What are the diseases of watermelons and their treatment, preventive measures
Diseases of watermelons, their prevention and treatment are the main concern of gardeners when growing this demanding melon crop. In addition to creating comfortable conditions for growing, watermelons need careful care and timely detection of signs of the disease.
In order to avoid the death of the plant, it is important to correctly identify the pathogen and eliminate it. Let's consider the most common diseases and how to deal with them.
The content of the article
What diseases do watermelons have?
Diseases of watermelons are mainly of a fungal origin, isolated diseases are provoked by viruses. Almost any disease can leave a grower without a crop already at the seedling stage. Knowledge of the signs of the disease, methods of treatment and constant monitoring of plants will keep the fruits intact and safe.
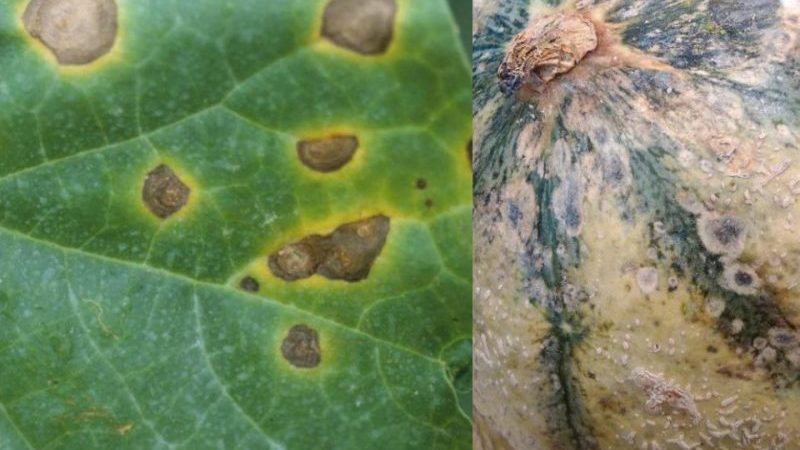
Anthracnose
Anthracnose (copperhead) is a disease that can cause significant damage to the crop. As a result of the defeat of melons and gourds by anthracnose, rotten fruits and stunted plants can be obtained. The causative agent is a phytopathogenic fungus.
Brown or yellowish spots of an indefinite shape appear on the leaves of the plant, with time the spots expand, then the ovary is deformed, the development slows down or completely stops. Brown or black spots appear on stems and fruits.
For reference. The wet season is most favorable for the development of the disease. During the growing season, the infection is spread by insects, through inaccurate watering or with the help of rain and wind.
To combat the disease, it is necessary to establish an irrigation regime, excluding excessive soil moisture and providing the plantings with full ventilation and the flow of light. At the initial stage of anthracnose manifestation, processing of watermelon plantings with “Previkur” is allowed.
An important preventive measure is the destruction of post-harvest residues... It is necessary to return watermelons to the previous site after 6-7 years, having previously disinfected the seeds.
Root rot
Refers to fungal diseases. Pathogenic microorganisms infect the melon soil, then the root system becomes infected, then the plant completely. Typical signs of infection are brown weeping spots at the bottom of the stem and root, yellowing and withering leaves, cracked and decaying roots.
Wet cold weather, sharp temperature changes contribute to the development of root rot, so it is important not to overflow the beds, loosen the soil, and regularly feed the bushes.
Dried and weed plants must be removed in a timely manner, the soil must be periodically disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate. Treat watermelons with a solution of "Fundazol" (0.1%).
Powdery mildew
The disease is characterized by the appearance of whitish spots with a mealy bloom. Fungal infection first affects old leaves, then spreads to young leaves and shoots.
As a result, the development of fruits slows down, and ovaries form worse. Watermelons are deformed, they can become covered with various rot. The fruit is not juicy to taste, with a low sugar content.
Spraying the affected plants with a solution of calendula, dandelion or garlic is effective.
Preventive measures:
- during the growing season to treat melons and gourds with disinfectants ("Kuprozan");
- every 7-10 days fertilize the plants with crushed chalk / lime;
- soak seeds in "Immunocytophyte" before sowing.
Peronosporosis
Another name for the disease is downy mildew. It appears as large brown spots covered with an oily film. Also among the symptoms are drying leaves, lilac bloom on the back of the leaf plate, cessation of fruit growth. The infected parts of the plant turn brown and die.
Treat with copper oxychloride or Acrobat. The affected areas are cut off, the sections are treated with activated carbon. Timely disinfection of garden tools, regular weeding and removal of plant residues reduce the risk of infection.
Mosaic
Mosaic disease is relatively rare in watermelons. There are two types of viral disease: cucumber mosaic and green mosaic. The type of pathogen and external signs are significantly different. With cucumber mosaic, adult plants are affected: the leaves are deformed, areas of yellowish or light green color are observed on them, tuberosity and swelling are visualized.
The green mosaic is characterized by a convex bulge on the plant; the mosaic color occurs quite rarely. Greenhouse plants are more susceptible to the disease.
For reference. The mosaic virus is more common in the Kuban, Crimea, and the Caucasus region. The carrier of the virus in the warm season is aphid. In the cold season, plant debris, roots of perennial plants, and weeds can become pathogens.
Almost the only treatment option is the complete elimination of the crop. A drug to eliminate a viral disease has not yet been developed. You can try to save the crop by spraying the plants every 7 days with Karbofos, but only if signs of a viral mosaic are detected in time.
Read also:
Causes and treatment of mosaic on cucumbers.
Fusarium
A fungal disease that affects the root system of a melon culture. It is difficult to detect the activity of the fungus at an early stage, but with the utmost care, alarms are noticeable already when growing seedlings. Fungal infection can be present in the ground, live on plant debris for 5 years.
Of the symptoms - the appearance of orange spots on the roots, covered with a light pink bloom. Obvious external signs indicate neglect of the disease, treatment in such a situation is useless. Sick bushes are removed, the soil is treated with a solution of copper sulfate. The rest of the watermelons are treated with fungicides as a preventive measure. At an early stage, you can try to save the crop with an antifungal mixture: wood ash, colloidal sulfur (1: 1), water.
Bacterial spot
This is one of the most common diseases of melons and gourds, from which up to 50% of plantings can die.
Signs of Bacterial Spot:
- the appearance of watery spots with a green-yellow edging, which merge over time;
- dark rounded growths on watermelons;
- blackening leaves.
Infected bushes are removed, but at the initial stage, you can try to save the plant. To do this, cut off all the leaves that have even the slightest signs of infection, be sure to capture at least 0.5 cm of the healthy part of the leaf. After each cut, the knife is treated with alcohol. The soil is compulsorily disinfected, as well as implements, containers and structural parts of greenhouses.
Rot (white, gray)
The disease develops exclusively in conditions suitable for it: with high humidity and cold weather. The causative agent is a parasitic fungus, the signs of white and gray rot differ slightly, as well as the principles of treatment.
White rot is characterized by the appearance of a whitish coating on the lower leaves (resembles cotton wool), the structure of the leaves changes - they become translucent and watery.Over time, the plaque darkens and becomes dense, the shoots begin to rot, the top of the bush withers.
The plant will have to be destroyed if most of the bush is infected with white rot... At an early stage of detection of fungal activity, the affected areas are removed. The knife must be disinfected. The sections are treated with activated carbon or colloidal sulfur. It is recommended to treat the bushes with “Acrobat” or “Topaz” three times every week.
With gray rot, brown weeping spots appear on the leaves and on the watermelon itself, covered with a grayish or black bloom. Plants can be saved by means of copper sulfate and crushed chalk (1: 2) or by spraying with Topaz, Sumileks, Teldor preparations.
For reference. By planting calendula, marigolds or mustard leaves around the melon, you can prevent infection with fungal infections. These plants secrete phytoncides that have a detrimental effect on fungi.
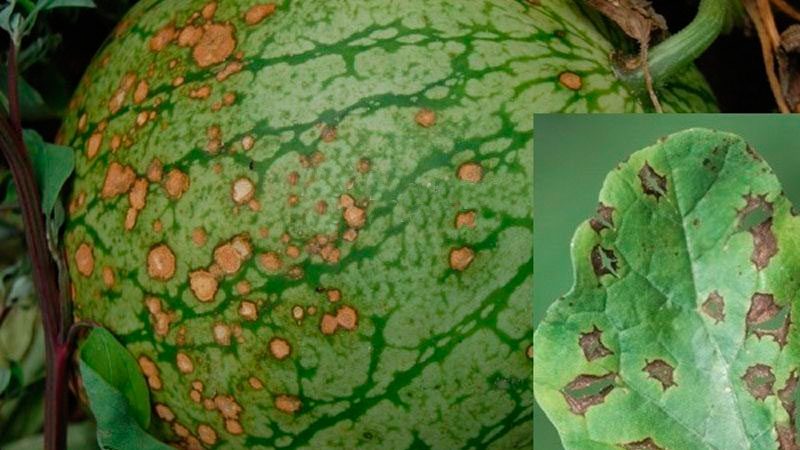
Leaf rust
The causative agent is a parasitic rust fungus. It manifests itself as brown bumps on the bushes, which crack over time, and spores of a rusty fungus spill out of them. The shape and size of the tubercles may vary.
To cure the plant, infected shoots and leaf areas are cut off, the bushes are treated with fungicides. As a preventive measure, nitrogen fertilizers are minimized.
Olive spot
A fungal disease that affects all aerial parts of the plant. In most cases, the berries suffer, they form ulcers of a gray-olive color, from which a cloudy liquid oozes.
In case of untimely treatment, the plant dies in 5-10 days. For disinfection use "Kartotsid" or "Oxyhom". At an early stage, Bordeaux liquid is effective.
It is interesting:
Why watermelons and tops turn black
Blackened watermelon is not uncommon for domestic farmers. Growing melons and gourds, gardeners may face this problem due to inappropriate climatic conditions and, in particular, frost. Watermelons and tops begin to darken - if rescue measures are not taken, the crop is lost.
If the watermelons are grown in greenhouses, it is recommended to artificially heat the greenhouse. When growing melons in an open field, you need to choose the right planting place and time. Damage to the ovaries can be avoided with good lighting and ventilation of the site, correct watering and enrichment of the soil with minerals, and compliance with the rules of crop rotation.
Infection with fungal diseases also explains why crops turn black. This is the main sign of the activity of fungal microorganisms. Anthracnose and Fusarium are the most harmful for the harvest.
Watermelon pests and control
The melon crop is attacked not only by fungal diseases; pests, of which there are also many, also cause significant damage to the crop.
Among them:
- Melon aphid. She destroys flowers and ovary, sucking out all the juices. To scare off aphids, it is enough to use folk remedies - to process the plants with infusions of onions, garlic, wormwood, tobacco crumbs. The planting of the garden bed around the perimeter with herbs is effective. Use insecticides for large numbers of insects.
- Spider mite. Unblown flowers, ovaries, tops of shoots are tightened with thin translucent threads, resembling a cobweb. Insecticides are ineffective since they are not insects but arachnids. Apply acaricides: "Omite", "Neoron", "Apollo".
- Wireworm. Its activity is evidenced by through holes on the berries, which lead to their rot. To combat the larvae, traps are set in the ground - jars of potatoes or beets. Traps need to be changed several times a week, and trapped individuals must be destroyed. In case of strong activity, “Thunder-2”, “Diazonin”, “Zemlin” will help.
- Sprout fly... Larvae infect seedlings, the second generation - an adult plant.The crop rots quickly. To combat them, insecticides are used, the soil and leaves are treated. Seeds are soaked in Fentiuram solution before planting. The planted plants are sprayed with Iskra Bio in a few days.
- Thrips. They not only harm the plant, but also carry dangerous diseases. They look like small black dots on the leaves of a watermelon. It is recommended to use "Fitoverm", "Karate", "Vertimek" or "Spintor". It may take 3-4 treatments at intervals of 7-12 days. It is better to remove the affected parts of the plant immediately.
For reference... Folk remedies are effective only at an early stage of the invasion of pests.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures are the most effective method of control, since pathogens remain viable for several years in the soil, equipment, weeds and plant debris.
The main methods of prevention:
- Use seeds of healthy fruits for sowing, disinfect them.
- Choose for sowing well-ventilated, well-lit areas where pumpkin crops have not been grown for the last 3-4 years.
- Loosen the soil regularly.
- Feed plants with nutrients and trace elements.
- Maintain a comfortable temperature regime for soil and air.
- Do not touch the leaves during morning and evening watering with water heated to 22-25 ° C.
- Do not store damaged or rotten fruits with healthy berries.
- In areas where the incidence of the harvest was noted, burn plant residues.
- In the fall, the soil cleared of plants is dug up onto the bayonet of a shovel and the earthen coma is turned over.
Conclusion
Compliance with the rules of adequate care and prevention will avoid the development of crop diseases. When difficulties arise with the cultivation of melons and gourds, modern methods of treatment with the help of fungicides, insecticides, acaricides and some folk remedies help.
The advanced stage of plant infection requires the destruction of diseased plantings.