How and why to use urea after wheat flowering
The quality indicators of grain depend on the amount of protein and gluten it contains. The production of these substances is positively affected by nitrogen. If the soil is saturated with nitrogen compounds, the yield will improve, and the number of lodged cereals will decrease. Urea is most often used as a fertilizer, and it is applied not only before sowing, but also after flowering.
The rules for adding urea after wheat flowering will be described in detail in this article.
The content of the article
Why feed wheat after flowering
If the soil lacks nutrients, few leaves and seeds will form on the crop.
If you saturate the plant with building material, the grain will be of high quality, and the crop will receive reliable protection from adverse environmental conditions and pests.
What is urea good for
In the soil, nutrients are in a difficult to access form. Their rates during sowing crops are determined taking into account the planned yield and soil condition.
Urea is a fairly mobile element... Its organic molecules are able to instantly pass through biological membranes, thereby accelerating the absorption process. Within 2-3 days, urea becomes an integral part of plant protein.

Properties and effects of urea
For feeding wheat most of all, it is carbamide, which has a neutral reaction, even at increased dosage.
It is assimilated by the culture, activates the process of photosynthesis, rarely causes negative changes in the form of leaf burn. Therefore, fertilizing wheat with urea after flowering is an important technological method.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of feeding:
- the granules instantly dissolve in water without forming a precipitate;
- the drug promotes the rapid growth of vegetative mass;
- in wheat grains, the concentration of protein increases, productivity improves;
- the plant does not accumulate nitrates (if the dosage is observed).
When using urea, the metal elements of the sprayers do not corrode, since aqueous fertilizer solutions have a neutral reaction.
Disadvantages of urea:
- in the form of a solution, the urea temperature is lower than the air temperature;
- can not be mixed with alkaline preparations, wood ash, chalk, calcium nitrate;
- if the dosage is exceeded, there is a risk of leaf burns.

It is interesting:
Simple rules for a record tomato yield - feeding tomatoes with urea.
When is it necessary to feed cucumbers with urea and how to apply it correctly.
Terms of introduction
Granular urea is introduced 5-7 days after flowering. Re-feeding - after 3 weeks.
How to properly feed wheat with urea
Wheat is fed with nitrogen fertilization by root and foliar methods.
Winter varieties
These varieties are demanding on the composition of the soil; high acidity is unacceptable for them. Urea is introduced for winter varieties parts. This is the most effective method of increasing yields, as in the autumn period urea "comes out" of the soil more actively.
Due to the fractional nitrogen intake, the drug level is controlled in the root zone. This allows for increased tillering and dense stem formation.
Attention! The predecessors are taken into account, after which roots and stems remain in the ground.After leguminous crops, the concentration of nitrogen fertilizers is reduced.
With the introduction of 30-60 kg of urea, the yield of winter crops will increase, but a significant increase in the concentration of protein in the grain will not be observed. Increasing the nitrogen dose to 100-120 kg / ha will allow the protein to accumulate.
The concentration and method of adding urea are determined taking into account the composition of the soil in the region:
- clayey and loamy - the amount of carbide is reduced, since the movement of water in the soil is slower;
- sandy and sandy loam - dressings quickly go to a depth without lingering on the surface, so the volume is increased.
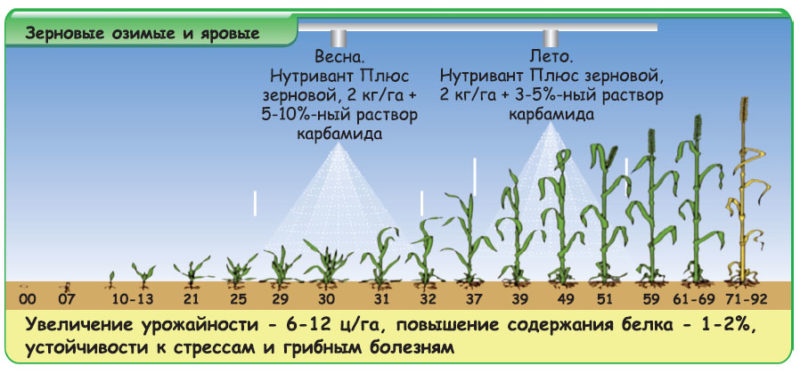
Top dressing is applied for winter wheat according to the schedule: during flowering and in milk ripeness. Then the ear will be fully formed, and the number of grains will increase.
Urea is added 3 times a year:
- In a minimum amount - in the fall before planting. An increased concentration of fertilizer will weaken the growing season and prevent the crop from surviving the winter.
- In early spring, before active growth begins.
- Before the culture leaves the tube.
Spring varieties

If nitrogen fertilization was not applied to the soil in the autumn, this is done in early spring during the planting of a spring crop.
Since nitrogen is in the soil in an unstable amount, it is not worth adding it in an increased concentration in the fall. The root system in spring varieties is not as developed as in winter varieties. Before sowing summer varieties, a single high dosage of urea is required. It is irrational to use feeding in fractional form, since the growing season in spring wheat is 2 times shorter and the culture consumes most of the food before it goes into the tube.
Reference. The presence of phosphorus preparations in the soil is important. Phosphorus strengthens the root system of spring wheat. If the root is poorly developed, the crop will not be able to assimilate nitrogen and potassium, and the yield will decrease by a third.
Rate, dose of fertilizer
For foliar processing of wheat, 1 tbsp is bred. l. urea in 10 liters of water. Spraying is carried out in the evening or early in the morning. It is important that the weather is not rainy.
For foliar application of winter wheat, the application rate depends on the phase of the crop development. During the flag leaf period, the concentration of urea in the solution should not exceed 10%. The dose of top dressing with ready-made solution for cereals is 100-150 kg / ha.
The use of urea for sowing
Urea is introduced into the soil before sowing directly into the grooves. The fertilizer is sprinkled with a small layer of earth - in this case, the urea will not come into contact with the seed.
Reviews

Experienced farmers share their examples of the use of carbamide in wheat care.
Andrey, Krasnodar: “I have been using urea as a fertilizer for a long time, and not only for wheat. I apply it before sowing and after flowering. It works - my harvest has become not only high, but also of high quality. Besides, urea is an excellent means of preventing pests. "
Oleg, Kislovodsk: “I have been practicing this method of feeding winter wheat for a long time. Among the advantages are low cost, high efficiency and safety for plants. But in this case, it is important not to exceed the dosage, otherwise the leaves can be burned - I had one such bitter experience. "
Conclusion
Urea is an essential fertilizer for wheat. It is introduced in moderate dosage before or during sowing, as well as after flowering. This increases the quality and quantity of the harvest, protects plants from the negative effects of the environment and pests.