Stably productive variety of honeysuckle "Iziuminka" from Russian breeders
The highlight is a variety of edible honeysuckle, bred by Russian breeders, with a high yield, unpretentiousness and resistance to low temperatures. In the article, we will tell you in detail about the features of this variety, the methods of propagation of bushes and the requirements that Zest makes for planting and care.
The content of the article
What is this variety of honeysuckle

The highlight is a mid-season honeysuckle variety. It is characterized by slow growth during the first 3-4 years. Fruiting begins 3-4 years after planting. The average yield is 27 c / ha or 0.9-1.4 kg per bush.
The crop is harvested when the berries reach full color. The fruits are stored in the refrigerator for no more than three days.
Brief history of origin and distribution
The variety was obtained by breeders V. S. Ilyin and N. A. Ilyina in the South Ural Research Institute of Horticulture and Potato Growing as a result of free pollination of Kamchatka honeysuckle.
It was entered in the state register of Russia in 1999 with admission to cultivation in all regions.
Characteristics and description of the bushes

The bushes are medium-sized - 1.2-1.3 m in height, slightly spreading with a compact crown of reverse conical shape and thin curved shoots of brown color with a violet-lilac shade, pubescent.
The leaf plates are slightly fleecy, broadly lanceolate, of medium size, concave in shape with a pointed and twisted apex, light green in color.
During the flowering period, pale, bell-shaped flowers of medium size appear on the bushes.
Resistant to temperatures
The bushes withstand a drop in air temperature to -50 ° C practically without loss, during flowering they can withstand frosts down to -8 ° C.
Reference. With prolonged winter warming, the bushes can open fruit buds, which will die due to the returned frosts.
Moisture and drought resistance
At high humidity, caused by over-watering or the proximity of groundwater, the risk of root rot increases. At the same time, a lack of moisture and prolonged drought negatively affect the yield and taste of berries.
Disease and pest resistance
The raisin is immune to viral diseases, but under unfavorable climatic conditions and improper care it can be affected by powdery mildew and various types of spotting.
Of the pests, the honeysuckle fingerfly, aphids, scale insects, leafworms can attack the bushes.
It is interesting:
Frost-resistant early-ripening variety of honeysuckle "Lakomka".
An early-ripening resistant variety of Vasyugan honeysuckle.
Characteristics and description of fruits
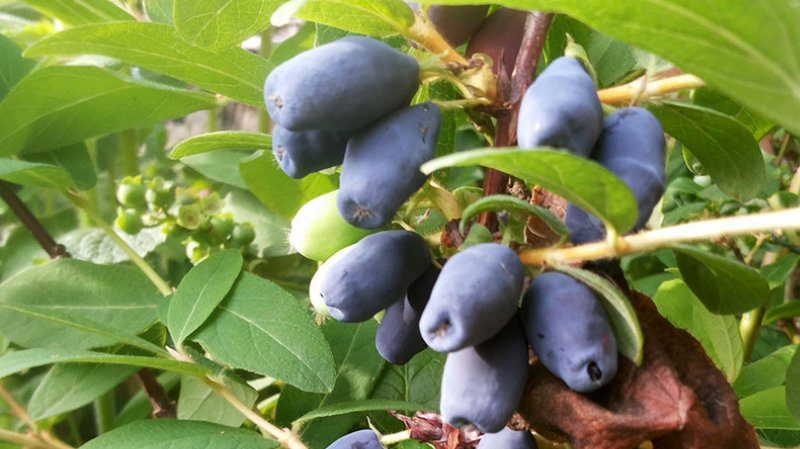

Berries are elongated-oval, large, reach 1.8-2.7 cm in length and weigh an average of 1.1-1.6 g, with a bumpy surface, covered with a dense, but not hard, bluish-blue skin with an intense layer gray wax bloom.
Fruits contain 13.9% dry matter, 7.4-8.9% sugar, 2.1-2.2% acid, 31-48 mg vitamin C, 950 mg vitamin P (P-active compounds).
The pulp is fibrous, aromatic, has a pleasant sweet and sour taste with spicy notes, without bitterness.
Areas of their application
Berries Raisins are consumed fresh, frozen, dried.Fruits are also suitable for various types of processing, including making juices, preserves, jams or preserves.
Due to the decorative appearance of the bushes, especially during flowering, they are often used to decorate parks, squares and gardens.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety

Main advantages:
- stable fruiting;
- large-fruited;
- there is no tendency to shedding berries;
- frost resistance;
- immunity to viral diseases;
- decorative type of bushes;
- great fruit taste;
- unpretentious care.
The disadvantages of Honeysuckle Zest include a relatively low yield and the need for replanting pollinating varieties.
Growing technology
For good fruiting, honeysuckle bushes provide comfortable conditions: they choose a place suitable for planting, carry out planting at the optimal time and competently care for the plants.
Optimal conditions
For planting honeysuckle, choose a light, shaded place, protected from gusty winds. The permissible groundwater level is 50 cm. The variety develops and bears fruit best of all on fertile, loose soil with good aeration, moisture permeability and weak acidity. The best option is sandy loam and loam.
When choosing seedlings, they prefer biennial specimens with 2-4 elastic shoots 30-40 cm long and a branched root system.
Terms and rules of landing
Due to the early growing season in spring, honeysuckle is planted on the site in the fall: in late September or early October.
Reference. Spring planting is permissible as soon as the soil thaws and before the buds wake up.
Landing rules:
- Dig holes 40x40x40 cm in the prepared area.
- Fill each with two-thirds of the nutrient mixture (half of the excavated soil, two buckets of humus or compost, 200 g of double superphosphate and potassium salt each).
- Form a hill at the bottom of the pit, place a seedling on top, spread its roots along the slopes.
- Fill the hole with soil, tamp it - the root collar is deepened 3-4 cm.
- Water the bushes, pouring 10 liters of water under each.
- Mulch the soil in a circle near the trunk with a 4 cm layer of sawdust, dry straw or humus.
Further care
The bushes are watered on average once a week or 10 days, focusing on the condition of the soil: it should not dry out, but waterlogging is also unacceptable.
The next day after watering or rain, the soil is loosened to improve the access of moisture and oxygen to the roots of plants, and weeded to get rid of weeds.
Top dressing begins to be applied in the third year after planting seedlings according to the scheme:
- from early spring to mid-summer, every two weeks - a solution of ammonium nitrate (30 g per 10 liters of water) at the rate of 1-1.5 liters under a bush, mullein or bird droppings;
- after picking berries - a solution of nitroammofoska (25-30 g per bucket of water) or slurry;
- autumn - 5 kg of compost, 100 g of ash and 40 g of double superphosphate per 1 sq. m.
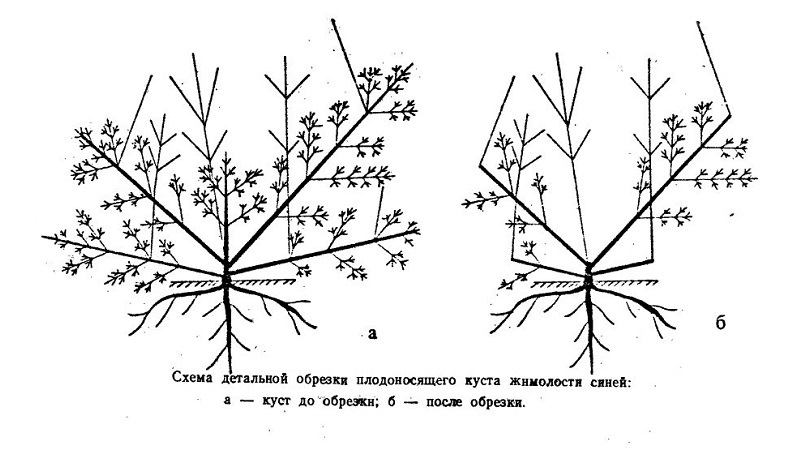
When the plants become too thick, cut out some shoots growing from the ground and dry, old, damaged and short branches. In the spring, sanitary pruning is carried out, getting rid of the tips of the shoots damaged by frost and disease.
For bushes over 6-7 years old, rejuvenating pruning is carried out, completely cutting off the shoots and leaving hemp of 40-50 cm or removing 2-3 old branches, leaving the same number of young ones.
Possible problems, diseases, pests
Diseases and pests that, under unfavorable conditions, can infect the Zest:
| Disease, pest | Signs | Treatment, prevention |
| Powdery mildew | The leaf plates are covered with a white powdery bloom. | In early spring, plants are treated with a solution of copper sulfate, "Fundazol" or "Topaz". |
| Different types of spotting | Various color, color and shape of spots appear on the leaf plates. | |
| Honeysuckle fingerfly | Pests eat seeds and berry pulp. Not fully ripe fruits darken, wrinkle, crumble. | After harvesting, the bushes are treated with drugs such as "Karbofos" or "Chlorofos". Among the special preparations they choose "Decis", "Eleksar" or "Inta-Vir" in case of attack by leaf-eating pests, and "Actellik", "Confidor", "Rogor-S", if sucking insects attacked the bushes. |
| Honeysuckle aphid | Insects feed on the sap of the leaves, they dry and wither. | |
| Shields | Bushes dry and die slowly. | |
| Leaf rollers | In the caterpillar stage, insects roll up the leaves of plants, braid them with cobwebs, and settle inside. The foliage dies. |
Wintering
Preparing honeysuckle for winter consists in removing all fallen leaves, pruning the bushes if necessary, cleaning the trunk circle from the used organic mulch and covering it with a new layer of mulch.
Reproduction
Raisins bushes propagate vegetatively: by cuttings, layering or dividing the bush.
Reference. With seed propagation, the plant loses its varietal characteristics.
Cuttings are harvested in early spring, before the buds open. Choose strong annual shoots with a minimum diameter of 7-8 mm and cut them into pieces 7-12 cm long so that each has 2-3 buds. The cuttings are soaked for a day in a solution of a growth stimulant (Kornevin, Heteroauxin), after which they are planted in a container with a peat-sandy substrate and covered with a film. Plants take root after 30-35 days.
For reproduction by layering in the spring, a horizontal low-lying shoot is chosen on the bush, the bark is slightly incised on it, bent to the ground, fixed, sprinkled with soil and watered. When the shoot takes root, it is separated from the mother bush and planted in a permanent place.
Plants over 6 years old are propagated by division. In early spring or late autumn, the bush is dug up and divided into several parts with a sharp sterile tool, which are planted in a prepared area and watered.
Council. When dividing the bush, the shoots are cut by a third.
Features of growing this variety, depending on the region
Honeysuckle Zest makes standard planting and growing requirements regardless of the region's climate.
Pollinating varieties
The highlight is a self-infertile honeysuckle variety. In order for the bushes to tie fruits and give a crop, suitable pollinator varieties are planted nearby:
- Zarnitsa;
- Goryanka;
- Atlant;
- Viola;
- Enchantress;
- Altair.
Reviews of summer residents
Gardeners who tried to grow the Raisin liked the variety.
Valeria, Omsk: “We planted several varieties of honeysuckle, including Raisin, four years ago. The berries of this particular variety liked the taste - they are sweet, with sourness, while the astringency is felt. The harvest is still small, but this is not the main thing - we planted bushes primarily to create a hedge. In addition, they read that the yield increases over time. "
Julia, Saratov: “Zest has been growing at the dacha for a long time. We didn't really look after the bushes, only from time to time we pruned, because the bushes were getting very thick. The berries are incredibly tasty, but there are not many of them. Although we have enough for a family. We mostly eat them fresh and freeze them a bit for the winter. I haven’t tried to cook jam, but the neighbor does it and it turns out delicious ”.
Read also:
Frost-resistant early ripe variety of honeysuckle "Lakomka"
Conclusion
The highlight is a fast-growing, unpretentious variety of honeysuckle, characterized by high immunity to many diseases and a pleasant sour-sweet taste of berries. Due to the high degree of frost resistance, Zest is successfully cultivated in all regions.