What can you plant honeysuckle next to and why is it important
A climbing bush called honeysuckle is a frequent visitor to European gardens and parks. In Russia, this plant is not so popular, but thanks to its unpretentious care and tasty fruits, gardeners are increasingly planting it in their plots. Honeysuckle does not get along with all cultures. The article will tell you what you can plant honeysuckle next to and what kind of neighborhood will be unfavorable for the plant.
The content of the article
Crop rotation rules for growing honeysuckle
Each culture has a number of typical diseases and dangerous pests.
Nutrient requirements are also different. These factors are taken into account when planting honeysuckle bushes.
Crop rotation rules prohibit:
- plant plants of the same family on the same site for several years in a row;
- plant honeysuckle after crops that have diseases or pests in common with it;
- use the site after growing plants demanding the same set of nutrients.
Why is it important to follow the rules of crop rotation
Insect larvae and pathogens tend to accumulate in the soil... This creates unfavorable conditions for growing honeysuckle.
If a from the ground for a long time, the plant takes the same trace elements, an imbalance occurs... The nutritional value of the soil is replenished with organic and mineral fertilizers and the alternation of cultivated plant species.
Impact on growth and yield
Crop rotation significantly reduces the risk of disease and promotes fruiting... The root system provides enough nutrients, and the bush grows quickly.

What is the best place to plant honeysuckle
To honeysuckle pleased with a rich harvest and did not feel constrained in growth, she is provided with a supportive environment.
Exist several main reasons for plant incompatibility:
- the location of the roots at the same level in the soil layers;
- the release of harmful substances that inhibit the growth and development of neighbors;
- excessive shading by large trees and spreading shrubs;
- consumption of one set of nutrients, trace elements;
- diseases and pests common with nearby plantings.
Each option has negative consequences that will further complicate garden maintenance.... If you do not take into account the length of the roots of neighboring plants, you can end up with a barren area. Plants will suffer from nutritional deficiencies and their growth will slow down. The same will happen if you plant a bush or tree next to a honeysuckle that uses an identical set of nutrients for development.
Some plants release toxic substances into the environment through roots or foliage to protect against pests. However, such protection can harm other landings.
Do not plant a light-loving plant like honeysuckle in the shade of spreading trees. with dense foliage. Due to the lack of sun, the shrub will quickly wither away. In addition, it is practically impossible to prevent an epidemic of a common disease or an invasion of pests in such conditions.
Gooseberry compatibility
Gooseberry compatibility is high, therefore, such a neighborhood is permissible in the garden.However, these two shrubs must be planted at a distance of at least 1.5 m.
With raspberries
Raspberries are considered a freedom-loving plant - they have a powerful and developed root system that interferes with other crops. However next to honeysuckle, this bush feels good.
Experienced gardeners recommend planting raspberries a short distance from the honeysuckle, and in between sowing oats and vetch, which will saturate the soil with nitrogen and suppress the growth of weeds.
With currants
Currants and honeysuckle are similar in their unpretentiousness and frost resistance... The chemical compatibility of these shrubs is also high - the harmful substances secreted by honeysuckle will not harm the currants. However, this applies to black currant: in tandem, both crops will delight with yield. But next to red currants, honeysuckle will suffer from a lack of nutrients.
Attention! Barberry will be an excellent neighbor for honeysuckle. Its flowers attract insects, while the plant does not take away the microelements necessary for the shrub.
With grapes
The grapes need abundant irrigation, therefore neighbors pick up plants that will not suffer from excessive moisture.
Honeysuckle is one of them, water gives its fruits the best taste. Additionally, it protects the vine from root pests.
With cherry
Cherries give abundant shade, which is harmful to light-loving honeysuckle... In the shade of cherry trees, the shrub slows down and produces poor fruit. However, if you plant it at a distance of about 2 m, the bush will develop steadily and will not harm the fruit tree.

With blueberries
Honeysuckle does not like high acidity of the soil, and this indicator is necessary blueberries... Therefore, such a neighborhood is not recommended. Gardeners try to maintain a distance of 3-4 m between these plants. Honeysuckle is placed on the north side to protect thermophilic blueberries from the cold wind.
With blackberry
In this case, avoid planting honeysuckle next to creeping varieties of blackberries., since young seedlings of this plant need free space for full development. Next to kumanik, which grows vertically, honeysuckle feels great.
Bad neighborhood for a plant
Apricot, bird cherry and walnut release toxic substances into the soil around themthat can harm honeysuckle bushes. Spruce, pine, mountain ash, pear and apple trees have a dense crown and provide a lot of shade, in addition, they take most of the nutrients from the soil.
Fennel, hyssop and milkweed are aggressive crops, while strawberries and sea buckthorn are different rapid growth. The latter can still be found next to honeysuckle, but for this, the growth of its root system is limited by special slate structures.
Honeysuckle does not like drought and appreciates the abundance of moisture, therefore crops that do not need regular watering are not suitable for planting next to this shrub.
Planting pollinating varieties nearby
For a good harvest, it is recommended to plant several honeysuckle varieties... This will attract a large number of bumblebees and bees.
The best combinations of varieties:
- Berel - Amphora - Bakcharskaya;
- Cinderella - Nymph - Parambelskaya;
- Blue spindle - Chosen One - Morena - Blue Bird.
Best and worst predecessors
Shrubs are planted after potatoes, onions, carrots and beets... These plants do not deplete the soil and do not leave behind diseases or pest larvae. Legumes are ideal - they will saturate the soil with nitrogen, which will have a beneficial effect on the root system of the shrub.
New seedlings are not placed in place of old bushes... You should not do this in areas where strawberries, conifers, cherries and cherries grew.
At what distance to plant honeysuckle
Close planting of bushes next to each other should be avoided.... This will make planting and harvesting difficult.It is better to maintain a distance of 1.5-2 m and alternate between different varieties, which will extend the fruiting of the bushes for the entire season.
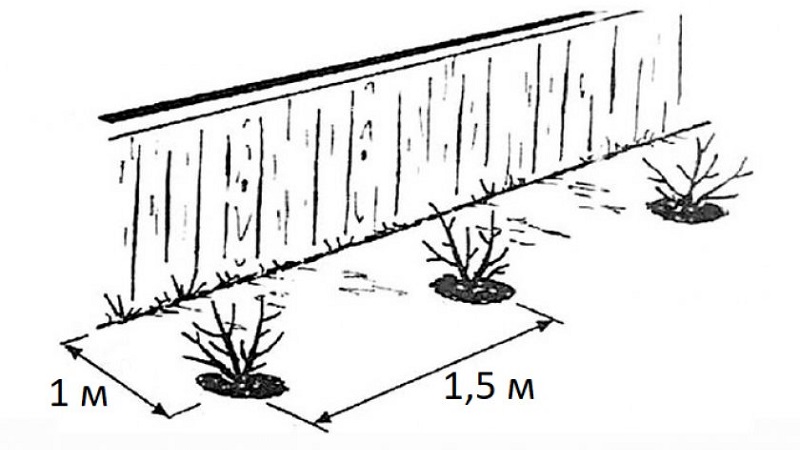
Do I need to plant two bushes next to each other
Planting two or more bushes is required for high-quality pollination.... Insects will transfer pollen from one plant to another, significantly increasing yields. You can place plantings in the corners of the site, agreeing with neighbors about the possibility of cross-pollination.
Conclusion
Honeysuckle has recently appeared on Russian sites, so many of the features of its cultivation are unknown to gardeners. According to the rules of crop rotation, a site is determined that is suitable for planting bushes. Having chosen the optimal neighborhood and observing the rules of pollination, they get a rich harvest of delicious berries.