How the formation of a pepper bush is made: instructions for beginners and common mistakes
Many people believe that caring for bell peppers comes down to regular watering, feeding, and protecting against diseases and pests. However, there is another measure that can significantly increase the yield of a vegetable - the formation of a bush. Read on how to do this correctly.
The content of the article
Is it necessary to form sweet bell peppers
Bush formation is an effective technique for increasing yields. and the size of the bell pepper fruit. Formation regulates the ground volume of the pepper bush.
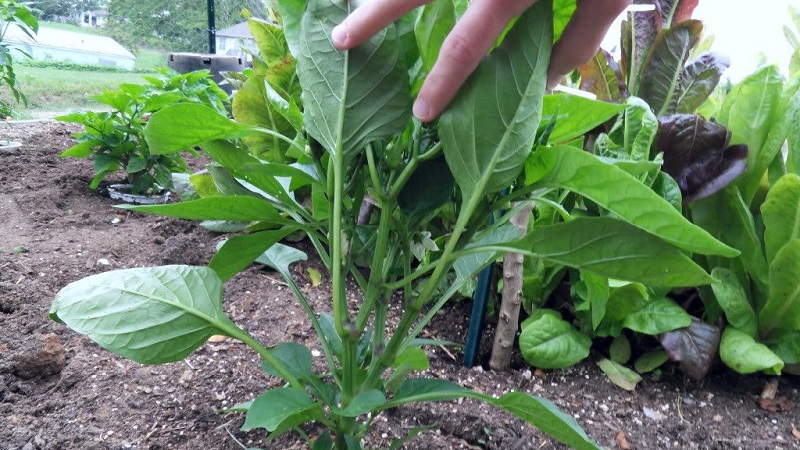

Some gardeners ignore this measure, believing that providing favorable conditions, the vegetable will already give a good harvest. However, this is not true for all varieties. Some do not cope with a large number of fruits on the bush, grow uncontrollably, spending energy on the growth of branches, and not on the fruits, which negatively affects the yield. In addition, the overgrown mass becomes a breeding ground for diseases and pests.
Variety value
Pepper formation is an obligatory stage in the care of tall varieties and hybrids this culture, those whose height reaches 1-1.2 m, for example,Cockatoo, Hercules, Apollo, Orange wonder.
It is not necessary to form medium-sized (Anastasia, Greek, Sweet dragon, Bagel, etc.) and undersized varieties (Chanterelle, Boneta, Timoshka, Fakir, etc.).
Stages and rules for forming a bush
Pepper shaping is not a one-time pinching or pruning of shoots, but an event of several stages.
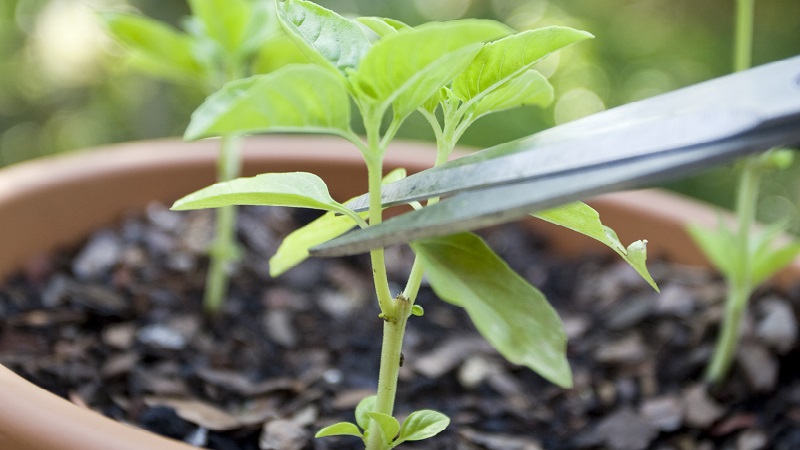
During seedling
Formation begins when the seedling reaches a height of 15-20 cm... As a rule, during this period, the sprout is divided into two branches in bell pepper, and a bud appears in the middle, which is called the crown. This bud is removed to allow the shoot to branch out further. In the future, fruits will form on each branch, increasing the yield.

In the greenhouse
When planting seedlings in a greenhouse, take into account that the bush should increase in volume by 2-3 branches... Varieties with high bushiness are planted in 3-6 pieces. for 1 sq. m. If the bushiness is average - 6-8 bushes per 1 sq. m. At this stage, pinch the pepper, cut off, remove the sterile shoots.
Attention!When the bushes take root, they are carefully examined in order to identify possible diseases and pests. The formation process only affects healthy plants.
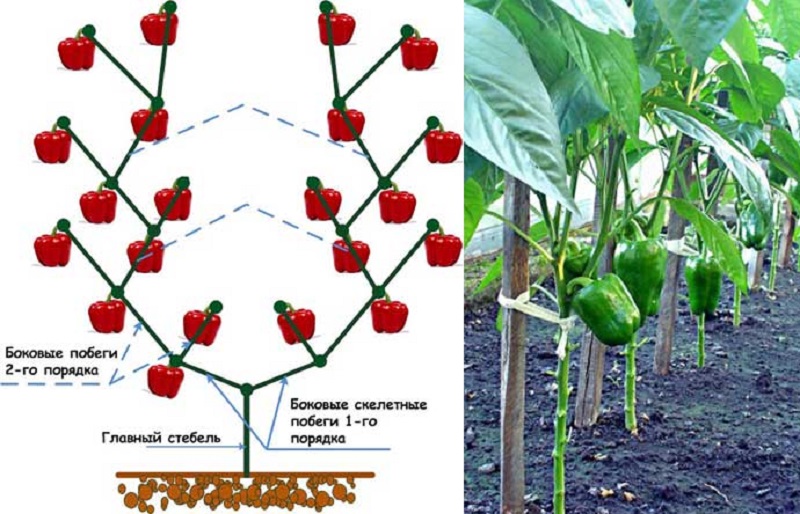
First of all, skeletal branches (branches of the first order) are determined... They begin their growth immediately after the branching of the central shoot. The processes from the leaf axils are called stepchildren. They are removed by pinching.
Skeletal branches of the first order are divided into shoots of the second order - as a rule, there are two of them. Of these, you must choose the stronger one - it will also be skeletal. Its function is to support the upstream shoots. The weaker second-order shoot is removed, leaving the leaf and fruit.
Skeletal shoots of the second order are divided into shoots of the third order... They do the same with them: they choose a more developed skeletal branch, the rest are removed by pinching.
On each skeletal shoot, new shoots and leaves form over time.... They must be removed gradually (no more than two sheets per day).Leaves shading the ovaries are cut first.
All the above procedures are repeated until the plant reaches a height of 1-1.2 m... Then the top of the bush is cut to stop growth and redirect all nutrients to the developing fruit. About a month and a half before the end of the harvest, the tops of all skeletal branches are cut off for the same purpose.
If you follow the instructions carefully, the result will be obvious.: 20-25 thick-walled peppers on each bush formed. Unformed plants will have many ovaries and small fruits.
In the open field
When grown outdoors, form only tall varieties of pepper... In medium-sized ones, only sterile and lower shoots, stepsons are removed. Low-growing peppers do not need shaping.
If desired, in medium-sized and undersized varieties, pinch the central shoots to enhance lateral branching.
Reference. Tall species should also be reinforced with side branches. To achieve this, the central stems are pinched at a height of 25-30 cm from the soil. The base of the bush should be no more than five skeletal shoots, the rest should be removed.
The next stages in the formation of a bush are to pinch off excess shoots... No more than five of the strongest shoots are left from each branch. The result is a voluminous bush. When a sufficient number of fruits appears on it, the shoots are pinched or pruned. The nutrients will be used for further fruit growth, not branches.
Suitable tool
Standard inventory is required to form pepper - garden shears (secateurs) or knife. The tool must be well sharpened and disinfected with any agent containing alcohol or chlorine.
How to form a bush correctly: step by step instructions
Form only healthy bushes... Clean instruments are used for the procedure to prevent infestation of the seedlings. Formation is the process of choosing a suitable variety or hybrid (only tall ones are used, since when ripe they give a rich harvest of large fruits), followed by planting in a greenhouse or open ground and carrying out pinching, pruning, and pinching procedures.
The formation of a pepper bush consists of several stages. Let's consider each in detail.

Removing the crown bud
The first stage of the formation of the future bush - removal of the crown bud. This must be done when the seedling reaches a height of 15-20 cm. The action ensures proper branching of the plant, and also promotes the flow of nutrients to the ovaries.
Removing excess and sterile shoots
Pepper bush formation continues when 10-12 leaves grow on it... At this point, unnecessary branches are removed, leaving only skeletal shoots. A similar procedure is carried out with all the newly appeared branches.
Over time on the plant empty shoots appear, located just below the fork the main escape. They get rid of them. They also remove leaves that block the lighting and do not take part in the nutrition of the plant. The ideal ratio is two leaves per fruit, the rest of the leaves are considered superfluous.
Dying leaves are also subject to removal., as they can provoke the development of the disease.
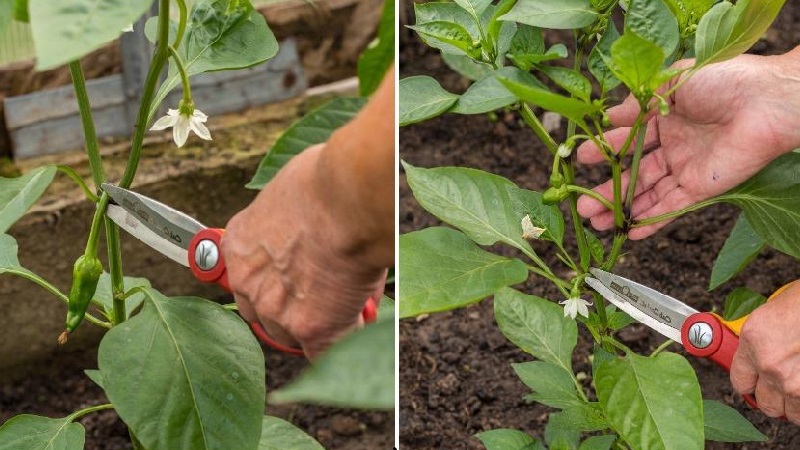
Topping
This stage is started when the fruits are formed on the bush.... Correct topping the main branches will accelerate the growth of the fruit. Pinching (pinching) is the removal of the tip of the shoot. As fruits are formed on the bush, the growth points on the skeletal branches are pinned. This allows the plant to concentrate all its energy on the development of fruits.
Reference. Also, the procedure is carried out as the shoots grow. In the stage of active growth, the tops are pinched once every two weeks, and in the resting stage, once a month is enough.
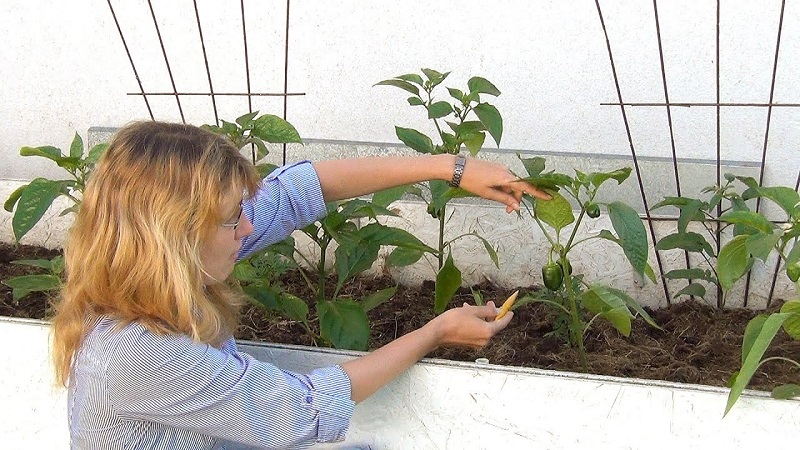
Stealing
After carrying out all the above procedures, carry out pinching - stepchildren and sterile buds formed in internodes are removed.

Common mistakes
Common mistake - pinching of bushes located at a distance of more than 20 cm from each other. With such rarely planted bushes, the green mass is left.
Reference. Many gardeners are in a hurry to remove new leaves and shoots. This is also a mistake. No more than two leaves are removed per day. Otherwise, the plant will experience severe stress and may die.
Insufficient attention of the vegetable grower to the disinfection of the instrument, with the help of which pinching and pruning is performed, can cause the plant to become infected. Disinfect the instrument with alcohol and chlorine-containing preparations.
Another common mistake - pinching and pinching in wet and rainy weather, which again increases the risk of infection. The procedures are carried out in dry weather, so that the sections dry out faster.
Many gardeners leave a large number of ovaries on the plant.mistakenly believing that fruits are formed from them. In fact, in this case, the plant spends energy on the development of unnecessary areas.
Is it possible and necessary to pick off the lower leaves
You can pick off the lower leaves of the pepper bush, and in some cases it is necessary... The feasibility of this measure largely depends on weather conditions. So, in hot and dry weather, the lower leaves are not removed, since they protect the soil from drying out. The sun's rays will destroy the plant without leaves in a short time.
If the weather is wet, the bottom of the pepper bush is exposed, since excess moisture accumulates in the leaves, which, in turn, provokes the development of bacterial and fungal infections.
Conclusion
So, don't rely entirely on nature when growing peppers. The formation of a bush is a necessary measure that greatly facilitates the process of growth and development of culture. The correct formation of the bush allows you to get a good harvest of large tasty peppers.