How gooseberries reproduce - all ways
Gooseberry is an unpretentious shrub that can grow and break in many regions of our country. It is loved for its delicious large berries, with a sweet-sour refreshing taste. Gooseberry fruits are delicious as an independent dessert, in the form of jam, compotes and even sauces for meat.
One of the advantages of this plant is its ease of reproduction. There are several ways to form new bushes from the old. Planting material is obtained by cuttings, layering and division. How and when to propagate gooseberries in different ways - read on.
The content of the article
Gooseberry breeding methods
Gooseberry cultivation is a task that even a novice gardener can cope with. This plant takes root well and quickly takes root in a new place.
It is possible to propagate the gooseberry bush in a vegetative and generative way. The first option is preferable, since in this case the characteristics of the mother plant are preserved, regardless of whether grade it is or a hybrid.
The generative method involves the propagation of gooseberry seeds. This is a lengthy process that requires patience and skill from the gardener. At the same time, the plant obtained from seeds often does not retain varietal characteristics. The berries are small and sour.
Advice! From a plant grown in the described way, a good stock is obtained for varietal gooseberries. It will be characterized by rapid growth and resistance to cold snaps.
Cuttings
The cuttings method of propagation of gooseberries is convenient for the ease of obtaining planting material. It is enough just to cut off a branch from the bush you like and the stalk is ready. All that remains is to properly prepare and root it.
The disadvantage of grafting is that not all gooseberry varieties take root well. Some of them die after landing in a permanent place. Gardeners' reviews indicate that out of 10 branches, sometimes only 3 take root.
Note! Cutting is useful when the bush is in another area.
A shrub no older than 10 years is suitable for grafting. Planting material collected from an older bush will take root less well.
Green cuttings
Before propagating gooseberries in summer, it is important to wait until the temperature outside does not drop below +20 during the day and +16 at night. The most favorable period is from early June to mid-July.
Correct propagation of gooseberries by green branches:
- Cut off healthy young shoots that have formed in the current year. They do it in cloudy weather or in the early morning on any day.
- The shoot is divided into parts from 8 to 15 cm long. Each of them should have several buds, from which shoots are later formed. The knife used for cutting must be sharp and disinfected.
- The planting material is soaked for 2 hours in a light pink solution of potassium permanganate. Then for a day immersed in a root stimulator "Kornevin" or "Heteroauxin".
- Different types of soil are layered in a pot or in a greenhouse nursery. The first layer is drainage (expanded clay, fine gravel, etc.), the second - rotted manure, then humus, peat and sand mixed in equal proportions. The soil is watered with a hot solution prepared from 1 bucket of water and 1 tbsp. l copper sulfate.
- The cuttings are washed under running water, then rooted. They are planted in rows to a depth of 2 cm.The planting pattern is 3x7 cm.
- Each stalk is covered with a film or bag. The seedlings are ventilated daily for 10-15 minutes.
- The soil is watered with warm water as it dries. Every other day, the cuttings are sprayed with warm water.
When the cuttings take root (this is evidenced by the emerging new shoots), the duration of airing is gradually increased, over time, completely removing the package. After that, the plants are planted in open ground. At first, they are covered with foil at night so that they adapt to new conditions.
Note! Green shoots take root quickly, but a significant part of the planting material dies when transplanted into open ground.
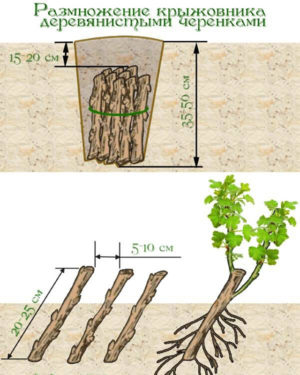
Lignified cuttings
Lignified shoots take root poorly and slowly. Many of them never form roots. But if the planting material nevertheless turned out, then after landing in open ground it almost always takes root.
Note! It is recommended to prepare at least 2 times more branches than is actually required.
You can collect lignified cuttings both in autumn and spring. In the summer, this procedure is not carried out.
How to grow a gooseberry from a twig that is woody:
- In the fall, after leaf fall or in the spring, while the buds have not yet woken up, branches 8-15 cm long are cut from the top of the bush. They should have at least 3 living buds.
- The cuttings are soaked in a growth stimulator for 24 hours. If their planting is not planned immediately after collection, then the branches are wrapped in a damp cloth or bag and placed in a cool place. Cuttings are planted in mid-autumn or spring immediately after the soil has thawed.
- The cuttings are planted in the ground at an angle of 45 °. The distance between the seedlings should be at least 15 cm. The soil around the seedlings is compacted and watered with a thin stream of warm water.
- A layer of peat or humus 5 cm thick is laid around the seedlings.
- Cover the cuttings with foil. As the soil dries, it is moistened.
- If the branches were rooted in the fall, then in the winter they are covered with snow. In the spring, they are examined, rooted specimens are selected and planted in a permanent place.
note! Branches from the bottom of the bush are not suitable for rooting, since they do not take root well. The age of the lignified branch should vary between 1-3 years.
Combined
Combined cuttings are considered the most reliable. At the same time, the stem method of gooseberry cultivation gives the best results. The planting material quickly takes root and takes root well in a permanent place.
The combined one involves the use of planting material obtained from a lignified one-year-old part no larger than 3 cm in size and a green shoot of the current year.
Gooseberry propagation in a combined way begins in May and continues throughout the growing season. Moreover, there are three types of combined planting material:
- With a heel. It is obtained by breaking off a green cutting so that a piece of a lignified branch remains on its lower part.
- Shank with a crutch. The green shoot is cut with part of last year's branch so that the cut goes along the old shoot.
- With a stand. Cut from the last year's branch so that the lignified and green shoot are perpendicular to each other.
The prepared planting material is soaked on bitches in a growth stimulator. Then they are planted, completely deepening the lignified part and the green shoot by 2-3 cm. The soil around the seedlings is compacted and mulched, then watered with warm water.
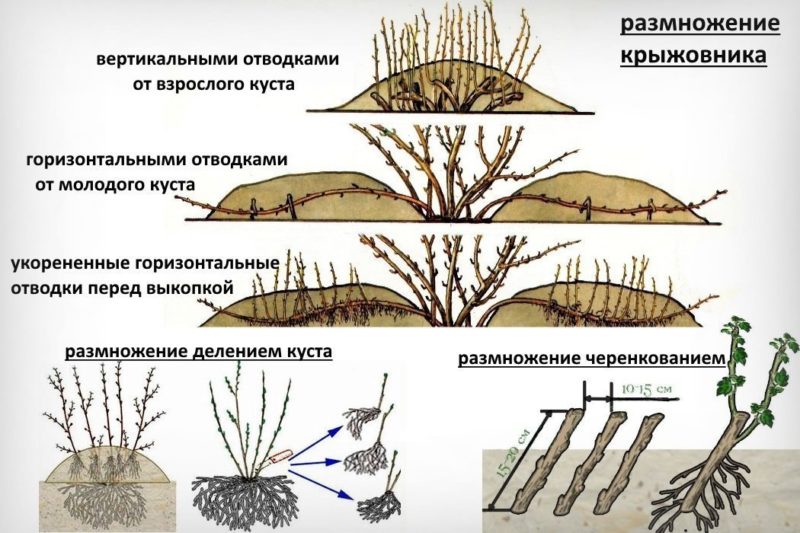
Layers from the bush
Gooseberry propagation by layering is considered the simplest and most popular method. Shoots not separated from the bush quickly take root. And this happens in 90% of cases.
The planting material separated from the mother plant takes root well in a new place. This is due to the fact that rooting takes place in the open field and the plant does not experience stress when conditions change at a constant location.
Before propagating gooseberry layering, the mother bush is strengthened. To do this, weed the area around it. Then rotted manure is poured near the trunk, which is mixed with the soil, digging it to a depth of 10 cm. The dug earth is leveled with a rake.
Sanitary pruning is carried out by layering a year before reproduction. During the procedure, all dry, diseased and weak branches are removed.
The most successful time for breeding a bush in this way is October. This is also done in the spring before the start of sap flow, in the second half of March.
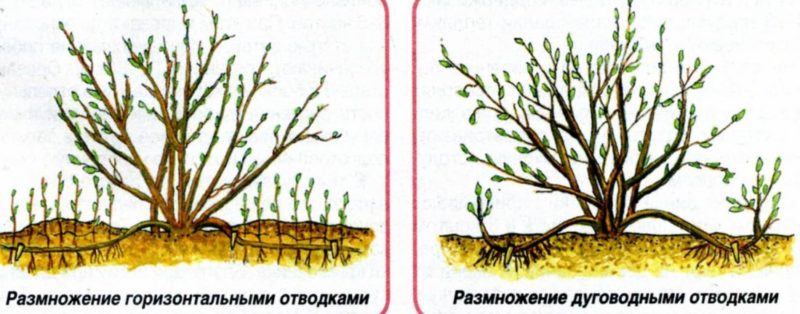
Horizontal
The easiest way to dilute gooseberries is by horizontal layers. In this case, several seedlings will be obtained from one shoot.
How to root a horizontal layer:
- For rooting, select several healthy branches at the bottom of the bush. Their age should vary between 1-3 years.
- To accelerate the germination of lateral buds, which contribute to the formation of a powerful root system, the lateral annual shoots are cut off by a third.
- A groove is dug in the soil in the direction of growth of the selected shoot. A branch is laid in it so that its end is on the surface of the soil. The shoot is fixed with staples and covered with earth.
- Buried layers are abundantly watered and mulched with humus or peat.
- During the entire growing season, the buried branch is watered as the soil dries out and fed at least 4 times. Top dressing should contain ammonia, potassium and phosphorus.
- When the shoots on the cut reach a height of 8 cm, they are spud. Re-hilling is carried out after 14 days.
- When the shoots take root (this happens at the end of summer), the branch is cut with a disinfected pruner from the mother bush. Layers are divided into seedlings according to the number of shoots with roots.
- The roots of each layer are shortened by a third. They are planted in containers for growing. They will turn into full-fledged seedlings next spring.
Vertical
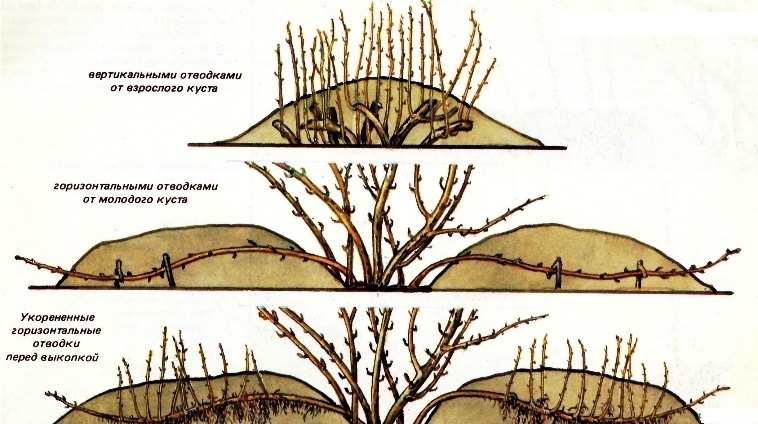
Reproduction by vertical layers allows not only to obtain high-quality planting material, but also to rejuvenate the plant. This method is used for old gooseberry bushes.
How to plant gooseberries in vertical layers:
- In early spring, branches older than 3 years are cut at the root, and young shoots are shortened by half. This stimulates the formation of new processes.
- When the length of young shoots reaches 15 cm, the plant is spud. The earthen mound should rise to half the height of the bush.
- Throughout the summer, gooseberries are watered and fed. If the soil falls, then re-hilling is carried out.
- In mid-September, the rooted layers are separated from the mother bush. They need to be transplanted to a permanent place. Protect for the winter with covering material.
Arcuate
Some gooseberry branches grow in an arc, dropping downward. They are used for reproduction in the case when you need to get only 1-2 seedlings.
Note! Sometimes arcuate layers take root without the help of a gardener. One branch produces 1 seedling.
Obtaining arcuate layers is not difficult. To do this, follow the step-by-step instructions:
- In the place where the branch touches the surface of the soil, a hole is dug up to a depth of 30 cm. Rotted manure is poured onto the bottom.
- A section of the shoot adjacent to the ground is laid in the hole. It is secured with a bracket. Top covered with a mixture of garden soil with humus.
- During the summer, the cuttings are watered and fed. At the end of summer, it will give roots. After that, the new plant is separated from the mother plant, dug up and transplanted to a permanent place.
By dividing the bush
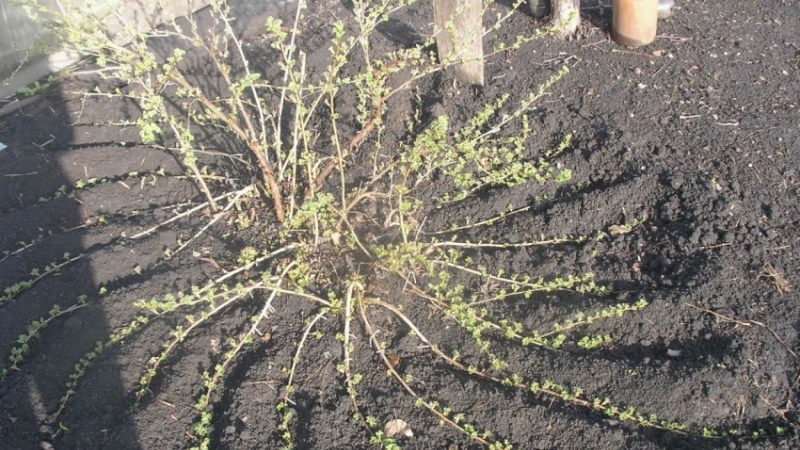

It is also possible to plant gooseberries by dividing the bush. In this case, several young ones will turn out from one old plant. The procedure is carried out in the following way:
- The bush is dug out of the ground. In this case, it is important not to cause serious damage to the root system.
- The root system is washed from the ground and examined. All diseased, rotten and dry areas are removed.
- The bush is divided into several parts and immediately planted in a permanent place.
Vaccination
Grafting gooseberries is a higher level task than propagating by cuttings and layering. This procedure requires care and following step-by-step instructions.
Advice! Gooseberry branches are grafted not only on gooseberries, but also on black currants.
Gooseberry is rarely vaccinated with budding, since its buds do not take root well. Usually cuttings are grafted into the split or by applying a cut of the scion to the cut of the stock.
In the first case, the lower part of the scion is grinded in the form of a thin wedge, and the scion is cut in the center. The scion wedge is inserted into the rootstock split. The structure is fixed.
In the second case, the scion and stock are cut at an angle of 45 °. The media are applied as evenly as possible to each other and fixed with a garden tape. For reliability, you can tie a peg.
Seeds
Seed-propagated gooseberries often do not retain their maternal traits. But it allows you to get a variety that is not yet on the site.
This is a lengthy process that requires the attention of a gardener:
- From ripe berries without signs illness take out the seeds. They are treated with a light pink solution of potassium permanganate and a growth stimulant, mixed with sand and poured into a box.
- A container with a sand-seed mixture is buried in a half-meter hole and sprinkled with a 20 cm layer of earth. They dig it out in the spring.
- In the greenhouse, a fertile soil mixture is prepared from humus, garden soil and sand. The soil is watered with a solution of copper sulfate. A mixture of seeds and sand is poured on top in a uniform thin layer. Then a layer of peat is covered with a thickness of 5 mm.
- When the seeds germinate and get stronger, they are thinned out. During the summer they are looked after, watered and fed. They are planted in open ground when the bushes get stronger.
Transplanting a bush to a permanent place
The best time to plant gooseberry seedlings in a permanent place is autumn. The plant is best grafted and rooted at positively low temperatures.
You can plant gooseberries in the spring. In this case, seedlings are planted as soon as the snow melts.
It is recommended to plant a shrub in a sunny and ventilated area of the garden. Groundwater should not be too close to the surface.
Planting instructions:

- For planting, holes are prepared with a diameter of 40-50 cm and a depth of 60 cm.The distance between the holes for the gooseberry should be at least 1.5 m.
- The soil taken out of the holes is mixed with 1 bucket of horse manure, 200 g of superphosphate, 60 g of potassium sulfate and 50 g of lime. A mound is formed from part of the mixture at the bottom of the hole.
- The seedling is placed in the hole, placing the roots evenly over the fertile mound. The remaining soil is poured into a depression, compacting the soil around the plant.
- The soil around the gooseberry is mulched and watered with plenty of warm water. The branches are cut so that each of them has 3 to 6 buds.
Gooseberries are transplanted according to the same principle. It is important to spread its roots evenly around the fertile mound.
Read also:
How can you process gooseberries from white bloom on berries?
Powdery mildew on gooseberries: signs, causes.
Gooseberry diseases and pests and methods of dealing with them.
Conclusion
Gooseberry is an unpretentious plant that can take root even in adverse conditions. It is easy to remove an entire plantation of plants from one bush - the culture quickly takes root and simply multiplies.
The choice of gooseberry breeding method depends on the variety, the age of the bush and the amount of planting material. However, reproduction by layering is considered the most reliable and easiest option to perform.