How to destroy whitefly on tomatoes: proven methods and methods of prevention
From the invasion of whitefly tomatoes can die within 12-14 days. To save the planting from a small insect dangerous for many cultures will help the knowledge of biology and weaknesses pest.
A detailed description of the pest, how and how to destroy a whitefly in a greenhouse on tomatoes - read the article.
The content of the article
What is a whitefly
Whiteflies, or aleurodids, belong to the family of small, equal-winged insects. There are about 1550 species of whitefly.
The danger for planting tomatoes is the greenhouse or greenhouse whitefly.
The pest is widespread. Infection occurs from imported plants, less often as a result of independent flights.
For the development of the insect, a warm, humid climate is necessary, so the whitefly appears mainly in greenhouses and greenhouses. Under favorable weather conditions, the moth in temperate latitudes reads from mid-June. Whitefly maintains constant activity only in the southern regions.
Biological features
From laying eggs to the appearance of mature whiteflies, it takes from 22 (at + 24 ºС) to 60 (at +12 ºС) days... The most favorable temperature for the pest is +18 - +24 ºС. At + 30 ° C, the life span of moths is sharply reduced, sometimes up to four days. The lower limit for the development of embryos, larvae and nymphs is +7 ºС.
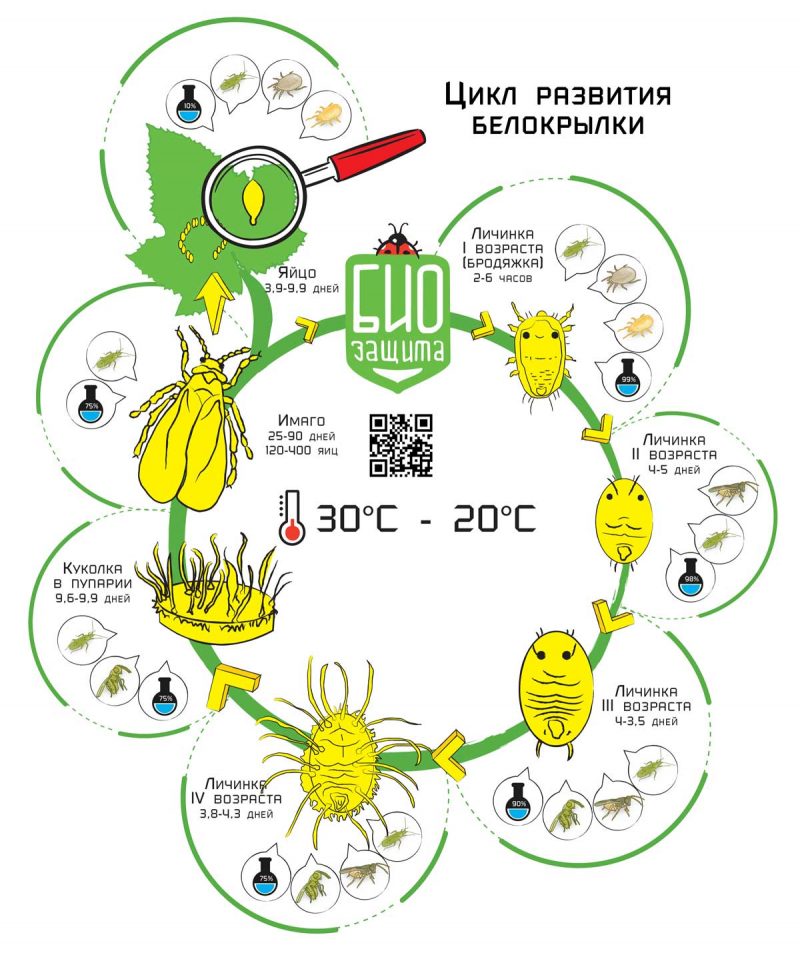 The life span and fertility of moths also depend on the fodder plant. When settling on tomatoes, the laying period is 15-17 days and the female manages to lay 35-40 eggs. On average, the number of the insect population increases 10 times per generation.
The life span and fertility of moths also depend on the fodder plant. When settling on tomatoes, the laying period is 15-17 days and the female manages to lay 35-40 eggs. On average, the number of the insect population increases 10 times per generation.
The life of a whitefly is divided into 4 stages: an egg, a larva, a nymph, and a sexually mature individual (imago).
A description of each of them is given in the table.
| Stage | Where to looking for | Description | Duration |
| Egg | The underside of young leaves | The clutches are crowded and scattered. Egg size 0.2-0.25 mm, attached to the surface of the leaf with a thin stalk. Initially pale green in color. After 1-2 days, it turns brown until the end of the embryo's development. | 7 - 13 days |
| Larva | The underside of the sheet | Immediately after hatching from the egg, the size of the larva is about 0.25 mm, the body is transparent, like a scale. She is mobile for several hours. Then it is attached to the sheet with the oral apparatus and starts feeding. In the process of vital activity, it releases a wax-like substance that creates a dense barrier. With growth, body length increases to 0.8-0.9 mm. At the end of development, it ceases to feed, the body thickens, the larva turns into a nymph. | 7 - 15 days |
| Nymph | The back of the leaves | About 0.8-0.9 mm long, whitish in color. Wavy bristles are located along the edges. At the end of the developmental period, a fully formed moth flies out through the formed stomata. | 10 – 16 days |
| Imago | After the transformation from nymphs, they remain on the same leaves, then they spread up the plant | The body is white or yellowish, 1.3-1.8 mm long. The wings are white, covered with a dusty coating. Females begin to mate and lay eggs 12-20 hours after emergence from the nymph. | Up to 20 days for females, 8 - 12 days for males. |
Whitefly generations overlap each other, so that the same plant contains insects of all stages of development: from embryos to adults.
Why is whitefly on tomatoes dangerous?
Both adults and whitefly larvae harm tomato plants.
Feeding on plant juices, the insect damages green cells. Waste products completely or partially cover the stomata of the leaf plates. The processes of photosynthesis and respiration are disrupted. Growth, flowering and formation of ovaries are slowed down.
On sugary secretions pests a sooty mushroom successfully develops, which manifests itself in the form of a dark bloom on the tops and fruits. The mycelium clogs the microscopic airways in tomato foliage and interferes with photosynthesis.
Whitefly is a carrier of viral diseases. The appearance of an insect is often accompanied by outbreaks of tomato mosaic, aspermia (there are no seeds in the fruits), etc.
Reasons for the appearance
Whitefly most often enters the site with infected seedlings or seedlings.
The prosperity of the pest is facilitated by:
- high temperature (above + 20 ºС);
- high humidity;
- lack of ventilation;
- thickened plantings.
Signs of pest infestation
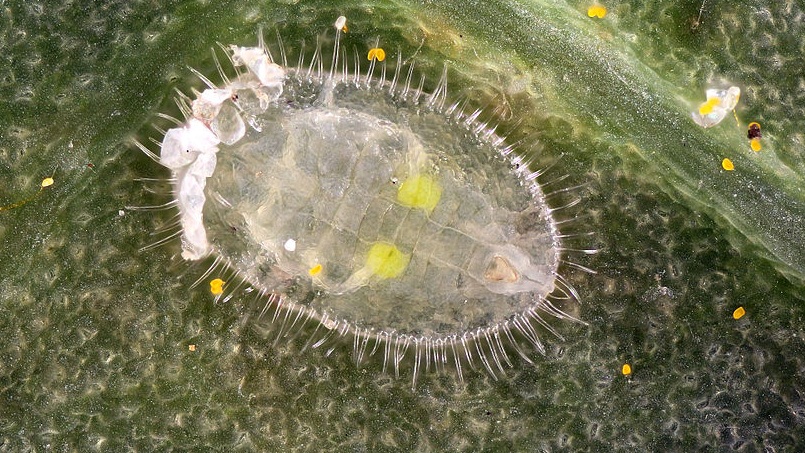

The presence of whitefly on tomato bushes indicates the following:
- White moths flutter over the beds. If you shake the plants, a swarm of insects will appear.
- On the back of the leaves, small transparent scales are visible - the larvae of the pest.
- White, sticky to the touch spots appear on the tops - whitefly discharge.
- Leaves curl, turn yellow and fall off. The growth and formation of fruits slows down dramatically.
- Dark brown spots on foliage and fruits signal the development of a sooty fungus.
Control methods
The methods of dealing with whitefly on tomatoes in the greenhouse and in the open field are similar. Only in the greenhouse it is easier to regulate the microclimate: regular ventilation will help to reduce the temperature and humidity.
To remove the whitefly, gardeners use insecticides and biological agents. Popular recipes are also popular.
Biological methods
Biological methods are to populate tomato plantings with natural enemies of the whitefly. The most famous entomophages are encarsia and macrolophus.
The use of such "biological weapons" does not harm humans, plants, or beneficial insects.
Encarsia

A representative of the vast family of wasp wasps. An adult lays eggs in the body of whitefly larvae. The hatched microscopic encarsias feed on the tissues of the host's body, and then pupate in it. Whitefly larvae thus turn black and mummify.
The adult encarsia feeds on the hemolymph of the whitefly larvae and nymphs, destroying up to 15 pests during its life (20-40 days).
To control the number of pests, five individuals per 1 m2 are sufficient.
Cages with encarzia pupae are hung in the greenhouse. In about a day, sexually mature entomophages fly out and they begin to destroy the whitefly.
Macrolophus
This predatory bug feeds on pest larvae and eggs.
The lifespan of an adult insect is 25-30 days. During this time, the bug eats up to 2,500 larvae and 3,500 whitefly eggs. Also, the presence of macrolophus helps to remove aphids. For the destruction and containment of the growth of the number of pests, 4-6 individuals per 1 m2 are required.
Live predators are sold in special bottles with a nutrient substrate. They are released evenly over the entire planting area.
Important! Entomophages are released in the evening and calm weather. It is necessary to populate living organisms on the beds no later than 18 hours after purchase.
For the development of encarsia and macrolofus, temperatures of 25-27 ºС and a humidity of about 70% are favorable, therefore they are used mainly in greenhouses.
The effect of beneficial predators appears gradually. Biological methods are best used as a prophylaxis or at the initial stages of whitefly infection.
Chemicals
Pesticides are effective in combating whitefly, subject to two simple rules:
With a single treatment, as a rule, only larvae and adults die - the eggs remain viable. Therefore, after 7-10 days, re-spraying is carried out.
Insects adapt quickly and develop resistance to "chemistry". To avoid this, the drugs are used only in the doses indicated by the instructions and do not use the same remedy during the season.
On a note... In case of significant damage, to destroy the newly hatched whitefly larvae, it is useful to release entomophages a week or a half after treatment with chemical preparations.
Examples of popular powerful whitefly medications include:
- Fitoverm - 5% aqueous emulsion of aversectin C. It has a nerve-paralytic effect, the death of pests occurs in 1-3 days after treatment. Does not cause resistance, it is safe for humans. Spraying is carried out 2-3 times during the growing season with an interval of 14-20 days. The crop can be harvested 3 days after processing.
- «Actellic»On the basis of pirimiphos-methyl - produced in the form of an emulsion concentrate, packaged in ampoules of 2 and 5 ml. It causes paralysis and almost immediate death of pests. Dangerous for humans and bees. Apply no more than two times per season. The waiting period before harvesting the fruit is at least 30 days after the last treatment.
- «Aktara»- contains thiamethoxam. In 15 minutes after treatment, the insects stop feeding and die within 24 hours. It goes on sale in the form of water-dispersible granules and a concentrated suspension. Low hazard to humans. Dangerous for bees. Used for root watering and for spraying plants. It is applied once. It is recommended to harvest the crop no earlier than three days after using the drug.
Important! When working with chemicals, strictly follow the instructions and observe safety measures.
Folk recipes
For preventive purposes and with a small number of pests, experienced vegetable growers recommend treating tomatoes with folk remedies.
Popular whitefly tinctures:
- Garlic... 15 g of chopped garlic cloves are poured into 100 ml of water and insisted for 5 days. For spraying, 5-6 ml of the resulting concentrate is diluted in 1 liter of water.
- Of yarrow... 200 g of chopped herbs are poured into 3 liters of boiling water and insisted for 2 hours. Filter and spray tomato bushes.
- Tobacco... 100 g of tobacco or makhorka is infused in 1 liter of water for two days, the beds are filtered and processed.
When spraying, the leaves are well moistened on both sides. Infusions should be applied every 3-4 days during the entire growing season.
To combat moths, special traps are effective. They are easy to make yourself. Grease a sheet of bright cardboard (for example, red or yellow) with honey or petroleum jelly and place on the garden bed. Butterflies will flock to the bright bait, stick to the paper and die.
Preventive actions
To protect against the appearance of a whitefly, the following measures are effective:
- Cleaning the beds from all plant residues.
- Autumn and pre-planting preparation of greenhouses: cleaning of all garters and equipment, washing structures and disinfecting the premises with insecticides.
- Freeze greenhouses until snow falls.
- Inspection of seedlings. Instances showing signs of infection are disposed of immediately.
- Regular ventilation of greenhouses.
- Planting no more than two tomato bushes per 1 m2 for tall varieties and no more than four for medium-sized ones.
- Compliance with the regime of watering and feeding plants.
Read also:
How to get rid of whitefly in a greenhouse on cucumbers.
Conclusion
Whitefly is a small butterfly that does great harm to tomato plantings in open beds and in greenhouses. Feeding on plant juices and poisoning the foliage with waste products, moths and larvae slow down the growth and formation of fruits, in advanced cases the tomatoes die.Pests cause viral and fungal diseases.
To combat the whitefly, insecticides are used, and entomophages are released into the beds. Infusions according to folk recipes are effective as a preventive measure and at the initial stages of damage. Cleanliness in the beds, autumn treatment of greenhouses with anti-insect drugs, maintaining plant health will prevent the appearance of the whitefly.