How to protect yourself from pepper pests in a greenhouse
When growing peppers in a greenhouse, the gardener is faced with a lot of unpleasant surprises. The most dangerous are pests. Insects spoil fruits, root system, leaves, stems. We will consider the description and photo of pepper pests in the greenhouse and their treatment in the article.
The content of the article
Causes and signs of pests on pepper

The main reasons for the appearance of insects on pepper are as follows:
- Flight from other cultures. For example, aphids are thrown from tomato, cucumbers... Pests attack both greenhouse plants and those growing in the open field.
- Contaminated soil... Often, beginners ignore pre-sowing decontamination work or transfer the land with insect larvae from an open area.
- Failure to comply with agrotechnical rules. Improper watering and feeding, as well as untimely work on the destruction of larvae lead to active reproduction of pests.
- Unfavorable climatic conditions... Some insects are attracted by heat, others by too wet soil. If you pour the peppers and do not air the greenhouse in time, the conditions will be favorable for the early development of diseases due to the influence of pests.
- Dense plantings. Sunlight does not penetrate between plants. The soil does not warm up and insects appear.
The signs of pests are as follows:
- weakened stem;
- pepper withers quickly;
- late blight, gray rot and bacteriosis appear.
In advanced cases, the diseased plant dies. Insects, along with infection, continue to infect neighboring peppers and other greenhouse crops.
What harm do they do to the plant
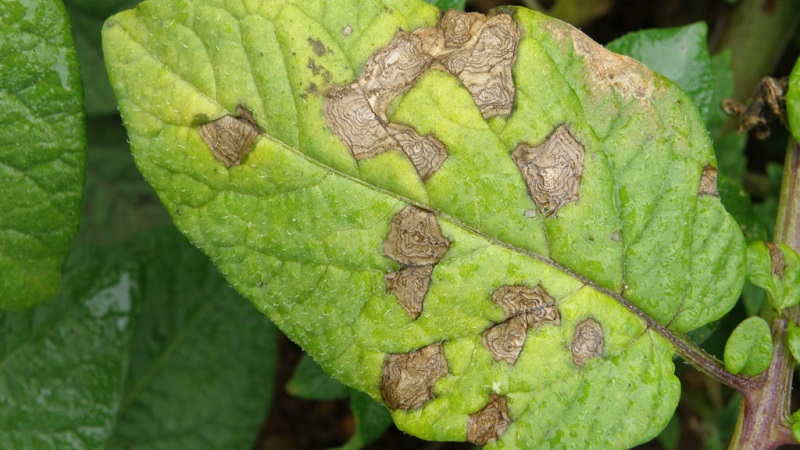

Insects suck juice from stems and leaves, devour roots and fruits. Most often, the larvae of adults cause the death of plants. Their secretions and waste products provoke the appearance of infections. This is late blight, gray rot and bacteriosis. They, in turn, destroy groups of plantations.
What are the pests of pepper in the greenhouse
Insects attack pepper even if all agricultural rules are followed. Therefore, at the first sign of their appearance, they immediately begin a struggle to save the pepper and neighboring crops.
Naked slugs
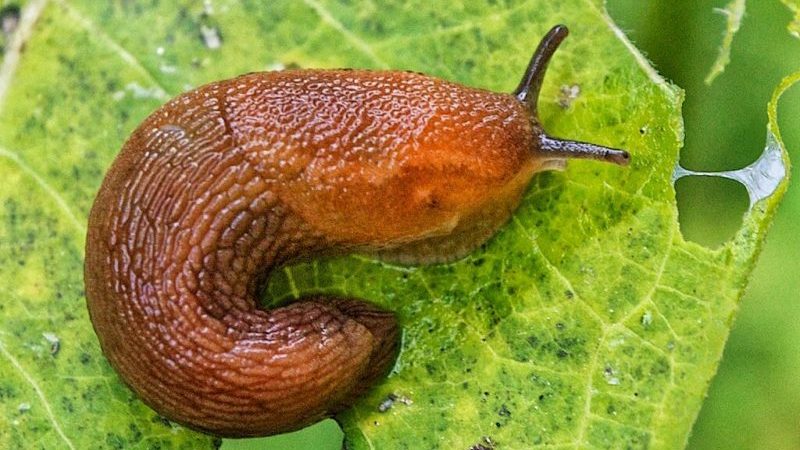

Molluscs without a shell look quite harmless. However, they are able to destroy not only peppers, but also cabbage, beets, and cucumbers. More often, adults attack young bushes.
Signs of appearance:
- rounded holes on the leaves;
- slimy traces;
- rotting pepper;
- excrement on the stem and leaf plate.
In the daytime, naked slugs hide under the ground, vegetation, boards, stones. A comfortable environment for them is thickened plantings, high humidity. But mollusks die in extreme heat, and are activated only during prolonged rains.
Shield
This insect spoils the green mass of the bush and fruits. The scutellum has a rounded body about 2 mm in diameter. The body is covered with a protective brown shield, so the pest is not visible.
In the photo - a scabbard on a pepper.
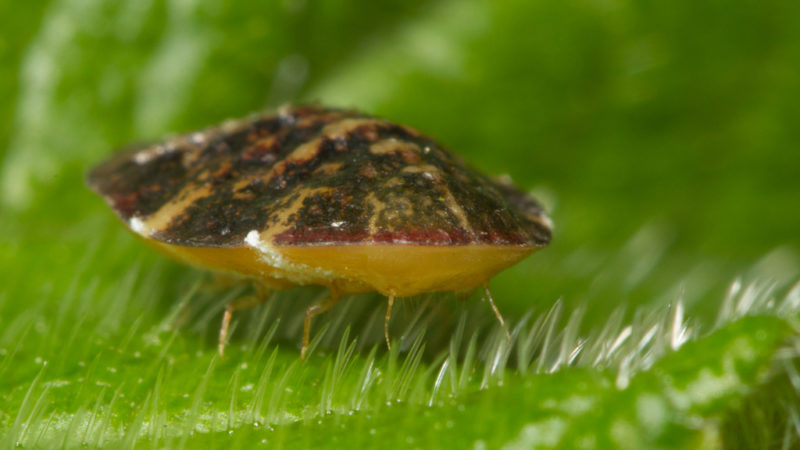

The danger is the larvae. They quickly penetrate the leaf plate, sucking the juice out of it. At the same time, the surface of the plant is covered with round dark plaques, a sticky bloom.
Reference. Female scale insects live in a sticky plaque that larvae continuously excrete. They move into a stationary lifestyle, constantly feeding on the plant.
Whitefly

This pest is not easy to find in a greenhouse, but traces of larvae in the form of twisted pepper leaves are noticeable.
Whitish butterflies lay eggs on the underside of the leaf plate. Then voracious larvae appear and begin to actively suck the juice from the plant.
Signs:
- twisted leaves;
- sticky honeydew;
- death of bushes.
Isolation of whitefly larvae is a favorable environment for the reproduction of pathogenic fungi. In advanced cases, pepper dies from bacteriosis.
It is interesting:
Aphid
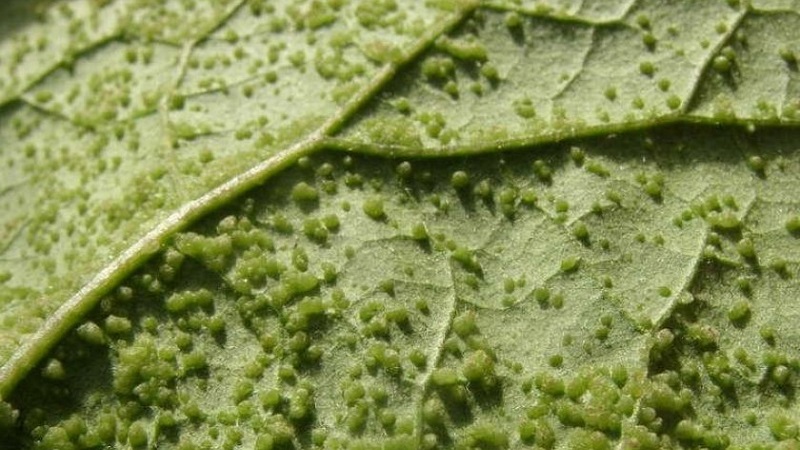

Light green small insects with a soft body suck juices from plants, eat leaves. Another danger of their appearance is the early arrival of a colony of ants. Aphid destroys all plantings, provoking their infection with late blight.
Signs:
- groups of green insects in individual areas of the pepper;
- transparent sticky coating on the leaves;
- ants;
- eaten edges of leaf plates;
- yellow, twisted leaves;
- cessation of the development of the bush, twisted tops;
- dried inflorescences and deformation of the fruit.
Ants do significant harm to the pepper, but they leave the greenhouse on their own when the aphid is completely killed.
Spider mite
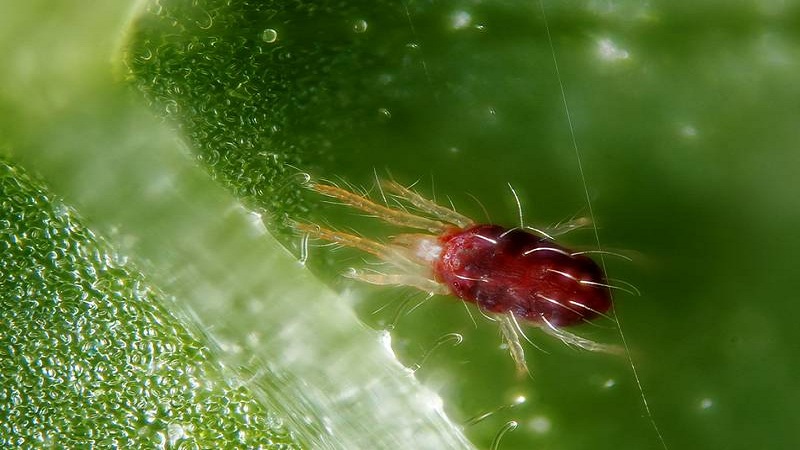

Mite sucks the juice from the plant, quickly destroys the green mass. Bottom line: the fruits do not ripen, the crop dies. Small arachnid insect settles in the inner part of the leaf. Then it moves to neighboring crops through water, soil, garden tools.
Signs:
- web;
- holes in the leaves;
- death of inflorescences and ovaries;
- yellow and wilted leaves.
When a cobweb appears on the leaf plate, they immediately begin to process the plantings, otherwise you can lose the entire crop.
Wireworm
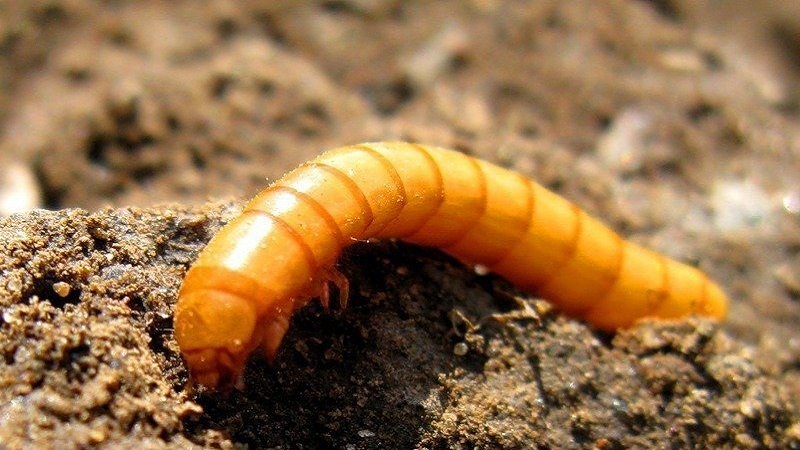

A dangerous pest that spoils the culture only underground. Signs of appearance: wilted top, weak stem. With serious damage to the bush, it is impossible to save the crop. The body of the click beetle larva is dark brown and has a hard surface. The length of an adult caterpillar is 5 cm.
The worm lives in the ground, feeds on the root system and young shoots. It does not die in winter, retaining its viability for up to 5 years. Caterpillars attack the lower surface of the stem and are visible in the upper soil layers.
Scoop
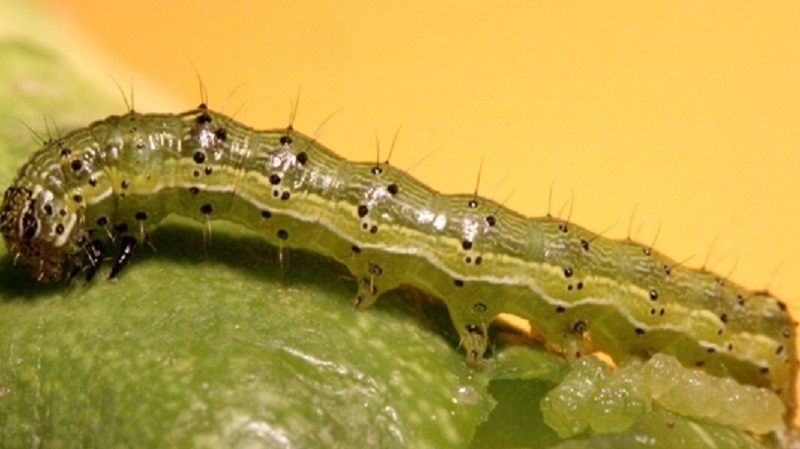

The pest is difficult to detect as it is only active at night. Caterpillars cause serious damage to the pepper, reducing the yield. The larvae hatch in summer and immediately begin to eat leaves and fruits.
Signs of appearance include the nibbled edges of the leaf plate, minor damage to the fruit, yellow and wilted greens, slow growth of the bush. During the day, green caterpillars are found in the upper layers of the soil.
It is interesting:
Thrips
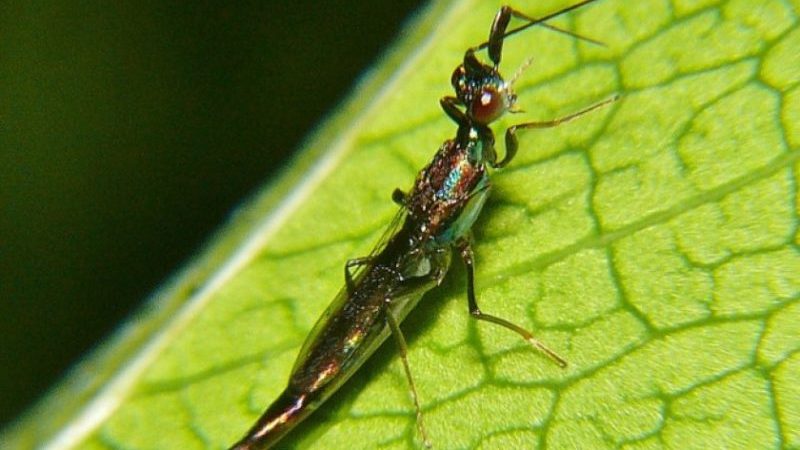

Insects reach a length of 1.5 mm, so they are invisible on the pepper. They jump to neighboring crops, quickly spreading throughout the greenhouse. Insects deprive the plant of juice, which ultimately leads to its wilting and death.
Signs:
- small yellow spots or stripes on the leaf plate;
- when you shake the bush, insects crumble in the form of oblong dust particles;
- yellowing and death of leaves.
Thrips are the main vectors of diseases. Pepper is often affected by bacteriosis, tobacco mosaic.
Colorado beetle
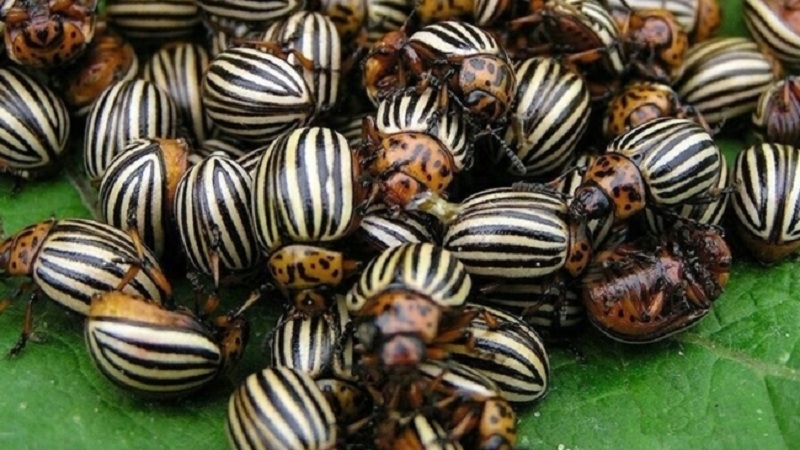

It is almost impossible to destroy the beetle, since it quickly acquires immunity to poison. Finding an insect and its larvae is easy. The body of an adult is covered with black and white stripes, the larvae are brown or pinkish. Clutches of bright orange eggs are located on the inside of the leaf plate.
Signs:
- colonies of insects on the stem, leaves, ground around the bush;
- laying of eggs;
- nibbled edges of the leaves.
Larvae and beetles eat pepper leaves, destroy inflorescences. Adults hide in the ground, tolerate winter well.
It is interesting:
How to escape from the Colorado potato beetle: how to process potatoes
Medvedka
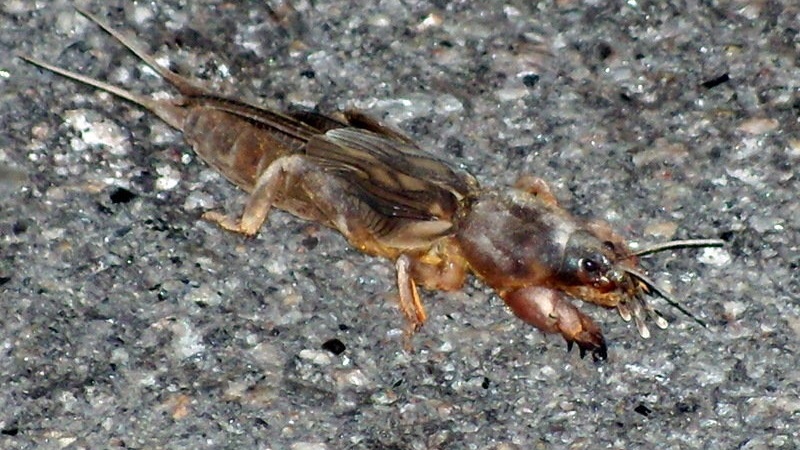

A large insect with a body length of up to 5 cm. It has large front pincers, a head with powerful jaws, and shortened elytra. Medvedka eats not only pepper, but also neighboring crops. Lives underground, breaking through narrow passages to the roots of plants. The pest is difficult to notice, since it damages only the underground part of the bush.
When an insect appears, large lumps of earth are visible next to the bushes. They develop larvae, which do not miss the opportunity to harm the roots of the pepper. The plant quickly withers, withers, dies.
Beetle larva
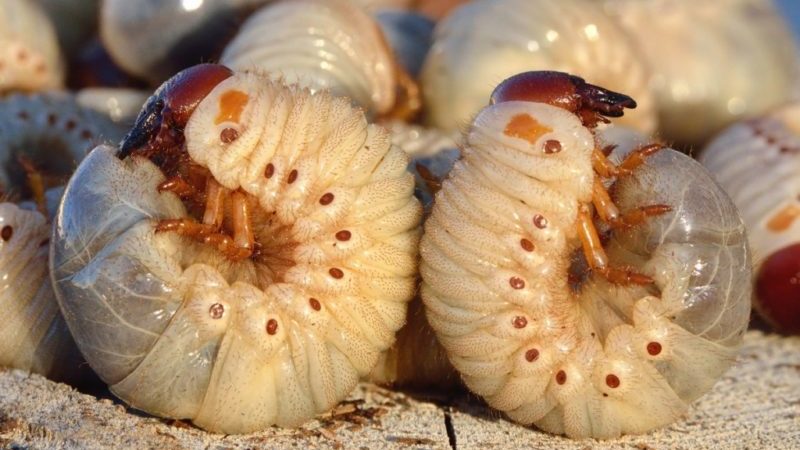

It lives in the upper soil layer, tolerates winter well. Has a thick white body, twisted into a ring. It has 3 pairs of dark brown legs. The gluttony of the larvae increases with age, they live for 4 years.
In summer, caterpillars burrow into the ground to a depth of 10-20 cm and eat the root system of the culture. Their favorite delicacy is young peppers.
Signs of appearance:
- white caterpillars in the upper soil layer;
- yellow and wilted green mass;
- the bush does not develop, stops growing, is easily pulled out of the soil.
The pest damages the roots, so the pepper loses its strength and dies.
Ants
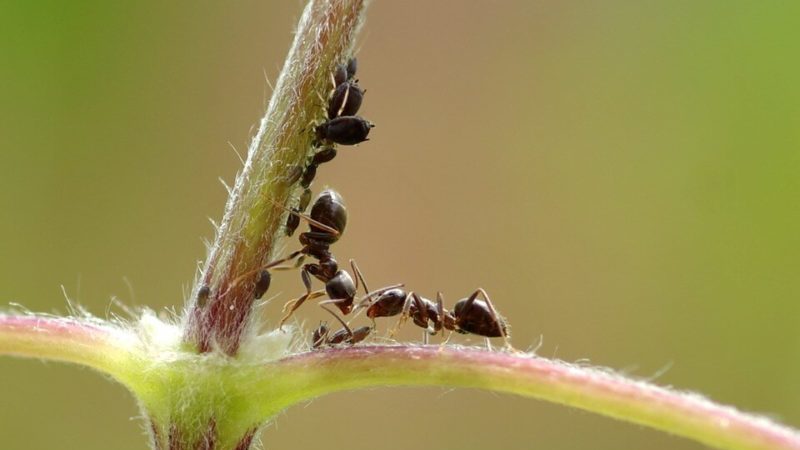

Insects harm peppers by raising aphids in the greenhouse. Aphids secrete sweet nectar, which causes the ants to create entire colonies, protecting them from other insects. Aphids begin to eat plants, causing the development of diseases.
Finding an ant is very simple: it moves quickly on the ground, on the stalks of peppers. Anthills have been formed near the crop.
Caterpillars
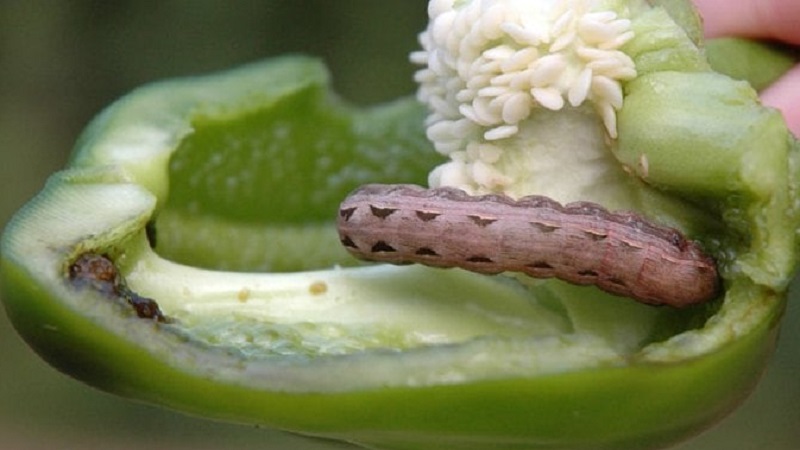

The main types of caterpillars on pepper: garden, exclamation, winter, cotton, gamma scoop, caradrina. They differ in appearance, but harm the same way: they eat leaves, interfere with the development of inflorescences, and destroy plantings.
It is easy to find them: there are holes on the leaves or they are completely eaten, individuals are noticeable, yellowed and twisted leaf plates.
Read also:
If caterpillars are bred in tomatoes - popular ways to combat a pest
Nematodes
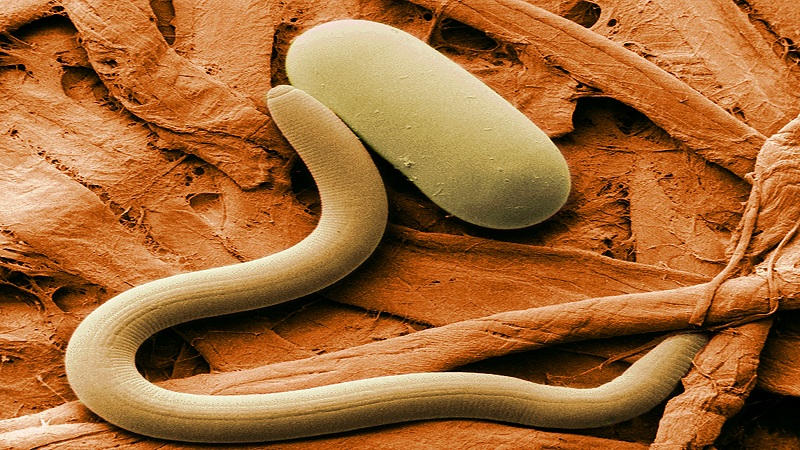
The worms form yellowish brown bumps on the root system of the pepper. They live at a depth of up to 50 cm, so it makes no sense to fight drugs with them. When worms appear, the plant withers and dries up.
Attention! The affected culture cannot be cured, so the bush is dug up and destroyed. Additionally, a layer of soil of 50 cm is removed. To prevent the appearance of a pest, inventory and planting material are disinfected, the rules of crop rotation are observed.
Other types of pests
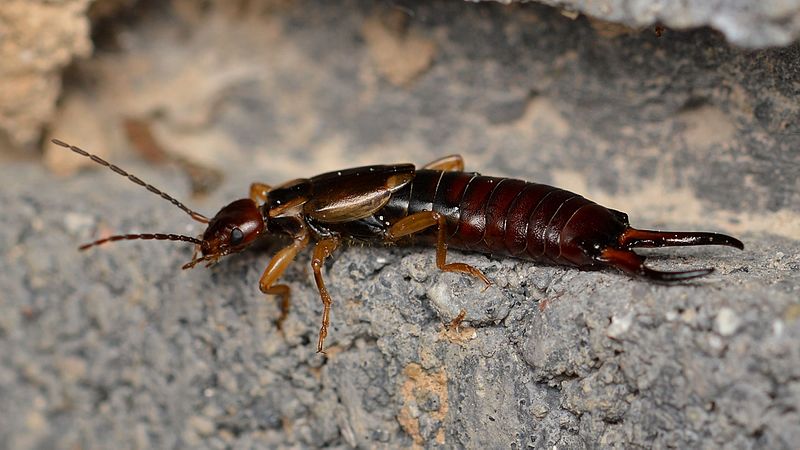

Large groups of two-tails in the greenhouse cause a lot of problems. They differ in their bright appearance: red head, long black body, two "horns" on the tail. During the day they hide in the ground, under boards, stones. The two-tails eat young peppers and fruits. Signs of their appearance: wilting of the plant, darkening of the fruit.
How to treat peppers from pests
Despite the variety of insects, experienced gardeners use popular remedies. These are chemicals, biological preparations, folk methods. All of them are aimed at the complete destruction of pests, but not diseases.

Mechanical methods
Colorado beetles and their larvae, caterpillars, bear, slugs are harvested by hand... For slugs, make traps in the form of grooves around the peppers. Severely affected plants are dug up and destroyed.
To remove worms remove the topsoil from 20 to 50 cm and replace it with disinfected soil. Small sucking insects are destroyed only with drugs.
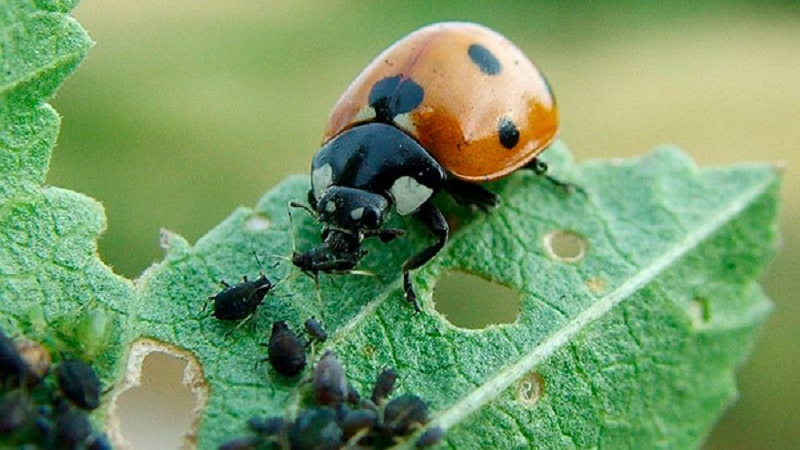
To combat aphids ladybirds are attracted to the greenhouse. They will quickly destroy the colonies, additionally get rid of ants.

Traditional methods

Effective only with a small number of insects. Popular options:
- Quicklime, crushed eggshells or coarse sand... Spread under bushes to kill slugs, caterpillars and worms. Soft bodies are damaged by large particles, so the pests die.
- Soap solution against sucking insects and spider mites. 40 g of laundry soap and 2 g of kerosene are dissolved in 10 liters of warm water. Water the soil abundantly once a month. Used at any stage of pepper development.
- Soap-ash solution. Add 1 tbsp to 9 liters of warm water. wood ash and 50 g of laundry soap. The resulting solution is sprayed on plants 1 time in 2 weeks. It is used before the formation of flowers, then after the appearance of fruits.
- Garlic infusion. Grind 200 g of garlic and pour 2 liters of boiling water. Insist day, then filtered and diluted with 10 liters of pure water. The solution is sprayed on the bushes 2 times a month. Enough 2 treatments after planting pepper in open ground.
Biological agents
Safe substances do not harm humans, peppers, neighboring crops. But they are used strictly according to the instructions. Manufacturers claim that biologicals can be used at any stage of pepper development.
The most popular: "Mycoafidin", "Verticillin", "Bicol", "Bitoxibacillin", "Fitoferm".
The products show excellent results in the fight against sucking insects, whiteflies, ants, but are ineffective against worms and caterpillars.
Pharmacy preparations
Safe and affordable drugs. They help to get rid of aphids, ants, thrips, spider mites, caterpillars, bear.
The following popular recipes are used:
- Iodine infusion. In 9 l of water, 1 l of milk whey and 10 ml of iodine are diluted. The composition is sprayed with bushes 1 time in 2 weeks. The treatment is carried out early in the morning or late in the evening to avoid sunburn on the leaves. Used at any stage of bush formation.

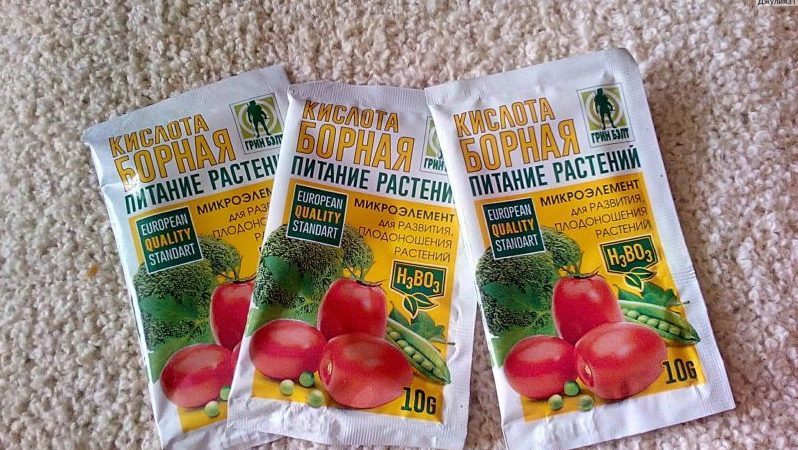
- Boric acid. In 10 liters of warm water, dissolve 20 g of the substance. The composition is poured under each bush in the amount of 0.5 liters. The treatment is effective during the fruiting period, since boric acid destroys pests and improves the taste of pepper.

- Potassium permanganate. A light pink solution is obtained, 500 g of wood ash (per 10 l of water) is added to it. The bushes are sprayed with the composition 1 time in 3 weeks during the entire growing season.

It is interesting:
Boric acid application for plants: tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers
Chemicals
They are considered extreme measures of struggle. They kill insects quickly and efficiently. Their disadvantage is toxicity. Therefore, during the blooming of pepper flowers, chemical preparations are not used.
How to treat peppers from pests in a greenhouse:
- "Bicol". Helps in the fight against Colorado beetles, aphids, caterpillars, scoop, wireworms. The substance is diluted according to the instructions (5 g in 10 liters of water), the beds are treated once a week until the flowers appear.

- Fitoverm. Effective against sucking insects. Dilute 1 ampoule in 10 liters of water, spray the leaves from all sides with the composition. In case of severe lesions, the pepper is treated 3 times before the appearance of inflorescences.
- "Lepidocide". Aimed at destroying the whitefly and bear. According to the instructions, a solution is prepared (30 g per 10 l of water) and the bushes are treated once a week before the start of fruiting.
- Arrivo. Kills sucking pests at all stages of their development. The mixture is prepared according to the instructions (3 g is diluted in 5 liters of water), the leaves are sprayed once every 2 weeks. Enough 2 times before the formation of inflorescences. Processing is carried out only in dry weather.
- "Nurel". Used against thrips, wireworms, caterpillars, worms, ants. The solution prepared according to the instructions (2 g per 5 l of water) is treated with pepper 2 times before the fruit begins to form.
Scheme and regularity of treatments
Chemicals and biologicals are used strictly according to the instructions.
Folk remedies are used up to 3 times a month. Treatments are carried out in dry weather, late evening or early morning. It is undesirable to use chemicals during the formation of ovaries and fruits. Better to switch to biological and folk remedies.
Precautions when working with chemicals

Use masks, gloves, tight clothing. Make sure that there are no exposed skin areas. After finishing work, clothes are washed, masks and gloves are thrown away. Containers and tools are stored in a separate room.
Pest prevention

The experience of summer residents has shown that it is easier to prevent insects from appearing than to desperately fight them later. Fundamental rules:
- alternation of plantings in the greenhouse;
- using only healthy, disinfected planting material;
- pre-sowing disinfection of soil, equipment, greenhouse structures;
- preventive spraying of seedlings with folk remedies;
- regular inspection of plantings for pests;
- compliance with the watering regime, dressing;
- timely weeding and loosening work.
Conclusion
Many pests can kill peppers. Chemicals, biologicals, pharmaceuticals and traditional methods will help get rid of them. Adults are easy to pick by hand. It is important for beginners to remember that it is better to follow preventive measures than to end up wasting time and money buying drugs.