We analyze the structure of the root system of carrots - what are its features
Carrots are an unpretentious crop, but sometimes when growing it, gardeners are faced with the fact that root crops are obtained in non-standard shapes or colors. In order to prevent this, it is important to know the structural features of the root system and the conditions favorable for the development of the vegetable.
The content of the article
Botanical description of carrots
Carrots are a biennial cross-pollinated herb of the Umbrella family. In the first year after planting, farmers get the harvest, in the second they collect seeds. Flowering in the first year of life is due to a violation of the rules of agricultural technology. In this case, the plant will not produce a root crop.
Inflorescences are complex umbrellas, consisting of rays of different lengths. During the flowering period, they are convex or flat, later - compressed. Flowers are bisexual small white, pink or pale purple.

Fruits are two-seed, oblong, with two rows of sharp bristles. Their different quality is the main reason for the uneven germination and development of plants. The best seeds are formed on central umbrellas and are harvested in August.
Important! The fruit shells contain an essential oil that quickly deteriorates, which is why the seed gives poor germination when stored for more than 2 years. The oil prevents moisture from entering the embryo, which delays its swelling and germination.
Root system characteristic

The root is thickened, fleshy. Usually oval, conical or cylindrical, up to 30 cm long and up to 5 cm in diameter. varieties and growing conditions, the weight is from 100 to 300 g, the color varies from light yellow to red-violet, white, white-green is found.
The varieties of red-orange root vegetables are the most valuable because they contain a lot of carotene. Provitamin A improves vision, strengthens the immune system, and has antioxidant properties.
Structure

Carrots have a tap root system, where the main one stands out well among all the roots. It is converted to a root vegetable. There are additional lateral processes - short and weakly expressed, similar to fine hairs, located in 4 rows.
The roots go 1.5–2 m deep, most of them are located at a distance of 25–30 cm from the ground surface. Thanks to this powerful suction system, carrots are saturated with oxygen and soil nutrients.
Root structure:
- Head (main shoot). It is a deformed shortened stem with internodes and axillary buds, on which the deciduous part develops.
- Neck (hypocotal knee). The upper part of the root crop, located above the soil. There are no leaves or roots on it.
- Main root. The lower part of the carrot, from which the poorly developed roots extend.
Composition
The root vegetable consists of a core and a bark, on the surface of which there are lentils (indentations). Air flows through them.
Between the inner and outer layers is the cambial layer, in which cells divide, due to which the carrot grows. Thin lateral roots with many processes in the form of hairs originate there.
Reference. Carrots are a rich source of carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins and minerals that are beneficial to the body. Therefore, it is used in many dishes and consumed in any form.
Functions
The main functions of the root system:
- It feeds the plant. Root hairs absorb water with dissolved minerals from the soil.
- Preserves the supply of nutrients (starch, other carbohydrates). As a result, the main root thickens and turns into a root vegetable.
- Converts the substances necessary for the plant: Reduces nitrates to nitrites, synthesizes some amino acids and alkaloids.
- Interacts with the roots of other plants, fungi, microorganisms that live in the soil.
The reserve substances deposited in the root crop in the first year of life are spent the next on the development of flowering shoots, fruits and seeds.
What does a root cross section look like?
Carrying out studies of cross sections, the root crop is treated with several solutions and examined under a microscope. However, 2 zones are visible in the section with the naked eye:
- external (bark) - wide, orange, covered with thin skin;
- internal - (rod, wood), narrower, light yellow.
The main share of starch and fast carbohydrates is concentrated in the bark, so the flesh at the outer layer is tender and sweetish in taste.
The best carrot varieties are those that have a thick bark and a small core.because the pulp is much more nutritious and tastier. The most valuable are plants with a small core of the same color as the bark.
The thin skin allows moisture to penetrate easily. In dry weather, without watering, the plant quickly dies, as it is affected by fungal diseases. With a long rainy period after a drought, the wood of root crops thickens, the bark cracks.
Favorable conditions for the development of the root system
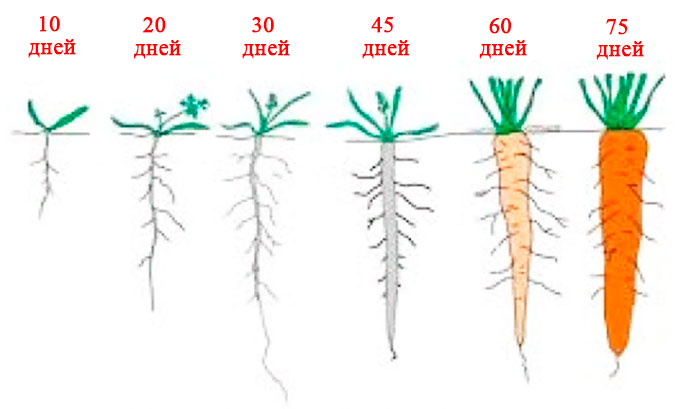
Carrots are a low-maintenance crop that grows under any circumstances. However, it is important to create special conditions in order to obtain large, tasty and mature roots, rich in vitamins.
Temperature
Although carrots are classified as cold-resistant crops, their development occurs in a certain temperature regime:
- The minimum values for seed germination are + 3 ... + 6 ° С. The higher they are, the faster the seeds germinate.
- The optimum temperature for the formation and development of root crops is + 18 ... + 20 ° С.
- Vegetables grow until late autumn, when the air temperature no longer exceeds + 8 ... + 10 ° С.
Temperature changes negatively affect the entire plant. Low positive values make the root crop lighter. In dry, hot weather and a lack of moisture in the soil, vegetables become coarse and deformed.
Shine
Carrots are a light-loving culture, which refers to plants with long daylight hours. With a short day, it grows more slowly, builds up mass worse, accumulates less nutrients, including carotene.
The density of crops and the presence of weeds significantly shade the plantings, as a result, the volume of the crop decreases.
Humidity
The harvest takes a long time (4-5 months). During the growing season, the culture is demanding on the level of moisture, which is equally important at all stages of development, especially during seed germination and intensive root formation. Despite this, in wetlands, in lowlands, flooded areas in garden beds, carrots give a poor harvest.
Important! With a lack of watering, the development of the root crop slows down, it becomes sluggish and bitter, releases side roots to search for moisture, which affects its appearance. With excess moisture, there is a risk that the carrots will crack.
In warm dry weather, the garden is watered 3 times a week, in wet weather - 1 time. Young plants are not irrigated very strongly: 4 liters of water is enough for 1 m². As you grow, the amount of fluid increases. The depth of moistening should correspond to the size of the root crops.
From the middle of summer, the vegetable is watered once a week, spending about 8-10 liters of water. Irrigation is completely stopped 3 weeks before harvesting.
The soil

The culture is undemanding to the soil, but with the correct composition, the yield increases significantly. Carrots are planted on slightly acidic or neutral soil. A suitable acidity index is 6-7 pH. The optimum humus content is from 4%.
Reference. Subject to all agrotechnical conditions, the yield is from 500 to 700 c / ha.
The mechanical composition of the soil is important. Carrots prefer light and loose soil: sandy loam, loam or black soil with loosening additives. The optimum density is 0.65 g per 1 cm³. If necessary, the composition is improved with sand and old sawdust. In heavy clay soil, root crops grow small, deformed and tasteless.
Vegetable culture is selective to its predecessors, among which are considered successful tomatoes, pumpkin, onion, garlic, potatoes, salad.
Conclusion
To grow a decent harvest of even and sweet vegetables, it is important for gardeners to have basic knowledge about the structural features of the carrot root system, its functions, and favorable conditions for development. The culture is provided with good illumination, optimal temperature conditions, soil composition and timely sufficient watering.