What to do if the potatoes inside became empty and why this happens
The formation of voids in tubers depends on the variety, growing conditions, harvesting technology and storage method. Hollowness is not considered a disease and is manifested in violation of planting care. These tubers can be eaten.
Hollowness with blackening, depressed spots are formed in infectious diseases. Affected tubers are removed from storage and destroyed. In this article, we will detail the reasons for the void in potatoes.
The content of the article
What is the hollowness of potato tubers
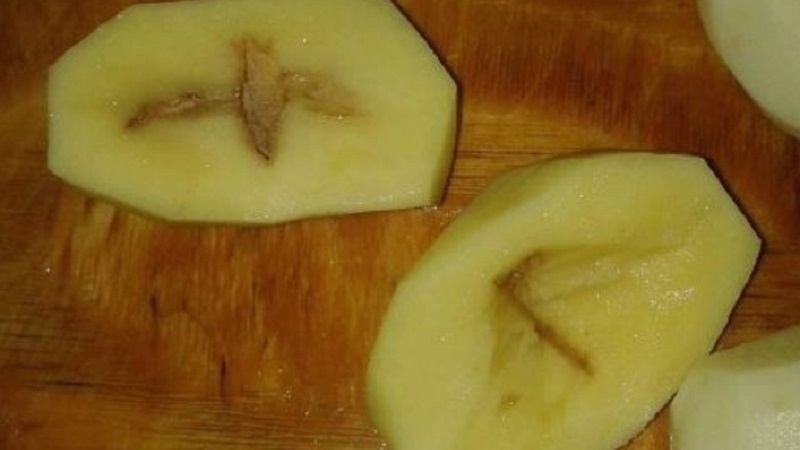
A hollow forms in the core of the potato. In varieties with rounded tubers, it has an elongated or star-shaped shape, in varieties with oblong tubers, it is rounded or oval..
The cavity is covered with a thin cream or light brown skin. If the hollow has cracks or branches protruding to the surface, the tuber rots.
Signs of infectious diseases that the potato received during the growing period, - depressed spots on the peel. Subsequently, voids form at the site of the lesion.
Why is the potato empty inside
Voids appear as a result of diseases - non-infectious, bacterial and fungal... Hollowness develops with improper agricultural technology.
Hollowness
Physiological disease that manifests itself with improper care... Voids of various sizes and shapes are formed as a result of lagging growth of internal tissues from integumentary ones.
Metabolic processes are disrupted, starch grains are destroyed, cells die off - as a result, cavities are formed. The voids are covered with corky fabric - a dense cream or beige skin.
Why does the potato become empty inside:
- Uneven moisture intake - after a long drought, there are heavy rains.
- Changes in air and soil temperature.
- An excess of nitrogen fertilizers.
- Boron deficiency in the soil. Tubers in calcareous sod-podzolic soils especially suffer from boron deficiency.
- The introduction of high doses of potash fertilizers - as a result, the need for potatoes in boron increases.
Hollowness is observed in large-tuber varieties most often... Such varieties as Yavor, Gatchinsky are prone to the formation of cavities.
Interesting on the site:
Why do potato tubers become crumbly during cooking?
Hollow with blackening
Dry rot of tubers develops as a result of damage by fusarium wilt... The disease reaches its maximum value by the end of storage. The pathogen enters the tuber from the side of the stolon. First, slightly depressed gray-brown dull spots appear on the surface. Then the peel shrinks, the pulp becomes dry and rotten.
In the future, voids filled with mycelium are formed at the affected area. The disease spreads rapidly from diseased tubers to healthy ones. The main source of infection is contaminated soil.
Phomosis infects tubers during storage... Depressed dark spots 2-5 cm in size appear on the surface. In the pulp, voids with a gray or black bloom are formed. The source of infection is infected tubers and plant debris in the soil.

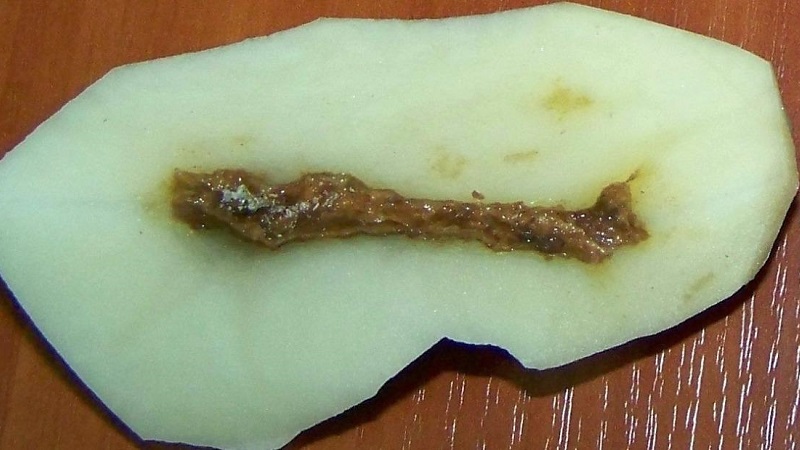
Potatoes are empty and brown
Winter scoop harms potatoes... A caterpillar 50 mm in size, light gray in color with two stripes on the body, gnaws cavities in the tubers, along the edges of which you can see the remnants of the peel.
Yellow-white hairy grubs eat holes in tuberswithout leaving the rind around the edges. Subsequently, the potatoes rot.
The common bear lives in humid lowlands... It eats up cavities in potatoes, which leads to rotting of the tubers.
Fusarium bacterial rot manifests itself during storage. May proceed as dry rot. Inside the tuber, voids are formed, covered with white, pink or orange mycelium. Sick potatoes have no smell.
Ditylenhoz of potatoes is determined by depressed dark spots in the form of dry rot on the skin... During storage, they increase, the tubers crack and dry out. The disease is caused by the potato stem nematode. Infection occurs in the soil during the growing season.
Blackleg - the pathogen enters the potato through stolons at the initial stages of tuberization. A colorless spot appears, which gradually softens. The affected area grows, a cavity is formed, the area is limited by a dark line. Rot has a wine smell first, then a sharp fishy one. During storage, the tuber core is affected, which then becomes hollow and black with a layer of sticky secretions.
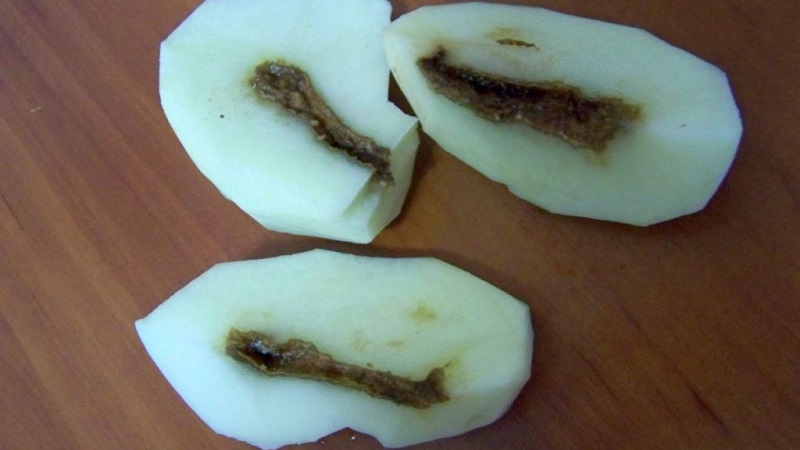
Should you store hollow potatoes?
Hollowness is found only when cutting tubers... These potatoes are stored until the next harvest. If putrefactive bacteria have penetrated into the hollow, the potato rots. They continue to grow the variety they like, selecting tubers the size of a chicken egg for planting.
Important! Potatoes affected by dangerous infectious diseases are destroyed. During storage, the disease develops due to tubers infected during the growing season.
What to do if the potatoes inside are empty
Large, impeccable-looking potatoes with a corky cavity are edible.
Tubers with signs of infectious diseases are destroyedto avoid contaminating healthy potatoes during storage.
Take a note:
Prevention of hollow potatoes
Dry the tubers before storing them.

Hollow prevention measures:
- Compliance with crop rotation.
- Destruction of plant residues after weeding and tops after harvesting potatoes.
- Timely pre-harvest leaf removal.
- The correct ratio of nutrients - potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen. Do not allow excessive nitrogen fertilization.
- On abundantly fertilized soils, plantings are thickened in order to reduce the area of plant nutrition.
- Careful bulkhead of potatoes before storing.
Boron is sourced from organic fertilizers: pork, horse and cattle manure. Poultry droppings contain insufficient boron.
The proportion of nitrogenous fertilizers should be approximately 1.5 times lower than the doses of phosphorus and potassium.
The average need for mineral fertilizers per 1 hundred square meters is:
- nitrogen - 0.6 kg;
- phosphorus - 0.9 kg;
- potassium - 1-1.2 kg.
Potatoes are planted in well-heated soil... On heavy soils, tubers are sealed to a depth of 5-8 cm, on light soils - 8-12 cm. In order to prevent the formation of a hollow due to temperature changes, they cover or spud during recurrent frosts.
To prevent infections, seed potatoes are sprayed with "Fitosporin-M" before planting. with stirring. The consumption rate per 100 kg of tubers is 0.4-0.5 liters of the drug, diluted in 6-7 liters of water.
Before laying, spray with the preparation "Maxim" - 0.2 l / 2 l of water. During storage, the potatoes are examined and the affected tubers are discarded.
Storage preparation:
- thoroughly cleaned of debris and old potatoes;
- before laying, the room is treated with bleach (3%) or a solution of copper sulfate (5%);
- maintain the temperature at + 2 ... + 7 ° C;
- provide ventilation to reduce the relative humidity of the air.
Infectious diseases spread rapidly with high humidity in the storage.
Conclusion
Now you know why blackness and emptiness appear in potatoes. Do not leave ripe tubers in the soil for too long. Timely digging prevents the formation of hollowness. If the tops show signs of disease, they are immediately mown.
Storage of the potato crop is the most important stage in the process of plant cultivation. The size and quality of the future harvest largely depends on the storage conditions of seed potatoes.