How to properly store potatoes without a cellar in the ground until spring
Some farmers face such a problem: having collected an unexpectedly rich potato crop, they realize that all the volume of vegetables is simply nowhere to store. However, you don't need to have a shed or cellar to store potatoes. There are other ways to keep the tubers safe.
We will tell you in detail about how to keep potatoes in the ground until spring without a cellar and how to make a pile for storing potatoes.
The content of the article
Optimal conditions for storing potatoes
To preserve the harvest throughout the winter and avoid rotting, special conditions are provided for the potato tubers.
Optimum storage temperature - + 2 ... + 4 ° С in the winter season. Air humidity should be no higher than 85%. If the temperature regime is not observed and it is much colder in the storage area, then the potato tubers freeze and acquire an unpleasant sweetish taste.
It is also important that the potatoes are not exposed to direct sunlight. This has a detrimental effect: in the sun, solanine, a poisonous substance, is produced in the tubers, and the potatoes themselves acquire a greenish tint.
Is it possible to store potatoes in winter without a cellar in the ground
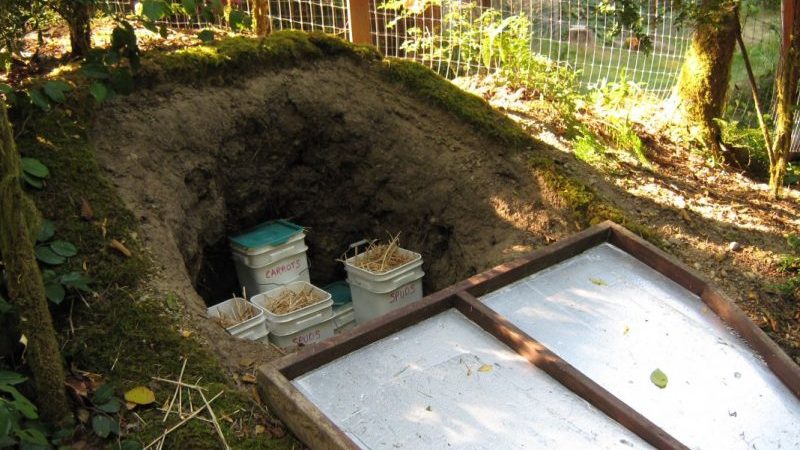

Storage in the ground is an alternative to a conventional cellar. An improvised cellar, subject to all building rules, will provide similar conditions for potatoes.
Pros of storage in the ground:
- savings - such storage does not require a special room, you do not need to additionally buy boxes or baskets;
- ease of transportation - storage can be provided in the same place where potatoes grew;
- simplicity - creating a pit does not require special skills;
- protection - with this method, small rodents and other pests will not be able to get to the potatoes.
Minuses:
- labor intensity - creating a pit requires significant effort;
- possible inaccessibility - in winter such a "warehouse" can be heavily covered with snow from above, which will make access to the crop problematic.
In-ground storage mode
The temperature range for potatoes is wide enough: + 2… + 12 ° С. Storage in the ground is the best way: the ground will provide the crop with the necessary heat, in winter the temperature will stay around + 3 ° С.
Council. Beet tubers can be placed on top of the potatoes. Beets are not afraid of freezing and will absorb excess moisture.
The earthen storage is covered to prevent precipitation in the form of rain and snow and direct sunlight from entering the pit.
Potato varieties suitable for this storage

Even a prepared earthen hole, which provides all the necessary conditions, does not guarantee that the harvest will last all winter and not deteriorate. It's all about the varieties of potatoes. Not all potatoes are suitable for long-term storage.
Early varieties are stored in any way for no more than 2 months. These include Aurora, Hostess, Rocco, The Riddle of Peter and others.
Late potato varieties do not cause problems and lie in a well-equipped store until next spring. These include Zhuravinka, Atlant, Gull, Slav and others.
Reference. Scarlett and Nevsky varieties are not late varieties, but they are perfectly stored throughout the winter.
Preparing potatoes for storage
Prepare potatoes before storage. At the stage of digging, the tubers are carefully removed from the ground so as not to damage them, since specimens with defects are stored much worse. The potatoes are sorted before being stored in an earthen hole.
If the storage location is remote, then the potatoes are carefully transported so that the tubers do not bump against each other. If the "cellar" is located near the place of digging, the tubers are cleaned of soil and thoroughly dried before immersion.
Important! To prevent rotting from affecting the harvest in storage, the potatoes are pretreated with infusions of wormwood and tobacco. You can also spray the tubers with a solution of copper sulfate and dry.
How to store potatoes if there is no cellar
There are many different ways to store potatoes in winter: in the ground, in the cellar, in the basement, on the balcony.... One of the oldest and most effective is storing potatoes in the ground. All the necessary conditions for temperature and humidity are created in the soil, ensuring high-quality storage.
There are also several storage methods in the ground: in a pit, trench or pile. By creating such a storage facility, you can save the harvest until spring.
Important! It is recommended to periodically sort out the crop sent to storage in order to weed out good potatoes from damaged tubers. If this is not done, then even one low-quality potato can cause massive rotting of the entire crop.
Storage in a pit
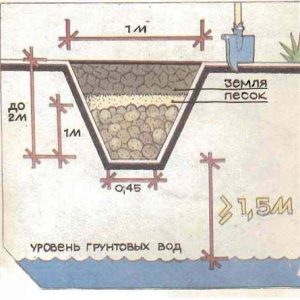
How bury potatoes for the winter into the ground? The pit is a simple potato storage set up right in the ground. On a plot of land, they dig a hole of the required size and depth of 0.7-1.5 m. The depth depends on the region of residence and the strength of the frost, that is, on how much the ground freezes.
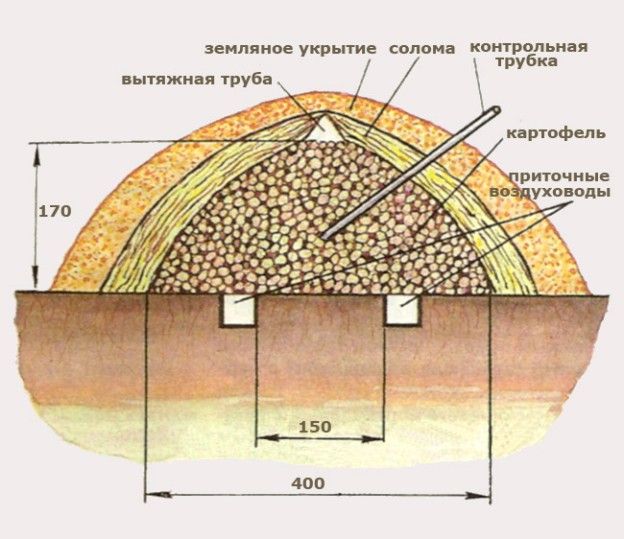
The bottom of the pit is lined with boards so that the tubers do not lie on bare ground. From above, the pit is also covered with boards, covered with a layer of earth and covered with materials with thermal insulation properties - for example, straw or sawdust.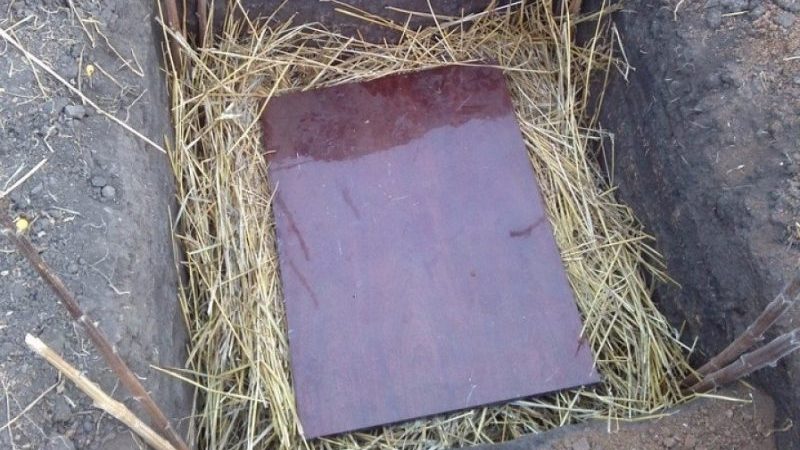
Often, such improvised cellars are equipped with ventilation. Before forming the roof of the pit, a plastic pipe is inserted inside, which will provide air exchange.
Important! From above, the ventilation pipe must be protected from precipitation or possible blockages.
Storage in trenches and piles
These methods are based primarily on the properties of the soil. Insufficient thermal conductivity and gas exchange in the soil create optimal conditions (temperature regime, humidity level) in trenches and piles to preserve the quality of the crop.
The dimensions and depth of such storage facilities, similar to the pit, depend on the geographical latitude. The more severe the winter, the deeper trenches and heaps are dug.
In southern latitudes, trenches are more often used to store potatoes, cabbage, and beets. In the north, piles are more common. There they leave not only potatoes for the winter, but also carrots, cabbage, beets, celery and other vegetables.
Burt do it yourself
Such method involves storing the crop directly on the ground and creating a protective layer on top. They try to place the burt in a place protected from cold winds with a groundwater level no closer than 2 m from the place of laying.
To protect the pile from water infiltration, drainage channels are made around the perimeter of the storage facility. To prevent the autumn and spring surface waters from stagnating in the storage area, drainage grooves are pulled out at a distance of 50 cm from the shelter.
The tubers are folded in the form of a pyramid no more than 1.5 m high. The potatoes are covered with insulation (straw) from above, which is sprinkled with a layer of earth. It is important that the soil layer is thicker at the edges than at the top of the pile.
DIY trench
A trench is dug of an arbitrary length, no more than 1 m wide and a depth of 0.7 to 1.5 m, depending on the degree of freezing of the ground. They make a trench on a hill so that the crop is flooded.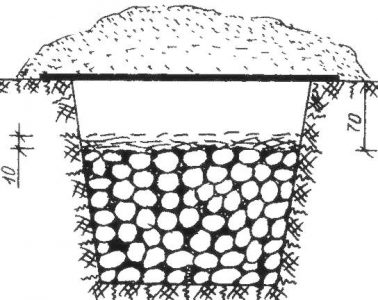
After the tubers are lowered into the trench, they are covered with insulating material: spruce branches, straw, sawdust. This layer extends to the edges of the trench. From above, the trench is sprinkled with a layer of earth 0.3-0.4 m.
Storage in a trench does not require additional ventilation, as there will be more than enough oxygen in the soil.
Tips & Tricks
Experienced gardeners using earth storage for potatoes recommend:
- cover vegetables with straw and earth in 2 stages - first with a thin layer to remove excess moisture, and then with another layer when the cold comes;
- do not use potato tops for shelter - this can lead to tuber disease;
- in spring, throw snow off the pile so as not to flood the crop in case of a sharp warming;
- after complete extraction of tubers in the spring, dig up the soil in the pit to a depth of 30 cm and disinfect with 5% copper sulfate solution.
Conclusion
Storing in the ground will protect crops in the absence of cellars... No special skills or tools are required to make a pit or potato trench. A piece of land is sufficient to equip such a storage place. According to its characteristics (humidity level, temperature), an earthen shelter is in no way inferior to a classic cellar.
When creating such a storage facility, it is important to take into account the depth of freezing of the ground and the possibility of groundwater leakage. Be sure to take care of the insulating layer and periodically touch the potatoes to remove spoiled tubers from the bulk.