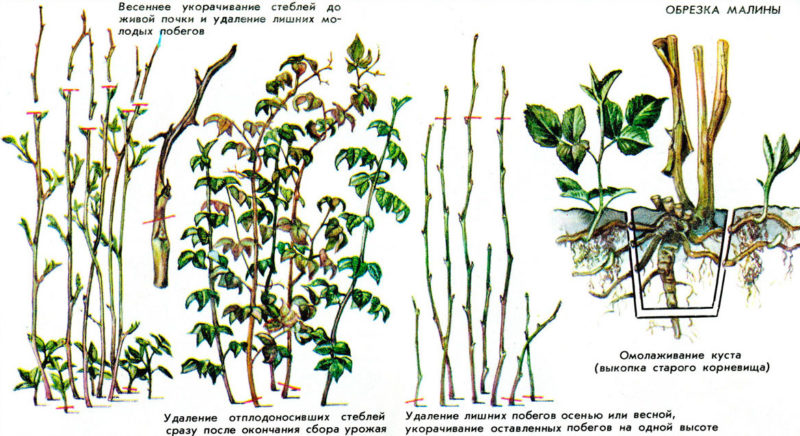
How to properly prune raspberries in spring: a step-by-step guide
Raspberries, despite their unpretentiousness, require annual pruning, if possible not only in autumn, but also in spring. The latter helps bushes and ovaries to form properly. In this article, we will tell you how to properly prune raspberries to get a good harvest.
The content of the article
Why prune raspberries in spring
Raspberry pruning is usually done in the fall after fruiting. In the spring, it is done for sanitary or formative purposes, removing frozen, damaged and broken shoots. The main goal of the procedure is to improve flowering and fruiting.

Is it obligatory
Raspberry - a biennial plant that blooms and bears fruit in the second year of life. Three-year-old shoots only thicken landing, take away strength from the young and reduce the overall yield. If it was not possible to carry out the procedure in the fall, it is worth postponing it to the spring than not at all. It makes no sense to leave three-year-old shoots on the bush.
Reference. Exist remontant varieties, which bear fruit already in the first year of life, therefore their pruning is carried out in a special mode.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spring Pruning
Main advantages:
- removal of dead, damaged shoots makes it possible to grow young;
- prevention of fungal diseases and damage by insect pests;
- increase in productivity.
Spring pruning has almost no disadvantages, its only drawback is that in spring it is difficult to distinguish two-year and three-year-old shoots from each other, since they are all covered with a brownish crust.
Timing of spring pruning
Spring pruning of raspberries is carried out before the buds open and the juices begin to move. During the day, a positive temperature should be maintained, at night there should be no soil frosts. In different regions, the timing varies depending on the weather conditions.
The average values are as follows:
- southern regions - early April;
- middle lane - early May;
- Urals and Siberia - the second decade of May.
Some gardeners prune raspberries after budding, because then you can clearly see which shoots are alive and which are dead. However, this is fraught with infection of the slices with fungal infections.
Types of procedure
Depending on the purpose, pruning is divided into several types.
Forming

This pruning is carried out for the aesthetic shaping of the raspberry plant, simplifies harvesting, and provides light and air to the stems and leaves. Such pruning also improves the access of pollinating insects to flowers.
During the forming pruning, not only the fertile, diseased and dried shoots are removed, but also the young shoots, since the plant takes a lot of resources to grow it. All broken and frozen shoots, which are necessary for fruiting, are shortened to the first bud.
A significant disadvantage is that young shoots are removed, which could begin to bear fruit the next year.
Sanitary
During sanitary pruning, all non-viable, weak and thin shoots are removed. The procedure is easier to carry out after swelling of the kidneys - then it becomes clear which of them are frozen.
After removing the dead branches, the shoots of the second year of life are shortened to the first bud. This stimulates better fruiting and limits their growth.5-6 strongest shoots are left on one bush.
Double according to Sobolev
Double pruning, or Sobolev pruning, is carried out in several stages. The first procedure is carried out after the formation of leaves at the beginning of June in young shoots of the current year, cutting off or pinching the top to a height of 12-15 cm. Shoots before pinching are called zero. This stimulates dormant lateral buds and active zero shoot branching.
The second time the procedure is carried out in the fall of the same year or next spring, cutting off the crown of branching shoots by 12-15 cm. The first or second green buds, counting from the crown, can serve as a reference point.
Reference. This type is only suitable for non-thickened plantings, since the raspberry tree will branch heavily. Double cropping is not suitable and remontant varieties.
How to prune raspberries in the spring for a good harvest
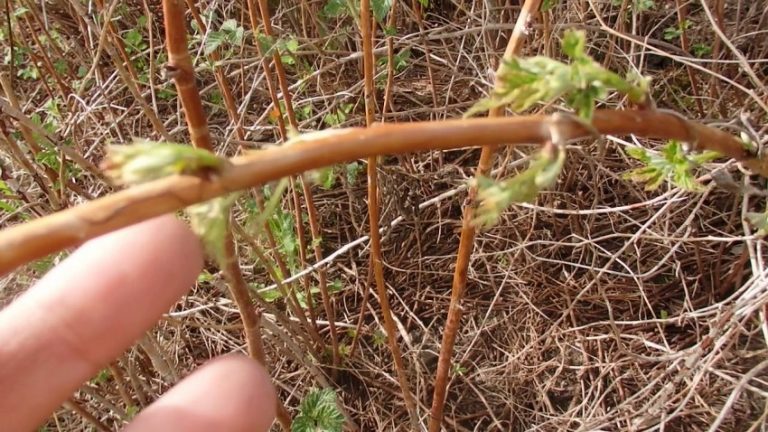

Trimming is a simple but important manipulation that requires a competent approach in terms of inventory and timing. Shoots are removed at the very root, if possible, comparing the stump to the ground.
Required materials and tools
To trim you need:
- sharp pruning shears or knife;
- rake;
- lopper;
- gloves.
Before the procedure, the pruning shears must be sterilized with steam or soaked for 15 minutes in a low-borne solution of potassium permanganate.
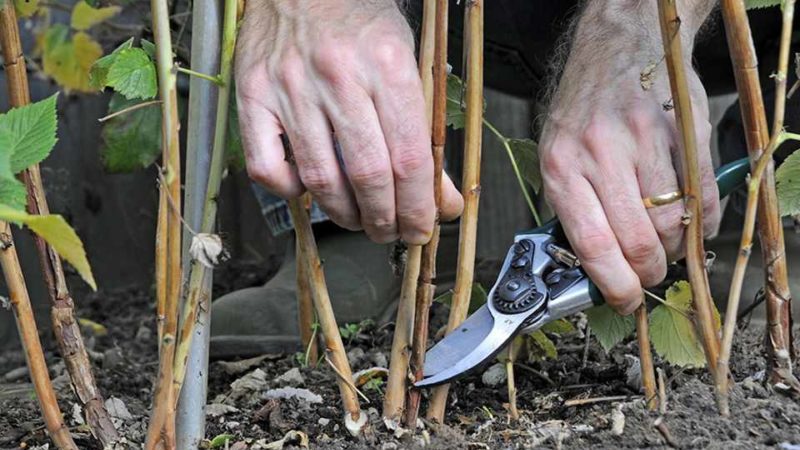
Step-by-step instruction
The pruning process is extremely simple:
- With a rake, they remove all the fallen leaves and slightly loosen the surface layer of the soil.
- The selected stem is separated from the main bush and slightly bent to the side.
- The pruner or knife is placed as close to the ground as possible. Too thick branches are pruned with a delimber.
- Cut the branch with a straight cut.
- In young shoots, the top is cut off to the first bud.
The nuances of pruning remontant varieties

Repaired raspberries, unlike ordinary varieties, bear fruit already in the first year of the branches' life and bloom twice a season, therefore, it requires special care when pruning in spring. If it was done incorrectly, the flowering and productivity of the bushes decreases.
Pruning of remontant varieties can be done in two ways:
- Cut out all root runs before sap flow begins. This produces a single but plentiful autumn harvest.
- Remove all shoots of the second year of life, leaving only annuals.
In such varieties of raspberries, pinching is not carried out, since this inhibits the formation of the ovary.
Tree-like
Pruning a raspberry tree is practically the same as that of a regular bush raspberry. To give the desired shape, remove all branches, leaving 2-3 of the strongest and healthiest. In shoots that have grown by a meter, the tops are shortened, launching lateral buds into growth. The next spring (or autumn), the lateral shoots are shortened to 30-40 cm. This pruning is similar to the Sobolev scheme.
Post-procedure care
Post-procedure care pruning includes pest control and feeding. Also, the raspberry can be tied up or left free at the request of the gardener.
Disinfection is carried out with Bordeaux liquid, spraying plants with a 1% solution. The treatment is repeated after the kidneys have awakened. The third procedure is carried out in the fall after harvesting in order to avoid insect pests from entering the soil.
Top dressing
As a top dressing, any complex fertilizer is suitable, which is applied according to the instructions. You can fertilize with ripe humus at the rate of 12 liters per 3 bushes. Humus is scattered between the bushes. On nitrogen-poor soils, additionally add nitroammofosk or nitrate (40 g) with the addition of potassium humate (5 g), diluted in 10 liters of water. After applying nitrogenous fertilizers, an additional 1 tbsp is scattered between the bushes. wood ash in each gap.
Tips and tricks from experienced gardeners
Experienced gardeners recommend:
- Cut off the shoots completely, sinking into the bush, otherwise the raspberry will grow, and the yield will drop sharply.
- The intertwined branches should not be left - this leads to a rapid incidence of planting.
- Dry shoots must be cut at the root.The quantity and quality of the crop depends on this.
- The largest branches are removed first, then the smaller ones. This is done carefully so as not to damage healthy buds on young branches.
Conclusion
Raspberry is an unpretentious, fast-growing shrub that bears fruit in almost any conditions. However, in order to get large, sweet berries, the plant needs regular care and feeding. Timely pruning allows bushes to form correctly and serves to redistribute vitality to flowering and fruiting, and not the formation of green parts.