What is feed corn, how to distinguish it from food and where to use it
Corn is one of the oldest cultivated food grains on our planet, native to South America. Local aborigines ate all parts of it: panicles, pollen, stems and grains.
In Russia it is grown both for grain and for silage. Two-thirds of the total harvest is used to feed livestock. In various industries, both grain and cobs and stalks are used. How to distinguish a forage crop from a food crop, what is the specificity of growing, storage and use - we will tell in the article.
The content of the article
How to distinguish feed corn from food corn
Both types of corn are edible. Therefore, if you were deceived by selling feed instead of food, do not be discouraged. Both contain dietary fiber, protein, and vitamins. But food, or sugar, corn is tastier, which is sweeter and juicier due to the presence of mono- and disaccharides.
Food grade fruits are not stored for a long time, they are immediately processed, canned, frozen.
In the photo - fodder corn.
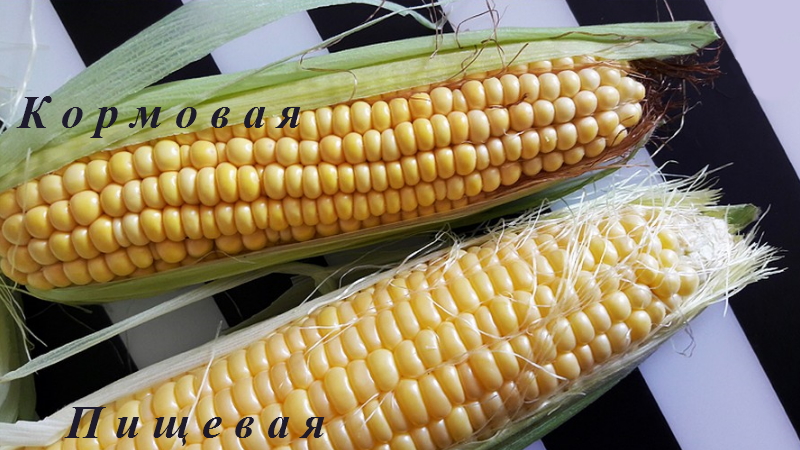

Appearance and taste
A fodder crop is distinguished from a food crop by the following qualities:
- the color of the grains on the cob is from bright yellow to orange, the food color is pale beige;
- boils for a long time - up to three hours, while food - 10-15 minutes;
- cobs are long and narrow, in edible cobs - short and thick;
- the skin of the grains is strong, tough, if it bursts when pressed, then the juice does not flow, while food grains are tender, soft and juicy;
- tasteless, and food - sweet, juicy and tasty.
Composition and properties of cereal feed
Among cereal fodder crops, corn has a high starch content - up to 70% and fat - up to 8%. However, corn grains are poor in ash, especially calcium. Protein substances make up about 9-10%. Corn contains not so many vitamins - A, PP, E and group B.
Of all cereals, corn has the highest energy value. 1 kg of corn grain contains 10-12 MJ of exchangeable energy for cattle, 13.4 MJ - for pigs, 14.4 - sheep, dry matter 850 g, crude protein 80-100 g. The digestibility of corn protein by cattle is 64.1 g, pigs - 70.51 g, sheep - 67.31 g, which is a high figure.
Corn is one of the main parts of animal feed and feed mixtures, suitable for all types of farm animals.
Growing field crops

Corn is an annual cereal, 1-3 m high, with large leaves up to a meter in length and an adult's palms wide... The stalk of the corn is filled with a loose pith. The roots of the plant are powerful. Corn also has aerial roots - props that increase the area of support for the stem.
Man cultivates more than 20,000 plant species, of which about 90 are field crops. Corn, according to the classification of field crops by Professor P.I. Podgorny is a cereal plant related to millet bread.
Millet breads differ from typical breads in that they are all heat-loving and light-loving plants of a short day with high drought resistance and less demanding on soil fertility.
Growing places
The conditions for growing a crop are determined by its origin.
Corn belongs to the Central American Genetic Center (southern Mexico, Central America, part of the Antilles) with moderate moisture, high temperatures with strong daily and seasonal fluctuations and a moderate growing season.
That is, initially, by origin, corn is not very suitable for growing in temperate latitudes. But as civilization develops, thanks to natural or artificial selection, modern varieties are able to grow and fully ripen in almost any conditions.
Features of growing and using fodder corn

Most forage varieties are not demanding on growing conditions and are capable of growing a powerful aboveground part almost everywhere. Corn does not depend on crop rotation; it can grow in the same place for several years in a row.
It is recommended to apply mineral or organic fertilizer to the soil at the stage of pre-sowing preparation, depending on the composition and condition of the soil. Before sowing, its surface-mechanical and herbicidal treatment is carried out.
After emergence, corn requires more frequent top dressingthan other grains. The need for fertilization is determined based on the parameters of plant growth and the quality of their ground herbaceous part. It is preferable to "feed" the plants by the foliar method, on the leaf.
Feed corn is one of the most diverse crops. It is used to make flour, starch, glue, ethanol, mixed feed, etc. In most countries of the world, it is technical (forage) varieties that are used for making corn grits.
Fields of application of feed varieties
A large number of feed types are harvested from corn:
- Green food - this is the aboveground part of the plant, mowed at certain stages of development.
- Silage Is a succulent food that is prepared by canning greens with limited oxygen access, an alternative to green food in winter. For the preparation of this type of feed raw materials, industrial varieties are used at the stage of wax ripeness.
- Meal - a mixture of grain, corn rods and wrappers for fattening pigs and piglets, making a vitamin mixture for poultry.
- Corn - feed, which is given to cattle and pigs in finely ground form, and to horses and poultry - in the form of turtle (coarse grinding).
For which animals are applicable
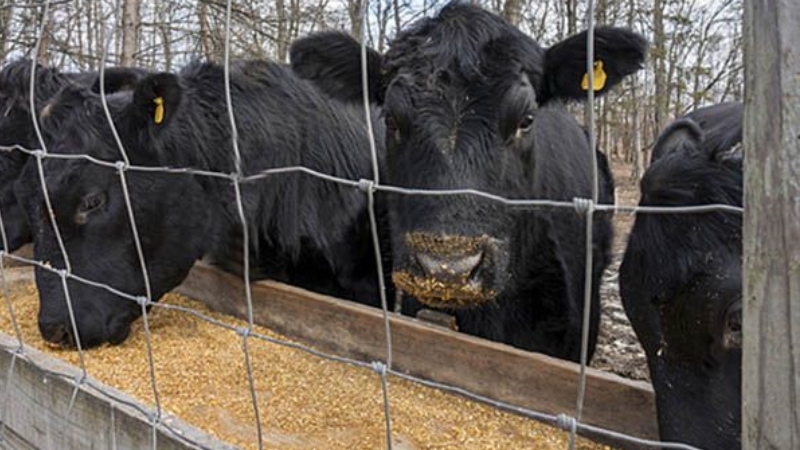

When used sustainably, corn is considered the best nutritional supplement for poultry and fattening animals. With her participation, fish bait is made.
For different animals, the application rates of corn in compound feed are different.
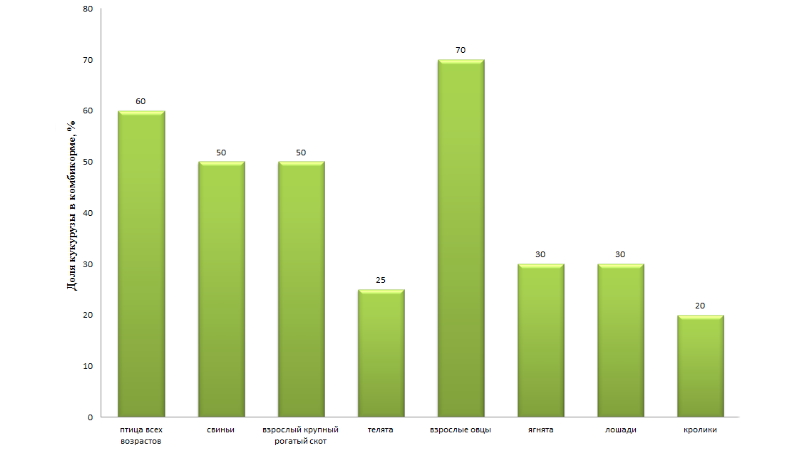
Attention! If the percentage of corn in feed is not observed, namely, with an excess of corn, the butter becomes soft in dairy cows, the meat becomes watery in pigs, and egg production in laying hens decreases.
What are good
Feeding using raw corn is considered to be the most effective, since the grains of this cereal contain more fat than barley or wheat, with a minimum amount of protein. When feeding animals, especially horses, freshly harvested corn on the cob, the animals eat this corn more slowly and digest it better.
As feed for pigs and piglets (as well as feed for poultry of meat breeds), industrial corn can be used in almost any form.
Important! Increasing the content of corn in the diet of animals up to 15% allows them to endure the cold season easier.
How to store
The grain of fodder corn is stored in clean, dry, odorless, not contaminated pests granaries in accordance with veterinary and sanitary rules and requirements for storage conditions.
The most common storage method is dry, based on the principle of xeroanabiosis (cessation of biochemical processes with partial or complete dehydration). In this case, corn with a moisture content of 12-14% is stored for 4-5 years in storage tanks and 2-3 years in silos of elevators.
Reference. Wet grain without drying is stored for a short time, with a moisture content of 20% - 6 days, 18% - 4 months, 16% - 9 months.
In practice, feed corn is usually not stored for a long time, but is used immediately for its intended purpose.
Another, equally common way of storing corn is chilled. It is based on the principle of thermoanabiosis: a decrease in the vital activity of biomass in grain at low temperatures.
Edible corn is stored worse than fodder corn. The main ways to store it at home on the cob or in grains are freezing and preservation.When cobs or grains are dried, the taste of the product changes, although the corn remains in this form for a long time.
Varieties and hybrids of fodder corn
For industrial cultivation, hybrid seeds are used. They are chosen taking into account the parameters of yield and resistance to climatic conditions of different regions, susceptibility to lodging and infection with diseases and parasites.
Forage varieties are less demanding on weather conditions, soils and predecessors, in contrast to food varieties, but nevertheless, when choosing, they take into account geographical conditions, resistance to diseases, intended use (for silage, for grain) and other characteristics.
Aurica is considered the best variety of fodder corn. This is an early ripe variety with a stem height of up to 170 cm. The length of the ear is 20 cm, weight is 220 g. Ripening period - 76-80 days. Productivity 1.4-1.8 kg per 1 sq. m. The variety is unpretentious and resistant to diseases.
Hybrids differ from varieties of higher yield, resistance to diseases and adverse environmental conditions.
The most popular maize hybrids included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements of the Russian Federation:
- An early ripening three-line hybrid Ross 188 MB. It is included in the State Register for the Central, North Caucasian and Middle Volga regions for grain and silage, for the Volgo-Vyatka for silage, for the Central Black Earth, Lower Volga and Far Eastern regions for grain.
- Three-line early ripe hybrid Nur. It is included in the State Register for the Volga-Vyatka region for silage, the Middle Volga region for grain and silage, the Lower Volga (8) region for grain, the Ural (9) region for grain, the Far East (12) region for silage.
- Three-line hybrid Katerina SV... It is included in the State Register for the Central Black Earth (5), Middle Volga (7), Ural (9), West Siberian (10) and East Siberian (11) regions.
- A three-line hybrid EU Volcano. Included in the State Register for the Central Black Earth (5) region for grain and silage.
- Simple hybrid Dolphin. It is included in the State Register for the Central Black Earth (5), Middle Volga (7), Lower Volga (8) and Ural (9) regions for grain.
- Three-line hybrid SI Respect. The hybrid is included in the State Register for the Central Black Earth Region (5) for grain.
Conclusion
Corn, regardless of whether it is fodder or food, is certainly healthy. It contains trace elements, minerals, dietary fiber, vitamins A, PP, E, B. In Russia, it is grown both for grain and for silage. The dominant part of the crop is used for livestock feed. Grains are used to produce feed, flour, flakes, canned food, starch, glucose, alcohol and other products. The cobs are used for the production of furfural, xylose, lignin. Stems are raw materials for cellulose and biofuel production.
Fodder corn is less demanding on growing conditions and grows even in the harsh conditions of central Russia. It is not demanding on soil conditions, it is drought-resistant and highly productive, which makes it an excellent forage plant.