Step-by-step instructions for pruning blueberries in spring for beginner gardeners
Garden blueberry is a popular shrub with large blue berries. The plant as a whole is unpretentious, but tends to run wild in the absence of care and regular pruning. There are fewer berries on such bushes, they become smaller and lose their taste. Let's take a look at how and when to properly prune blueberries.
The content of the article
Why prune blueberries in spring
Blueberries are a deciduous shrub, the closest relative of blueberries and lingonberries. Garden blueberries tend to thicken with new shoots over time, therefore they need regular spring pruning - both formative and sanitary. And if sanitary pruning is allowed throughout the year, then shaping pruning - only in the absence of sap flow either in late autumn or early spring.
Is it obligatory
Removing old and diseased branches is a mandatory procedure for every fruit plant, including blueberries. Without regular thinning of shoots, the culture runs wild - it bears worse fruit, the berries become small, and lose their taste. In dense plantings, an ideal environment is formed for the development of fungi and the reproduction of harmful insects.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spring Pruning
Some gardeners prefer fall pruning over spring pruning. Others, on the other hand, consider spring pruning to be the most correct. In terms of the pros and cons, the following positive aspects of the spring procedure stand out:
- the frozen parts of the shoots are removed;
- shoots that have not survived the winter are removed;
- rationing of tops and thinning of plantings is carried out;
- more complete improvement of culture.
Minuses:
- there is a risk of pruning too late and harming the shrub;
- too zealous approach there is a high risk of yield decline.
Timing of spring pruning
In spring, blueberries are pruned before sap flow and active vegetation. In different regions, they can vary according to the climate. If the heat comes early, the agrotechnical technique is carried out in the first decade of March. In regions with a harsh cold climate, pruning dates are shifted until the second decade of May.
Types of procedure
There are three types of blueberry pruning depending on the purpose: shaping, sanitary, and anti-aging.
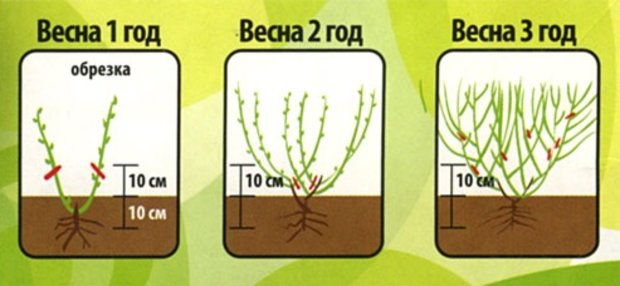
Forming
Formative pruning of shrubs is carried out either in late autumn or early spring, when there is no active vegetation and sap flow. In an area with a mild climate and relatively warm winters, it is allowed to carry out the procedure during the snowy season.
The first shaping pruning is carried out before planting so that only vertical branches remain in the bush. All growth and horizontal shoots are removed. The second time the procedure is carried out after planting the shrub, removing flower buds. They take too much energy away from the plant.
A whole blueberry crown is formed in the third year of life, removing small twigs at the base of the bush. Most often, such pruning is combined with sanitary and / or anti-aging.
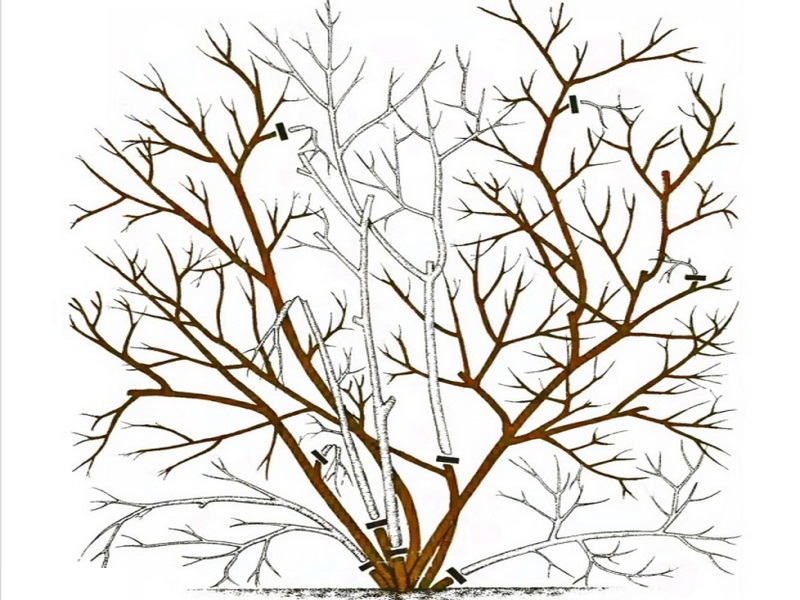
Anti-aging
It is customary to rejuvenate blueberry bushes at least once every five years.A significant part of the obsolete crown is removed, choosing the most dense, curved branches. In varieties with weak branching, maximum cutting is used - it activates growth.
Anti-aging pruning is carried out according to the scheme:
- The horizontally directed branches that grow to the main shoot are removed.
- The branches and shoots of the lower level are removed.
- Cut branches that thicken the crown and grow incorrectly.
- If necessary, remove thin shoots.
A properly formed bush consists of 12-15 skeletal branches.
Sanitary
Sanitary cutting is carried out not only in spring, but throughout the year when signs of insect or fungal infection are detected. In the spring, it is needed to remove branches frozen and dead in winter.
Important!Cutting off the damaged part, they capture 1.5-2 cm of an externally healthy area, since the lesion could have affected the deep tissues of the wood.
How to prune blueberries correctly in spring

The pruning technique is uncomplicated and includes steps common to most horticultural crops.
Required materials and tools
The following tools are required for the procedure: pruner, hacksaw, lopper.
Important! Tools before and during pruning are disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate, alcohol or chlorhexidine.
Additionally, you will need a garden pitch for processing large sections.
Step-by-step instruction
Cropping involves the following steps:
- Inspection of the bush and identification of shoots to be pruned.
- Removing dead branches.
- Removing frozen parts of branches.
- Removing branches from the middle of the bush, the growth of which is very small. Most often there are no new shoots on them.
- Removal of shoots without fruit buds.
- Removal of long hairless and overbranched shoots.
- Covering large sections (more than 2 cm) with garden pitch.
The removed parts of the plant are burned.
What to do with long branches
For plants with a spreading crown, most of the pruning is directed to the edges of the bush and less to the middle. In vertical varieties, more attention is paid to the central part to avoid thickening. Once every 5-6 years, all long branches are removed at the root to stimulate young shoots and form flower buds.
How to form bushes correctly
First of all, when forming bushes, thin and weak branches are removed, which have no promising fruiting. Then old branches older than 4-5 years of age are to be removed.
The formation of the bushes also depends on the variety: too weak shoots are removed from undersized ones, and old branches are pinched. In vertical varieties, only those branches are removed that thicken the bush.
Strong hybrids with a spreading crown require more frequent pruning. In such varieties, bent lower shoots are removed, as well as old and weak shoots in the center of the bush, leaving 5-6 skeletal branches and several young one-year shoots.
It is interesting:
How to properly prune raspberries in the spring: a step-by-step guide
Step-by-step instructions on how to prune currants in the spring to have a good harvest
How to properly care for honeysuckle in spring - feeding and pruning
The nuances of pruning a young seedling
Young bushes are pruned for better tillering. Here, low-lying shoots and branches are removed, which grow inside the crown and interfere with ventilation. In seedlings of the first year of life, peduncles are necessarily removed.

Adult plant
An adult plant for 3-4 years needs proper formation. In such bushes, branches of the second order are removed, especially those growing deeper into the crown, the damaged tops are cut off. After long fruiting, when too many stems have formed, the bushes are cut to zero for complete rejuvenation.
Low-growing varieties
In low-growing varieties, shoots of 6-8 years of age are subject to cutting. Removing one or two old shoots stimulates shoots and flower formation on young branches. Interlaced branches are also to be cut.
Post-procedure care
After the procedure, large sections are covered with garden varnish to prevent the development of fungal diseases. All branches are burned without fail. The crown and the soil around the bush are sprayed with solutions of urea, growth stimulants and fungicides.
Important! The mulch must be examined and, if there are signs of decay, it is completely changed. The old mulch is burned together with the trimmings.
Tips and tricks from experienced gardeners

Experienced gardeners recommend the following:
- Remember to remove mulch before pruning. Before starting work, the soil is freed to the very ground, while the mulch is examined, the unusable one is burned, and the good one is returned to its place after the procedure.
- Do not spare the old branches - they only block the access of light and air to the crown. In addition, old branches in the fall will not fully cover the bush for the winter.
- It is advisable to prune blueberries from the second year of life. This will affect the number of flower buds and, accordingly, the yield of the bush in the future.
Conclusion
Pruning blueberries is the key to high yields and plant health. It is carried out in a period of complete rest before the onset of sap flow. The procedure must be carried out regularly, and once every five years cut the bush "to zero" for its complete rejuvenation.