and form them. When the plants adapt enough, and their root system is well established in the soil, the main stem is tied to a support with wire or twine.
As it grows, remove excess shoots, weak and yellowed leaves, parts infected with infection or pests. If a large number of barren flowers appear on the bushes, they first try to dry the too moist soil, if this does not help, pinching is carried out, removing male flowers.
How to pinch cucumbers in a greenhouse correctly
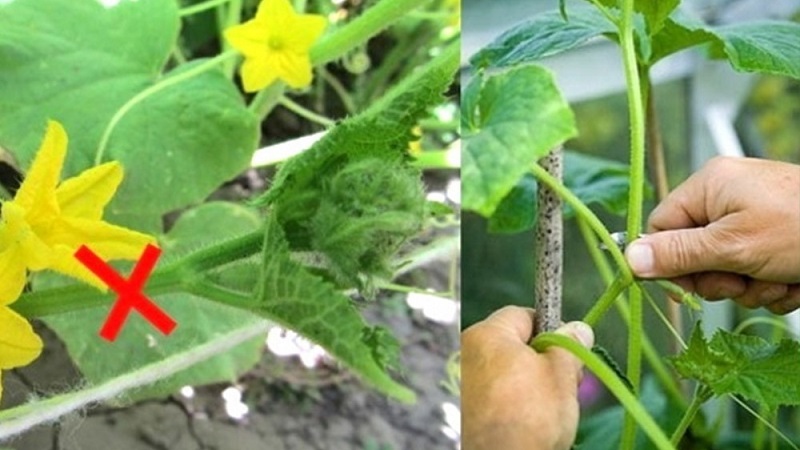

Separate parts of the plant with sharp scissors or hands using the index and thumb, strongly squeezing the stem and gently pinching off the unnecessary. Thin young stepchildren are easier to clean by hand as they are soft and brittle. If pinching is carried out using instruments, their blades are pre-sharpened and disinfected.
Leave hemp 0.5-1 cm high. Remove male flowers, antennae and stepsons in the axils of the leaves. You cannot rudely break off the stem, tear off the growth point.
Reference! Pinching is not required for modern bush varieties with determinant lateral processes. The ovaries of such bushes are often formed by "bouquets", so the removal of growth points will disrupt the natural process and lead to an overload of the plant with fruits.
The event is held on a dry day, when the above-ground part of the bushes is already completely dry after watering. This procedure not only stimulates the appearance of ovaries, but also rejuvenates the plant.
According to the classical scheme of insect pollinated varieties and hybrids
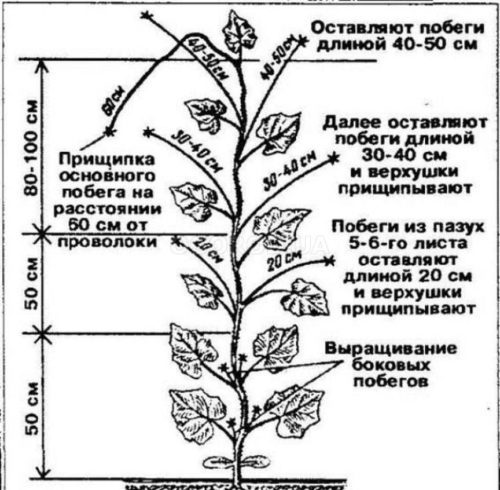
The load on the bush according to the classical scheme increases gradually from the bottom up: the higher the plant, the more shoots, ovaries and leaves are left:
- When the main stems grow to a height of 50 cm, a "blinding zone" is made. To do this, remove all lateral shoots that have appeared below the 6 leaf axils.
- To a height of 100 cm, all lateral processes are pinched over the first leaf, leaving 1 ovary.
- At a height of 100 to 150 cm, only 3-4 shoots are left, processes are formed with 2 ovaries and the same number of leaves.
- A stem over 150 cm long is thrown over a trellis, 3-4 of the next lateral processes are pinched above 3-4 ovaries.
- The upper growth point of the main lash is removed when the distance from the hanging crown to the ground begins to equal 60–70 cm.
Many growers offer a suitable shrub formation pattern on the seed package. In this case, it is better to follow the recommendations.
Scheme of pinching self-pollinated species

On cucumbers, which are not pollinated by insects, female flowers form mainly on the lateral shoots. Therefore, the pinching is done so that a lot of processes appear. How to pinch self-pollinated cucumbersthat grow in the greenhouse:
- After the formation of the first 3 ovaries on the main stem, they are removed.
- The crown of the main lash is removed above 6 true leaves, stimulating the growth of lateral processes.
- The lateral shoots are pinched, leaving 3-4 ovaries on each, carefully tied up, avoiding tangling.
Not all self-pollinated varieties need to be pinched, but for late cucumbers this procedure is mandatory.
Pinching parthenocarpic varieties and hybrids
Such plants form mainly female flowers, which most often form on the main stem. Plants are distinguished by a high rate of shoot formation, therefore pinch carried out not only for formation, but also to avoid excessive thickening.
A step-by-step diagram of how to pinch such cucumbers in a greenhouse:
- Blinding is done in the axils of the first 4 true leaves, they are removed along with the flowers.
- The fifth and sixth shoots are shortened, leaving 20 cm.
- 3-4 shoots that appear above are pinched at a distance of 40 cm, and 3-4 shoots that have grown even higher are left 50 cm long.
- After another 5-6 leaves grow, pinch the main stem.
Hybrids are removed stepsons and extra tendrils that form in the leaf axils. Make sure that the upper long processes do not tangle.
Experienced gardeners recommend cutting off the corners of the upper, too large leaves, if they shade the lower shoots, reduce their lighting. Such actions will not do harm, but will increase the area of exposure to sunlight on the lower tiers of tall and powerful bushes.
Further care
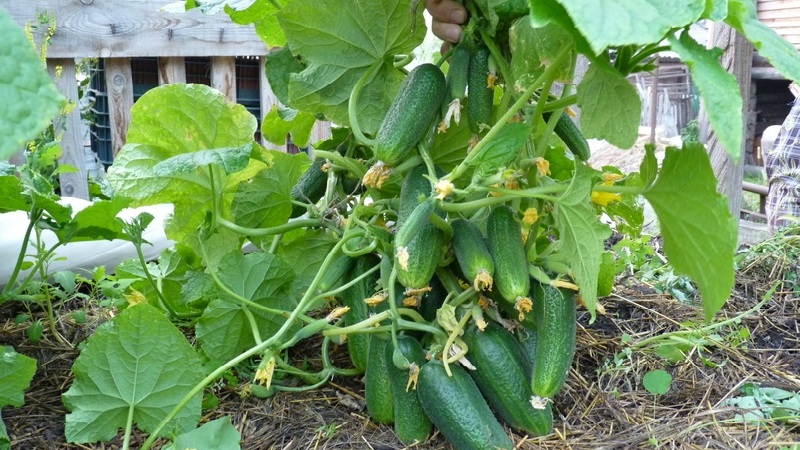

The treated plants are sprinkled with crushed wood ash to disinfect the cut sites, dry them and avoid the development of infections. To prevent pinching from causing severe stress to the crop, after the procedure, cucumbers are fed with organic fertilizers.
Watering carried out more carefully than usual, trying to prevent water droplets from getting on the hemp remaining in the places where parts of the plant are removed.
Conclusion
Pinching is a necessary procedure to increase the yield of cucumbers, improving the quality of fruits.Depending on the variety and type of plant, various schemes for the formation of bushes are used. Care for cucumbers is carried out regularly, do not allow tangling of lashes or excessive growth of green mass. The procedure rejuvenates old, overgrown bushes.