What is good about a watermelon without seeds, what varieties are there and how to grow it
Seedless watermelon appeared on the tables and garden plots of Russians relatively recently. Unusual varieties of melons attract with convenience in consumption, preparation of desserts and canning. Features of hybrids, rules of cultivation and care - in our detailed instructions.
The content of the article
What are these watermelons
Melons are propagated with the help of seeds, which ripen in the pulp of the fruit. Watermelons, in which they are not, require special growing conditions. They have all the advantages of the usual varieties - sweetness, aroma, high content of vitamins, minerals and fructose.

History of origin and distribution
The first seedless watermelons were raised by Japanese breeders. The successful experience of Kyoto University in changing the chromosome set of traditional watermelons led to the emergence of the first unique varieties in the 40-50s of the XX century.
Following the land of the rising sun, the technology was mastered by the breeders of the USA, Bulgaria, Holland and other countries. Only in the XXI century, seedless watermelons appeared in our country and immediately gained popularity among consumers.
Now the volumes of cultivation of such varieties are comparable to the traditional ones. Buyers prefer to purchase seedless watermelons, since they have practically no waste and the aesthetics of use are much higher than those of varieties with seeds.
Important! Despite the fears of some adherents of proper nutrition, such fruits are not genetically modified, since the genes of other representatives of flora or fauna did not participate in their creation.
Features:
The traditional watermelon is a diploid because it has two sets of chromosomes. The seedless varieties are triploids, which have acquired new properties due to the action of colchicine. To grow such watermelons, the manufacturer cultivates three varieties of melons. This is necessary for pollination of those flowers that will give fruits with the desired properties.
Advantages and disadvantages

The main advantages of seedless watermelons are the high sugar content, ease of use, and high yield.
Minuses:
- high requirements for temperature and humidity: when the temperature drops to + 3 ... + 5 ° С, the plants die, as well as with a lack of moisture;
- seedless varieties are more prone to traditional attacks by pests and diseases of melons;
- the inability to grow such watermelons without the use of pollinating varieties;
- when technical ripeness is reached, harvesting should be carried out immediately, otherwise there is a risk of losing the crop.
Growing fruit without seeds requires scrupulous adherence to technology and careful care.
Seedless watermelon hybrids
To date, breeders have already bred several dozen hybrids, some of which have become widespread in Russia.
Ecstasy F1
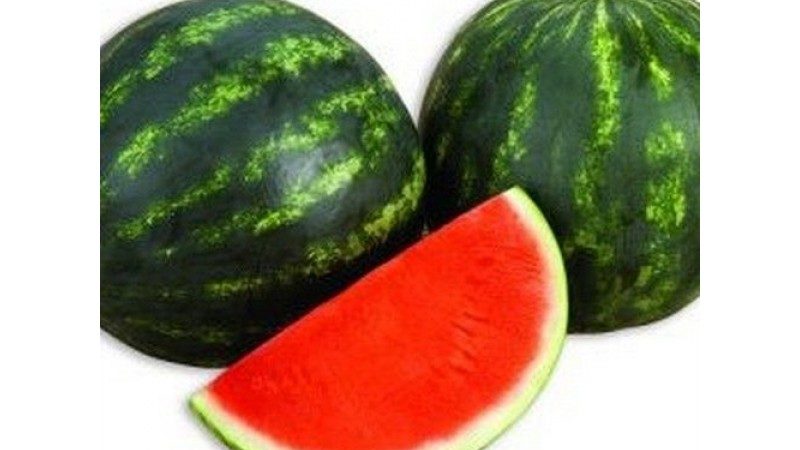

A hybrid of an average ripening period - 75-80 days from germination to technical ripeness. Ideally round fruits weighing from 1.5 to 2.5 kg. The rind is dark green, with light stripes, shiny. The flesh is crispy, firm, intense red. Productivity - 90-95%. It is unpretentious in care, picky about soil and moisture level. It tolerates transportation and storage well.
Imbar F1

An early hybrid reaches maturity 60-65 days after germination. The rind is dark green with black stripes.The pulp is juicy, yellow, sweet. Fruit weight - from 4 to 6 kg. A productive, heat-loving hybrid, demanding to care for.
King of Hearts F1
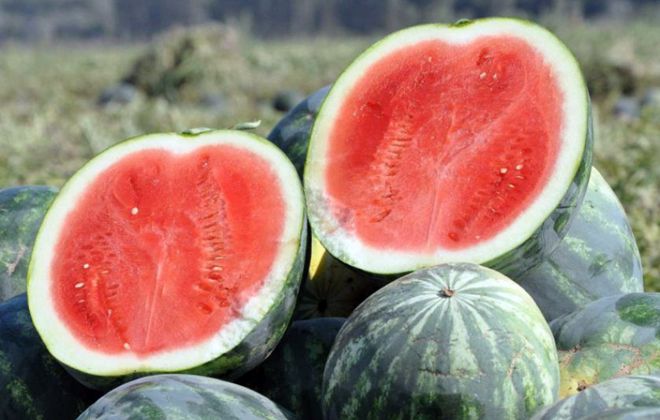

Medium early hybrid, ripening 75-85 days. The fruit is oblong, the skin is thin. The pulp is crispy, very sweet, bright red. Fruits reach 7-9 kg in weight. Requires the presence of a pollinator variety.
Regus F1

An early ripe hybrid for open ground and greenhouses. One pollinator is planted for every two Regus F1 seedlings. The fruit is round in shape, with a light green peel covered with thin dark stripes. The pulp is pinkish-red, sweet. The mass of ripe watermelons is from 6 to 8 kg. Resistant to various diseases of melons, it tolerates transportation and storage well.
Boston F1
An early highly productive hybrid. Fruit weight reaches 7-8 kg. The peel is thin, light green, with dark prickly stripes. The fruit is round in shape, the flesh is reddish-pink, sweet, juicy.
Boston F1 is cultivated in a wide range of climatic zones. Storage resistant, transportable.
Crimson Sweet F1
One of the most popular early maturing hybrids. Round fruits reach a weight of 8-9 kg. The peel is shiny, thin, light green with dark streaks. Outwardly it resembles the Astrakhan watermelon. The pulp is raspberry-red, with a characteristic aroma, sweet.

F1 sagas
Mid-season hybrid with high productivity rates. Fruits are oval, weighing 9-11 kg. The peel is light green with dark stripes. The pulp is red, with increased sugar content, aromatic. In cooking, they are used fresh, for fermentation and preparation juices, smoothies, desserts.
Yellow Buttercup F1
Medium early hybrid with a ripening period of 75-85 days. Fruits are round, large, with an average weight of 8-10 kg. The peel is shiny, light green with dark stripes. The pulp is bright yellow, juicy, sweet and aromatic. Designed for the southern regions of the Russian Federation.
The nuances of growing seedless watermelons

Seedless hybrids require special care in cultivation. Most are susceptible to diseases characteristic of melons... In open ground, they are grown, as a rule, in the south of Russia, in other regions, mainly in film greenhouses and hotbeds.
Seed germination of such watermelons is low, therefore, the choice of planting material should be approached responsibly and purchased only from trusted firms. It is better to buy seeds with a stock if the gardener plans to get a crop not only for himself, but also for sale.
Favorable soil temperature for germination is + 18 ... + 20 ° С, therefore, provided that the summer is short, in most regions of Russia, the seedling method of growing is preferable.
The sterility of seedless hybrids requires the presence of pollinating varieties. For every two seedless plants, one pollinator seedling is planted. There are no requirements for a specific variety, the main thing is that it must have seeds.
Seedling and non-seedling planting
Most often, seedless hybrids are grown through seedlings. In open ground, they are sown only in the south when the soil warms up to optimal temperatures.
Several methods are used for growing seedlings:
- on wet cotton pads;
- on paper towels or toilet paper;
- in individual trays or containers with soil for melons.
It is absolutely impossible to soak the seeds of hybrids. In this case, they will rot.
When sowing in trays, the soil is disinfected with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and well moistened. The seeds are immersed in the ground with the sharp end down, deepening no more than 1 cm. Containers with seedlings are placed on windowsills or shelves with lighting. For seed germination, an air temperature of at least + 25 ° C is required.
Shoots will appear on 4-6 days. Watermelons are watered sparingly, avoiding drying out and waterlogging of the soil. After 4-5 weeks, the plants are planted in a greenhouse or open ground.
With the seedless method, the seeds are sown in prepared soil.To do this, the area for planting is dug to the depth of a shovel bayonet, harrowed and well watered. The recommended seeding method is staggered. One plant should have at least 1.5 sq. m of food area.
Care

Further cultivation of watermelons consists in loosening the soil at least once a week, watering and feeding. Drip irrigation or sprinkling from a hose is considered optimal for seedless watermelons.
The leaves of mature plants are large enough to protect the fruit from sunburn and retain moisture in the soil. Trellises are prepared for strong-growing watermelons, the rest are grown in rassteel.
Important! Almost all hybrids produce many lashes, so most of the lateral shoots are removed, otherwise the plant will not be able to provide adequate nutrition for all the resulting ovaries.
Fertilize hybrids 2-3 times during the growing season. For feeding, complex mixtures are used, but without nitrogen content, since its high content leads to cracking of the fruit.
Weeding is necessary in the first 3-4 weeks, in the future, the abundant foliage of watermelons does not allow foreign plants to develop.
Common problems
Hybrids are susceptible to diseases of melons and pests, therefore it is necessary to fight for plant health from the first days of planting in the ground. To protect against the most common diseases crop rotation rules apply. Hybrid watermelons grow well after potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants and other nightshades, legumes.
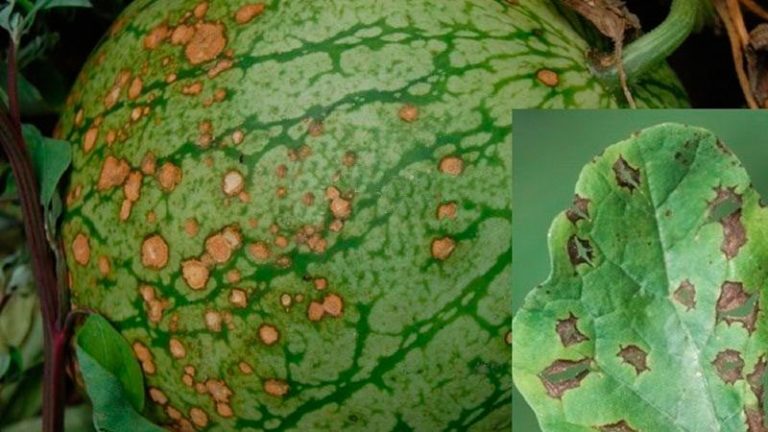
The most common diseases:
- powdery mildew;
- rot;
- anthracnose;
- fusairosis wilt;
- mosaic;
- spotting.
For the prevention of diseases, dead plant parts are promptly removed, the soil is deeply loosened, the bastan is mulched, and weeds are removed.
It is impossible to fight fusarium - the disease affects watermelons, starting from the roots. Therefore, when signs of disease appear, the plants are weeded out and burned. Anthracnose recedes after spraying the plants three times with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid. Processing is carried out every 7-10 days.
When root rot appears, watermelons are watered with a weak solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect the soil. After 2-3 days, the plants are treated with preparations containing metalaxyl.
Bacterial spot is not treatable, the plants are destroyed, and the soil is disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate. Powdery mildew recedes after processing watermelons with Bayleton, Topaz or Planriz. From white and gray rot, watermelons are sprayed three times with an interval of a week with fungicides, for example, "Acrobat MC" or "Topaz".
Watermelon pests:
- wireworm;
- spider mite;
- aphid;
- tobacco thrips;
- cucumber beetle.
To prevent the transfer of pests from their usual plants, watermelons are not grow next to carriers, for example, potatoes, cucumbers, tomatoes. For treatment against insects, insecticides are used: against ticks "BI-58", against thrips and aphids - "Fitoverm". Spraying is carried out on young plants and after flowering.
Reproduction of seedless watermelons
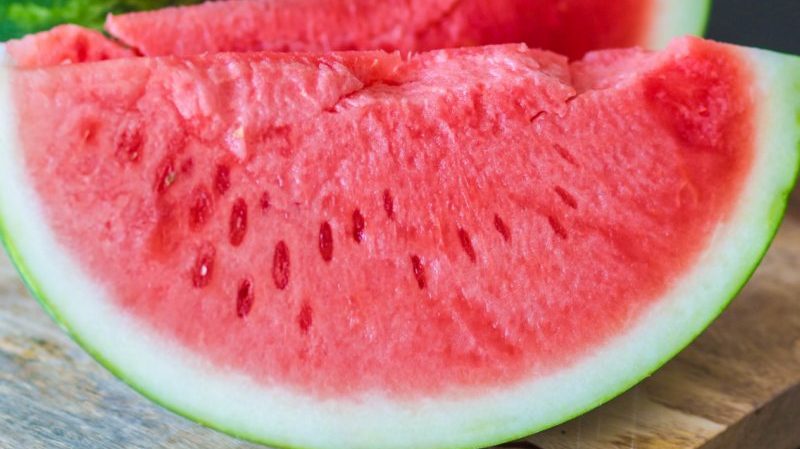

It is impossible to do this at home. Breeders take ordinary watermelons with two sets of chromosomes (diploids) and treat them with a mutagen. In our case, it is colchicine. The result is a hybrid with four sets of chromosomes (tetraploid). Then a diploid and a tetraploid are crossed and a triploid is obtained, in which there are three sets of chromosomes, so it is sterile and has no seeds.
Reviews
There are many gardeners who like to experiment with new watermelon hybrids. Our readers shared their observations, useful for summer residents.
Valentina, Rostov-on-Don: “I grow watermelons without seeds - this is the main direction of my farm. There are many buyers, the goods are not stale. In my farm, the entire area occupied by watermelons is equipped with a drip irrigation system, so the cost is low, I can easily compete with the producers of traditional stone fruit varieties. "
Igor Nikolaevich, Mozhaisk: “For the third year in a row I will grow Crimson suite. I like this variety for its unpretentiousness, disease resistance and high yield. The whole family and our friends are delighted - the watermelons are delicious, sweet, pitted. I grow it in a greenhouse, I get about 100-120 fruits per season and we eat them until the New Year. "
Svetlana, Astrakhan: “Last year I tried to grow it for the first time - only three seeds out of 10 emerged. But the harvest pleased me - I collected 32 watermelons. Last time I grew seedlings, this time I plan to go straight into the ground, they say, this is how hybrids grow better in our region. "
Conclusion
It is not difficult to grow a seedless watermelon subject to technology. In central Russia, it is preferable to do this in greenhouses or film greenhouses, in the south - in open ground.
The best hybrids for the Russian Federation: Crimson Sweet, Imbar, Regus, Sagi. All of them have already been tested by domestic gardeners and farmers and have shown good results. Hybrids are well transported even over long distances and can be stored for 4 to 7 months, subject to temperature and humidity conditions.