Delicate, fragrant Veles grape variety from Ukrainian breeders
The Veles hybrid is a vivid example of successful breeding work. The grapes are in great demand in the market and the interest of winegrowers. This is facilitated by the attractive amber-pink color of the berries, large clusters, balanced sugar and acid content and a pleasant nutmeg aftertaste. In this article, we have collected information about growing a hybrid and its distinctive characteristics.
The content of the article
The history of creating a hybrid Veles
The authorship of a hybrid of grapes called Veles belongs to the Ukrainian breeder from Zaporozhye V.V. Zagorulko. Culture refers to the dessert type. The first cuttings went on sale in 2009, and in 2010 the hybrid was presented at the international competition "Golden Bunch of Grapes" in Crimea. There he won two gold medals in the categories "People's Tasting Commission" and "Professional Tasting Commission". Large clusters with purple seedless berries and nutmeg aroma immediately attracted attention.
To obtain a hybrid, the breeder used seedless Rusbol of the selection of the Novocherkassk NIIViV them. Ya. I. Potapenko and his own hybrid Sophia. The seedless Kishmish Radiant became the paternal form. The main goal of the breeder was to convey the valuable trait of seedlessness. As a result, he managed to create one of the best dessert hybrids with excellent taste and adaptability to growth even outside the parental region. Veles is successfully cultivated in Ukraine, Russia and Belarus.
Culture is not included in the State Register of the Russian Federation, since it has not yet passed all the tests.
Interesting! Veles is a Slavic battle of fertility, wealth, wisdom and good luck, second in importance after Perun.
Characteristics and description of the plant
The bushes of the Veles hybrid are distinguished by their high vigor. Crowns of young shoots of green color with a bronze tint.
The leaves are large, rounded, of medium width, three-lobed, wrinkled, with deep side cuts, open type. Wide domed denticles are located along the edge of the leaf.
The flowers are bisexual, capable of self-fertilization. However, when using manual pollination, the yield increases significantly.
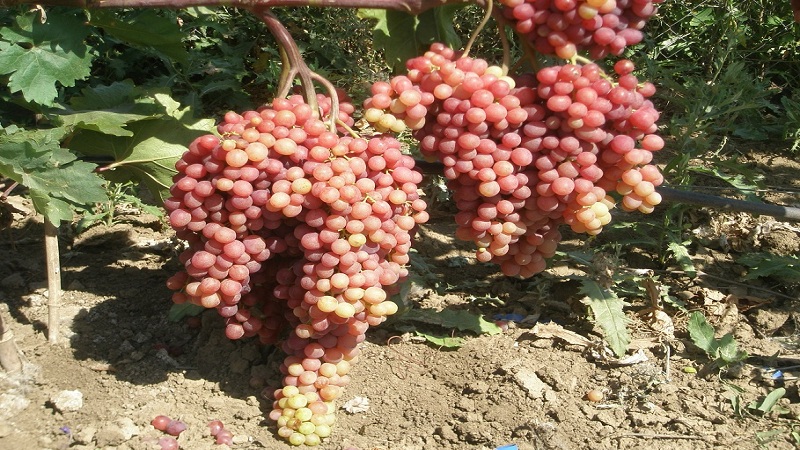
The hybrid is not prone to peas... The bunches are large, cylindrical or conical in shape, loose or medium-dense, 20-30 cm long. Maximum weight - 3 kg, average - 800-1550 g. Berries do not deform and do not rot due to their free arrangement on the brush, in conditions of excessive moisture they slightly crack.
The comb is medium, the fruit legs are long, light green, dense. Berries are oval in shape, weighing 5-7 g, will remain on the bush for a long time, do not fall off until 1.5 months and gradually turn into raisins.
The skin is thin, almost invisible when consumed, golden pink in color, with a slight waxy bloom. Color intensity varies with ripeness and light level.
The pulp is dense, tender, juicy. The taste is balanced, the ratio of acid and sugar is harmonious, the aftertaste is pronounced nutmeg. The sugar content of the berries of removable ripeness is 16.5-19 g / 100 ml, the acidity is 6-7 g / l.
The bones are absent or presented as small primordia. This raises the tasting score of Veles.
The hybrid belongs to the group of grapes with a very early ripening period.The crop is harvested 90-105 days after budding. The yield of Veles is average, but stable - 10-15 kg per adult vine.
In the photo - Veles grapes.

Sustainability
The frost resistance of the hybrid is average - the vine can withstand frosts down to -21 ° C. This indicator significantly exceeds the resistance of other representatives of raisins.
Before the onset of cold weather, the shoots have time to get stronger along the entire length. The fertility potential of the hybrid is high. 2-3 inflorescences are formed on each shoot.
Berries rarely damage wasps, despite their thin skin. Budworms are indifferent to culture. The grapes are resistant to fungal diseases - mildew (downy mildew) and oidium (powdery mildew).
Advantages and disadvantages
Hybrid advantages:
- attractive appearance;
- pleasant balanced taste and nutmeg aftertaste;
- resistance to peas and berry deformation;
- stable yield;
- resistance to attacks of insects and fungi;
- high level of transportability;
- unpretentious care.
Disadvantages:
- average frost resistance;
- cracking of berries at high humidity.
Growing features
To obtain a rich harvest, it is recommended to follow the rules of planting and caring for the vine.
Terms and rules of landing
The Veles hybrid is propagated in two ways: inoculation on the stock and cuttings.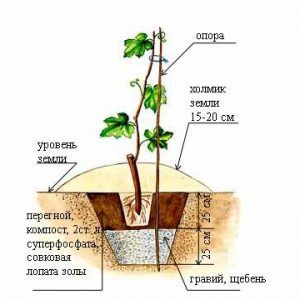
The best time to graft grapes is from March to May, depending on the region. The new bush enters early fruiting after grafting onto the old stock. In the fall, cuttings with 2-3 eyes are cut, the tips are dipped in liquid paraffin, wrapped in film and placed in the refrigerator until spring.
Spring bush rootstock cut off, leave a stump, level the cut and clean it. The stalk is cut with a wedge and soaked in water for 10-12 hours. Then they place it in a split in the center of the stump, tighten the place of attachment with a cloth and apply a layer of clay.
The second method is planting seedlings. Healthy cuttings with 4-5 buds are placed in a container of water at the beginning of February, or planted in moist soil so that they take root.
Veles is planted in nutritious air and moisture permeable soil, ideally in black soil. The landing site should be warmed up by the sun.
Important! A site with a high groundwater table, swampy area for grapes is not suitable.
Landing is performed in the direction from south to north. The bushes of the hybrid are large and require a lot of space for growth and development. When planting, observe a distance of 1.5-2 m. The distance from trees and buildings is 3-4 m.
The pit is prepared in 2-3 weeks: 80 cm deep, 80 cm in diameter. The bottom is lined with a mixture of earth, humus and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. Pour 3-4 cm of soil without impurities on top. The seedlings are dipped into the "Humat" growth stimulator. The concentration of the solution is 0.5 mg / l.
Planting is done carefully so as not to damage the delicate root processes. The rhizome is completely covered with earth, the surface is compacted, watered with 20-30 liters of water and mulched with sawdust.
Care features

Veles prefers to grow on land with moderate humidity, so watering is performed regularly after the top layer dries. The need for moisture increases during the periods of leaf emergence, flowering and bunching, after harvest. The installation of a drip irrigation system helps to facilitate vineyard care.
Mulching retains moisture in the soil and reduces watering. Sawdust, peat, straw or humus are used as mulch, which also serves as a fertilizer.
The vine is fanned out into 4 arms. To maintain the shape, regular spring pruning is performed - 6-8 eyes are left on each vine.
The hybrid is characterized by the ability to form a large number of stepchildren. When growing grapes in the middle lane, they are removed, but in the south they are preserved, since a second wave of the harvest is formed on them. Under favorable conditions, the bunches ripen in October, but the berries are slightly smaller in size and contain more acid.
Reference. Shrub supports are made in the form of trellises, single supports or arches.
In the fall, the vine is pruned, remove unripe parts and excess shoots. In regions with cold winters, shelter for the winter, having previously connected with beams. The vine is laid on the ground and covered with dry foliage or straw, dense film or agrofiber.
For normal development, grapes are fed with potassium, phosphorus, iron, zinc and boron (for example, 10 g of ammonium nitrate per 1 m²). It is important to apply top dressing after flowering, otherwise the plant will begin to actively gain green mass. The vine gets organic compounds from mulch during watering. At the beginning of fruit ripening, add 20 g of "Nitrofoski", 30 g of superphosphate, 50 g of ash per 10 liters of water (consumption per 1 m²).
Shrub formation involves controlling the number of eyes during spring pruning. No more than 35-40 pieces are left on one bush. Fruitless and weak shoots are removed, and one brush is left on the fruitful ones. These procedures unload the vines and ensure stable fruiting.
Possible problems, diseases, pests
Preventive measures reduce the likelihood of infection by pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Agrotechnical techniques: timely pruning, pinching, tying shoots, removing weeds and maintaining looseness of the soil. In this case, the leaves around the brushes are removed in a normalized manner, since the golden-pink tint of the skin appears only in partial shade.
Despite the fact that Veles is immune to fungal infections, preventive processing fungicides are needed. A solution of Bordeaux liquid and colloidal sulfur is effective.
Council. Use fabric bags or nets to keep birds away from the bunches.
Features of cultivation depending on the region
For a culture, + 2100 ° C of total active temperatures is enough to achieve full ripeness. This quality allows it to be grown in the northern regions, provided that the vine is sheltered for the winter. In the south, Veles manages to re-harvest on his stepsons.
In regions with cold winters, the hybrid is cultivated as a semi-covering and covering culture. The fan and squat shaping allows you to remove clusters and create thermal insulation in regions with frosts from -21 ° C.
Semi-covering method keeping the bush on the trunk protects the reserve lightweight part from severe frosts. When the main part dies, the bush is restored from the available reserve. This method is practiced in areas where the air temperature in winter rarely drops below -21 ° C.
Harvesting and application of the crop

Harvested in late July and early August. The brushes are cut with pruning shears; they cannot be broken off. The second crop ripens in October. The grapes tolerate transportation despite their thin skin. The brushes are placed in shallow wooden boxes.
The harvest is stored in the cellar for up to 3 months. The brushes are hung on taut twines for better preservation. Grapes are used fresh and for processing into jam, raisins, wine, compote.
Reviews
The growers' reviews about the Veles hybrid are only positive.
Ivan, Krasnodar: “I planted this variety three years ago. I heard about him from Ukrainian relatives and was eager to grow up in his country house. The grapes are beyond praise, I picked the first bunch in a year. A year later, he received a large harvest. The bunches are large, weighty. Mine reached 2 kg. The berries are dense, do not crack, sweet, nutmeg, there were bones, but small, imperceptible. "
Zoya, Bryansk: “Veles grapes have been growing with me for 5 years. Fruiting is stable, yields are average, but I grow it solely for the taste and appearance. The brushes are large, the berries do not rot, they are evenly colored as they ripen. The year before last there was a heat, seeds appeared in the berries. Last summer was mild and pitted. Caring for the bushes is standard - pruning, feeding, watering. "
Conclusion
The Veles hybrid is a product of the breeding work of V.V. Zagorulko.The culture appeared relatively recently, but managed to gain popularity among amateur winegrowers.
The grapes have an attractive appearance, the berries have a balanced taste. The plant is characterized by stable fruiting, insect and fungal resistance. There are no difficulties in leaving. Agricultural technology involves moderate watering, fertilizing, pruning, tying vines, shelter for the winter in regions with a cold climate.