Why do you need pruning grapes in the fall and how to carry it out correctly
Formation grapes Is not an easy task for beginners. But competent pruning is the key to obtaining a stable harvest of delicious berries. We will tell you in detail how to prune grapes in the fall.
The content of the article
The meaning of autumn pruning
The vine has an interesting feature - polarity. It manifests itself in the fact that shoots from the upper eyes of last year's vine develop faster and better. In the middle and lower parts of the vine, the eyes develop weaker or do not shoot at all.
Many new buds and shoots grow every year. Provide them all with good nutrition plant can not. Therefore, vines form, leaving as many shoots as the root system can "feed".
Fall pruning is all about regulating growth and fruiting for the next season. A properly performed procedure contributes to high yields and uniform plant growth.
With the wrong approach, the balance is disturbed, which leads to the strengthening of one of the processes at the expense of the weakening of the other - growth / yield.

If the grapes are not cut
A free-growing vine is constantly lengthening, the arms expand, the size of the bush increases significantly. But the root system is not able to provide all the formed shoots and bunches with the necessary nutrition.
This leads to crushing of the berries and a deterioration in their taste already in the first year of free growth. The next year, the size and number of berries in the bunches will decrease even more, and after a few years the bush takes the form of wild grapes.
Types of trimming
Depending on the purpose, various types of pruning of the grape bush are distinguished.
Formative
This type of pruning is aimed at forming a strong skeleton of the bush in the first 3-4 years of growth. It can be a stamper (with two or more sleeves located close to the ground) or a stab shaping (the supporting sleeves rise above the ground).
Regulatory
Subsequently, regulatory pruning is carried out annually. It allows you to maintain a balance between the development of the bush and the fruiting process. With regulatory pruning, excess young shoots are removed.
Anti-aging
This type is used when the plant gets old and stops growing. The grape bush needs rejuvenation after 5-8 years of growth. In this case, the old sleeves are cut down and new ones are formed from the shoots located at the base of the bush.
Timing
Prune grapes in the fall begin 1-2 weeks after the foliage falls. They finish work before the arrival of frost.
In the southern regions, the vines are pruned from September to November. In the middle lane, this work is completed by mid-October. And in the Urals and Siberia - until the end of September.
Timely pruning allows the plant to recover before the onset of cold weather and winter successfully.
Technology of conducting
Mistakes made in the formation of a bush can reduce yields or leave no crop at all, and in the worst case, lead to the death of the plant. How to carry out this procedure correctly?

Required materials and tools
For the procedure, you will need a sharp knife or garden shears (pruning shears). The sharp tool makes a neat cut that will quickly overgrow.
Schemes
There are two main types of grape formation - standard and standard formation.
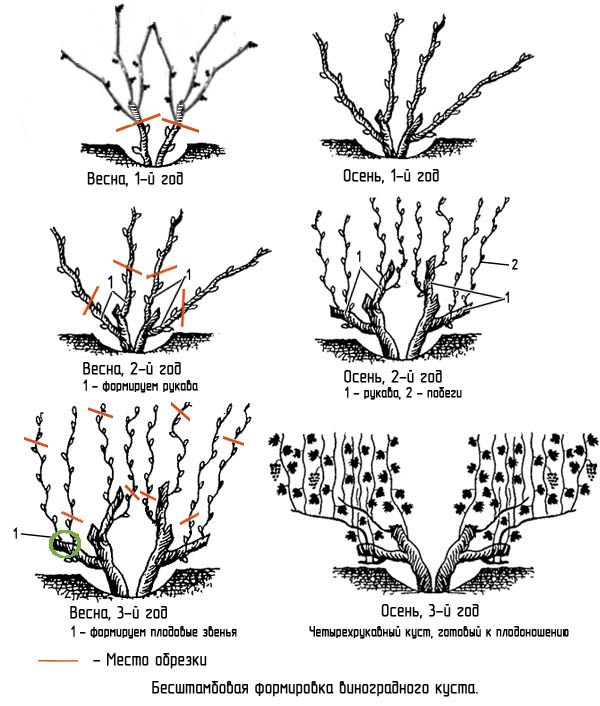
Stampless forming
The shape of the bush is set, gradually forming it over the first four years. In the first year, young shoots are pinched and weak and underdeveloped ones are removed. In autumn, 1-2, sometimes 4 shoots are left on the plant.
In the second year, 2-3 well-developed shoots are left, from which sleeves are formed. Each of them is cut into 2-4 buds. Two vines are left of these buds during the growth of the bush. In autumn, each of these vines is shortened to the length of the matured wood.
In the third year, two buds are left on the vine, located closer to the base. The shoots that have grown from them will form the sleeves of the bush. They are attached to the support horizontally and two eyes are left on each.
The shoots that emerged from the eyes are attached vertically. They form fruit links.
Need to know! The fruit link is the two lower vines on the sleeve.
In the third year, one fruit link is left on the plant. In the fruit link, the lower shoot facing the outside of the bush is cut into 2-4 buds - this is a replacement shoot. The shoot located above is cut into 6-8 buds - this is the fruiting arrow.
In the fall of the third year, the bush consists of two fruit links (one on each arm). Two vines are left on the replacement knot - the future fruit link. The fruiting arrow is removed, and a new fruit link is formed on the replacement shoot. This formation principle is repeated every year.
In the fourth year, the plant is considered complete. In the future, pruning is carried out every autumn according to the described principle.
Stamping
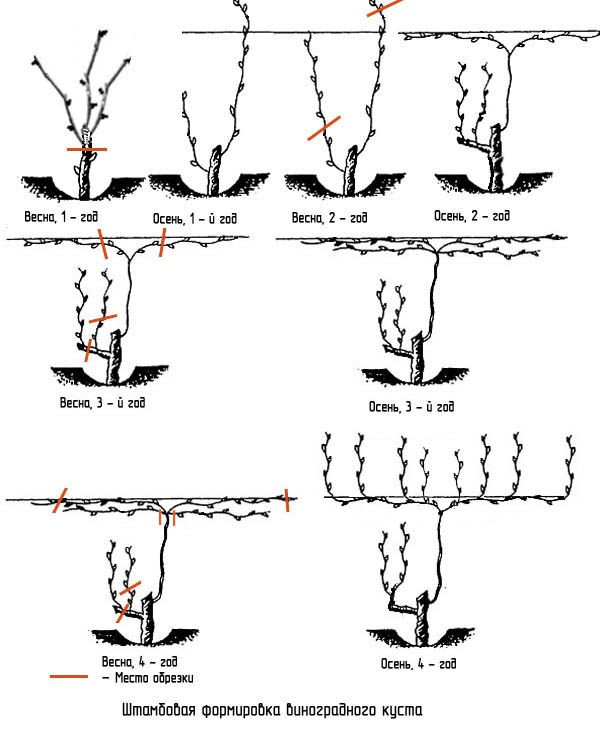
This type of plant formation is used in regions with a mild climate.
In the first autumn, two shoots are left on the seedling. In the spring of the second year, the shoots are pruned: the main one - into three buds, the second - into two. A more powerful shoot is formed as a stem, and the second is kept as a spare.
The stem is fixed vertically. In the fall, two shoots are left on the trunk and they are bred in different directions, fixing horizontally. The tips of these shoots are pinched. All other eyes on the standard vine are dazzling. On the reserve shoot, the vines are cut into 3-4 eyes.
In the 3rd year in spring, two long shoots, fixed horizontally, are cut into two buds. These will be the sleeves of the bush. Four shoots will grow on them in the summer - two on each shoulder.
The eyes dazzle on the main trunk. On the reserve, one vine is left, located closer to the base of the bush with two buds, the second is removed. By autumn, two branches will develop on this shoot, which are cut off as follows: the outer lower one - for two eyes (reserve), and the second - for six eyes (spare fruit arrow).
In the fourth year, in the spring, on the sleeves of the main stem, trimming is done for a fruit link. The shoot closer to the base of the stem is cut to a spare twig, leaving two buds, and closer to the top - to the fruiting arrow, leaving 5-6 or more fruit buds. There may be several such links on the sleeve. A crop is formed on the fruiting arrow.
All subsequent years, pruning is carried out according to the principle of a fruit link, consisting of a replacement knot and a fruiting arrow. Excess fruit links of the previous year are removed.
Pruning instruction
The blades of all tools used must be well sharpened and disinfected with an alcohol-based product.
The most convenient tool for cutting young shoots is a secateurs. A garden saw is used to remove old, thick vines.
The cut is made neatly at right angles, leaving an even and smooth stump. This will speed up healing as the area of the wound will be smaller than with a slanted cut.
Features by region

The choice of the type of grape bush formation is influenced by the climatic conditions of the growing region. In the south, where the climate is mild, they use an uncovered method of growing grapes. Here, shaping on a trunk (or fan method) is used, which allows you to get the maximum yield.
When grown in the suburbs, in the Urals and in Siberia without shelter for the winter, the vine freezes.Therefore, grapes are formed here so that you can wrap them up in the cold season. Here, a cordon (short-sleeved) formation scheme is used, in which the head of the bush is located close to the ground.
Care after pruning
After the completion of the autumn pruning procedure, the cut sites are processed to protect against infections. For processing, use "RanNet" - a special paste with an antiseptic, which disinfects the wound and promotes rapid healing - or melted garden pitch.
Shelter for the winter
Pruned and healed vines are sheltered for the winter. In regions with severe winters, this is a must. conservation of grapes.
They begin to cover from the beginning of October. The vines tied in bunches are laid on the ground and sprinkled with earth in a layer of 5-10 cm. You can first wrap the bush with covering material or burlap, and then cover it with earth.
Another way of warming is to cover the vines with wooden boxes, which are covered with a film on top.
It is also necessary to monitor the depth of the snow cover during the winter. The snow layer must be at least 40-50 cm thick.
Conclusion
Without the formation of vines, it is impossible to get a harvest of large and tasty berries. Growing freely, the bush occupies an ever larger area. The berries become small, and light access and air circulation inside the bush are difficult. This leads to the development of diseases and the spread of pests.
Therefore, autumn pruning is an essential step in vineyard care. The autumn pruning scheme is chosen based on the growing conditions.