What and how are bean seeds formed?
Mankind has been cultivating beans for about five thousand years. However, this culture came to Europe and Russia only in the eighteenth century. They eat seeds and beans of beans, which are rich in proteins, carbohydrates and vitamins.
This useful and beautiful plant is easy to grow in your backyard. To understand the nuances of caring for beans, we will get acquainted with the structural features and the pattern of germination of the bean seed.
The content of the article
What are beans seeds
The legume family, which includes beans, belongs to the class of dicotyledonous plants.
 Beans are an annual herbaceous self-pollinated plant. Depending on the variety, there are bush, semi-curling and curly forms.
Beans are an annual herbaceous self-pollinated plant. Depending on the variety, there are bush, semi-curling and curly forms.
The peculiarity of the structure of the root system of the bean is that nodules containing nitrogen-fixing bacteria are formed on the processes of the root. The symbiosis with these bacteria helps plants to absorb free nitrogen. The taproot penetrates up to 1 m deep into the soil.
Dry bivalve fruits are called beans or pods. They contain several kidney-shaped seeds of white, red or variegated color. Their sizes vary from 8 to 25 mm.
Interesting... Beans have significant nutritional value. Amino acids of the plant are similar in composition to proteins of meat and fish. The product contains vitamins, mainly of group B, minerals (potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus). Most of the nutrients are preserved during conservation and heat treatment.
Seed structures with photos and their meaning
The seed is formed after fertilization from the ovule and carries the embryo. The embryo contains two cotyledons or embryonic leaves, an embryonic root and an embryonic shoot. The peel protects the germ from drying out and damage. Let's take a closer look at what the structure of the bean seed embryo is.
Embryo shoot of a dicotyledonous plant
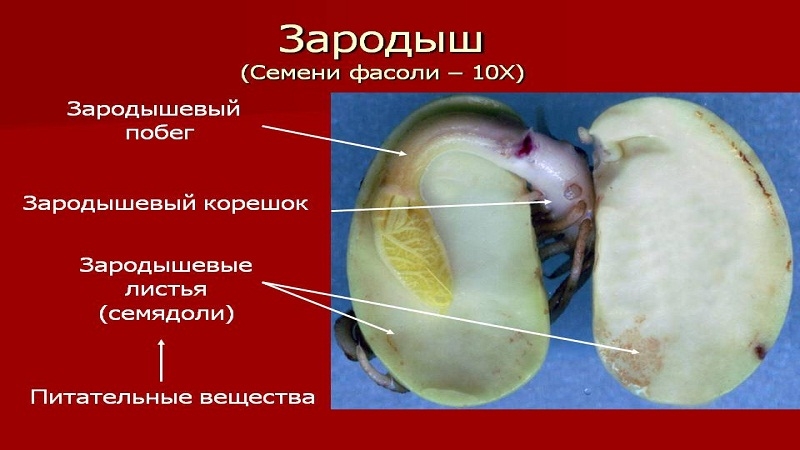
The embryonic shoot consists of the hypocotyl and the kidney.
The bud has a cone of growth and several buds of leaves. From these organs, the main shoot of the plant develops.
The subcotyledonous knee is located between the cotyledon node, from which the cotyledons extend, and the embryonic root. It looks like a stalk.
Under favorable conditions, the hypocotyl begins to grow first and pushes the embryonic root out of the seed. Then, actively developing in length, it bends in an arcuate manner and appears on the soil surface. After the sprout straightens up and takes out the cotyledons and the embryonic bud.
Embryonic root
The embryonic root consists of a clot of cells capable of intensively dividing, covered with a root cap. It first appears outside the seed, becomes fixed in the soil and begins to absorb moisture and nutrients.
The main (first order) root develops from the embryonic root. As a result of the branching of the main root of the beans, a perennial taproot system appears.
Cotyledons
As the seed ripens, the nutrients necessary for the development of the seedling accumulate in the cotyledons. After emergence on the soil surface, the embryonic leaves turn green and begin photosynthesis, ensuring the growth of the main shoot from the embryonic bud.
When the first leaves are sufficiently developed, the cotyledons dry up and fall off.
What is seed germination
Ripe seeds are dormant and can be in unfavorable conditions for a long time, keeping the embryo alive.
The transition from dormancy to vital activity is called germination. In the embryo, metabolic processes are accelerated, and the seeds swell. The root appears first, then the hypocotyl. During germination, the embryo develops using nutrients from the seed.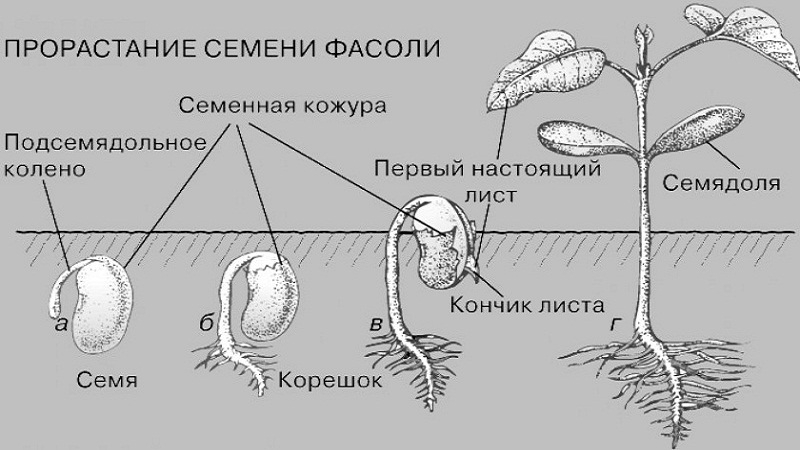
Conditions required for germination
Germination requires a combination of conditions: a living embryo, favorable temperature and humidity, a suitable light regime and oxygen access.
Temperature
Germination is possible only at positive temperatures. The range of temperatures favorable for sprouting differs for plants of different groups and geographic origin.
For beans, the minimum germination temperature is +8 - + 10 ° С, the optimum is +20 - + 22 ° С.
Humidity
Seed activation begins with good moisture. Water increases respiration and initiates the work of enzymes, under the influence of which the accumulated nutrients are converted into an assimilable form.
Fats are converted to fatty acids, starch to sugars, proteins to amino acids. Protein-rich seeds such as beans and peas need the most water for germination.
Oxygen
Oxygen is required for active metabolism for growth. This element is involved in synthesis reactions within cells.
Without access to air, the seed will not be able to germinate, it will die in dense soil or under a layer of water.
Light mode
Sunlight is essential for the reactions of photosynthesis - the formation of nutrients. In case of insufficient lighting, the seedling lags behind in development or completely stops growth.
Beans are demanding on the intensity of lighting, so they are planted in open, not shaded areas.
Read also:
Why bean sprouts are useful, how to sprout them correctly and cook them deliciously.
Conclusion
Inside the fruit (bean), there are 2 to 8 beans. The seeds are kidney-shaped, colored, depending on the variety, in red, white, black. The size ranges from 8 to 25 mm. Like any seed of a dicotyledonous plant, a bean consists of two nutrient-dense cotyledons and an embryo. The dense seed coat provides protection from damage.
For the germination of beans, a combination of favorable factors is required: a temperature not lower than + 10 ° C, high humidity, oxygen access and intense lighting. Bean seeds remain viable for 5-6 years. With proper germination and care, beans will delight you with a rich harvest of nutritious, healthy and tasty beans.