Tasty, large and rich in harvest gooseberry variety "Ural grapes"
Ural grapes - gooseberries with sharp thorns and delicious fruits. It is suitable for those who are looking for a proven winter-hardy variety for the Urals and the regions of the Middle Volga region. We will tell you about the strengths and weaknesses of the crop, the optimal conditions for it and the rules of growing, taking into account the climate.
The content of the article
Description of the variety
Gooseberry Ural grape is an early ripe, large-fruited variety. The name was given for the place of selection and for the special, grape flavor of the fruit.
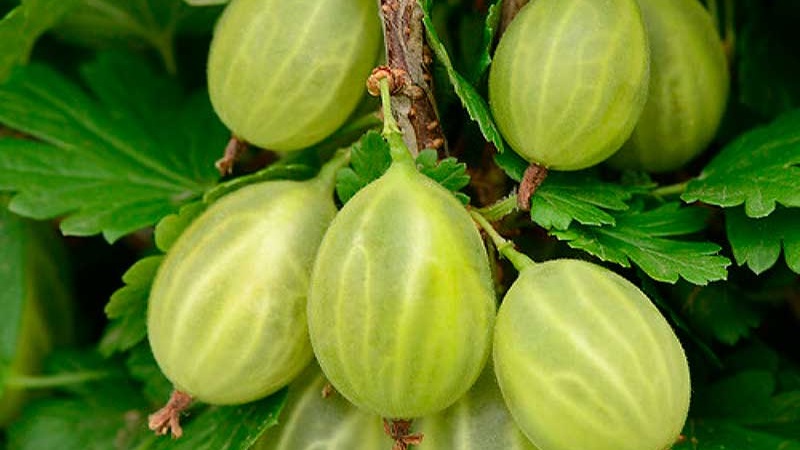

The variety was bred by Kh.Z. Levitin in 1959. at the experimental station of selective gardening in Sverdlovsk (Yekaterinburg). This gooseberry was obtained by pollination of the frost-resistant seedling Andreeva-1 with pollen of the varieties Sverdlovsky and Malinovy.
Characteristics and description of the bushes
The bush grows up to 1.5 m... The branches are directed vertically or with a slight slope. The crown is semi-spreading, of medium density. Annual shoots are green, without pubescence. Lignified branches are gray-yellow, with strokes. The shape of single buds is oblong, with a sharp tip. Bushes with powerful thorns in the middle of the branches - straight, of various sizes, triple and single. At the base and closer to the top of the shoots, the number of thorns decreases.
The leaves are three-lobed, juicy green, with a superficial sheen and light veins... The leaf plates are wrinkled, curved, with large teeth. Petioles - no more than 2 cm.
The buds are crimson, and the flowers are pale pink, almost white, about 12 mm in size.
Resistant to temperatures
The variety is winter hardiness... At a temperature of -30 ° C, freezing is not higher than 2 points. Bushes do not cover for the winter. Flower buds are resistant to recurrent spring frosts down to -10 ° C.
Reference. Freezing in points is determined by the degree of darkening of the branches on cross sections: 0 - no freezing, the color for the variety is normal; 1 - very weak, the cut color is yellow; 2 - slight freezing, light brown cut; 3 - strong, brown; 4 - dead branches (wood), cut color from dark brown to black.
Moisture and drought resistance
The plant does not lose productivity during the dry season... To keep the fruits large, gooseberries are regularly watered in hot weather.
Disease and pest resistance
Subject to agricultural practices, the Ural grape gooseberry is resistant to major pests and powdery mildew. But the vulnerability of the variety to spotting is noted.
Characteristics and description of fruits
Average fetal weight - 4 g... Berries without fluff, oval, bright green, with a slight matte sheen. Light-colored, slightly branched veins are visible on the fruits. The stalks are green. Dessert sweetness of the pulp is set off by the sourness of the dense skin. It tastes like grapes. The percentage of sugars is 9.9.
The variety is distinguished by the simultaneous ripening of fruits and their uniformity.... The berries do not crack from moisture, but they quickly crumble.
Productivity - up to 3 kg from a young bush and about 7 kg from a bush over five years old... The fruits are distinguished by keeping quality and resistance to long-term transportation.
Areas of use
The purpose of the variety is universal... Berries are prized for their sweet taste with a hint of grapes. They are eaten fresh, freezepreparing compotes, preserves, juices, jams and dessert wine. They go well with any fruit.
Reference. The presence of serotonin makes gooseberries a natural antidepressant.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The advantages of the variety:
 winter freezing not higher than 2 points;
winter freezing not higher than 2 points;- resistance to return frost;
- drought tolerance;
- large-fruited;
- dessert taste;
- simultaneous ripening of berries;
- high productivity;
- resistance to powdery mildew.
disadvantages:
- the tallness of the bushes;
- powerful thorns;
- rapid shedding of ripe fruits;
- susceptibility to disease (spotting).
Growing technology
Perennial gooseberry has been growing in one place for about 20 years.... If you choose the right site and planting time, the bushes of the Ural grapes take root and develop faster than other varieties. For a tall crop, the most important thing is the systematic thinning of branches. The main care does not take much time - this is watering, protection from weeds and pests, prevention of fungal diseases.
Optimal conditions
A slightly acidic or neutral soil is suitable for the variety.... Bushes grow on clay, sandy, loamy and sandy loam soils. The sites are selected bright, sunny, without strong drafts. Light shading is allowed.
Attention! Gooseberries are not planted in lowlands and often flooded areas. Constant waterlogging contributes to the development of fungal diseases.
Terms and rules of landing
Gooseberries are planted in spring and autumn... Experienced gardeners recommend doing this in the autumn - 1.5-2 months before the onset of frost. In spring, they are planted immediately after the soil thaws, but before the buds swell. This moment is easy to miss, and the plant will slow down or not take root.
Planting pit depth and width - 2 times the root part of the plant.
Work order:
 Fertile soil is mixed with rotted manure or compost 1: 1. Double superphosphate and potassium sulfate are introduced (a matchbox is enough).
Fertile soil is mixed with rotted manure or compost 1: 1. Double superphosphate and potassium sulfate are introduced (a matchbox is enough).- Clay soil is diluted with coarse sand.
- The 1/3 hole is filled with soil mixture, a bush is installed and the roots are straightened.
- The planting hole is filled with layers, each is tamped.
- The seedlings are watered abundantly and mulch the root zone.
- The branches are cut so that 5-7 buds remain on each.
Further care
Water the plants once a weekso that the water saturates the ground by 30-40 cm - this is about four buckets for each bush. In order not to provoke fungal diseases, plants are not watered with sprinkling. After harvesting, watering is stopped and the soil is moistened only before the onset of frost.
The soil is mulched... Mulch retains moisture and prevents weeds from growing.
In the spring, before bud break, sanitary pruning is carried out, the bushes are thinned out and treated with fungicides (Topaz, Fundazol). Pruning is repeated in autumn.
Top dressing is applied once a season, during spring pruning. Use organic fertilizers or a mixture of mineral supplements of nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus.
The harvest ripens in early July, at the same time... Harvested immediately, as they ripen, otherwise the berries will quickly crumble.
Attention! So that the bushes do not prick, they are watered abundantly 15-20 minutes before harvest.
Possible problems, diseases, pests
The variety is resistant to powdery mildew, But maybe severely damaged by mottling.

Major diseases of culture:
- Anthracnose (brown spots on fruits and leaves) is caused by dampness. Treat with a solution of colloidal sulfur.
- Rust (red bloom on the leaves) is sprayed with Bordeaux liquid 1%.
- Gray rot appears on fruits and shoots. They are immediately removed, and the bushes are treated with the "Actellik CE" insecticide.
- White spot affects the leaves. A solution of copper sulfate helps.
Common pests:
- Spider mites and sawflies appear during dry periods. Half a bucket of wormwood is brewed with boiling water and sprayed with bushes.
- Aphids settle on leaves. A solution of insecticidal soap helps.
- The moth moth larvae eat the fruit. Plants are treated with wood ash infusion.
- The bushes are protected from birds with nets.
Gooseberries are not sprayed at the time of flowering - pollinators will die and there will be no harvest.
 Frequent illnesses and decreased productivity are the result of violation of growing rules:
Frequent illnesses and decreased productivity are the result of violation of growing rules:
- the fruits have become smaller - lack of moisture;
- fungal diseases - insufficient ventilation of the bush and waterlogging;
- pests - drought, flooding, shading, weeds;
- seedlings do not take root - the planting time is wrong.
Other varieties of berries:
The most popular and productive gooseberry varieties
Wintering
In autumn, dry and old branches are cut... The ground is cleaned of plant debris and dug up to destroy pests and fungal spores. The soil is watered and mulched. The winter-hardy variety is adapted to low temperatures, so the bushes do not need additional protection.
Reproduction
Gooseberry Ural grapes propagated in three ways.
Layers
The procedure is carried out in the spring, before the buds swell, or in the fall, 2 months before the onset of frost... Near the plant, they clear the ground and form shallow grooves. The lower adult branches are bent to the ground and laid in grooves. The middle part of the branch is covered with a mixture of soil and humus. The sprouts that have broken through are re-added. When the branch takes root, it is separated from the bush, and the young seedling is assigned to a new place.
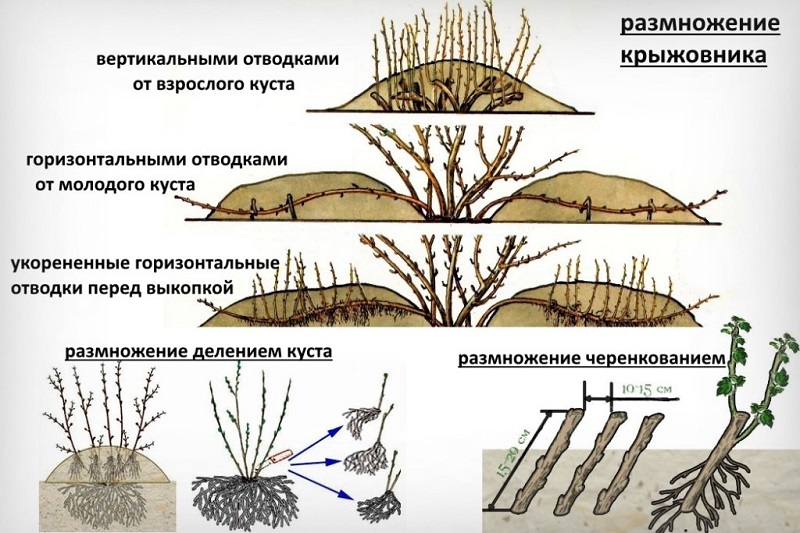
By dividing the bush
Work is carried out in the fall, when the gooseberry leaves the leaves.... After sanitary pruning, the bush is dug up and divided so that there are 5-6 shoots on each part of the root. Youngsters are seated, watered abundantly, the root zone is mulched.
Cuttings
Lignified cuttings 15-20 cm long are prepared during autumn pruning... They are disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate, cut at both ends and wrapped in cloth. Store in a cool place.
In February, the cuttings are rooted in a glass of water and covered with a bag. With the appearance of roots and leaves, they are planted in a nutritious substrate, and in the spring they are transferred to open ground. When propagated by green cuttings, they are cut in mid-summer. The length of green shoots is 40 cm. Leaves only at the top and root immediately in the open field.
Features of growing varieties depending on the region
In the conditions of the Middle Volga region, standard pre-winter preparation without additional cultural insulation. Propagate the plant by dividing the bush and layering preferably in the fall.
Autumn weather in the Urals is not stable. Due to the danger of early frosts, propagation and planting of gooseberries is best done in the spring. - during the summer-autumn period, the plants will get stronger and adapt. In the fall, a high soil cushion is formed under the bushes and tamped down. In winter, the root zone is additionally mulched with snow. This will slow down the thawing of the soil, prevent early bud swelling and protect against recurrent frost.
Conclusion
Gooseberry Ural grapes are valued for their large size, high yields and dessert taste. This early maturing variety is adapted to the conditions of the Urals and the regions of the Middle Volga region.
Frost-resistant bushes do not need shelter in winter, and flower buds withstand return spring frosts down to -10 ° C. The variety belongs to tall and fast-growing, subject to agricultural technology, it shows resistance to powdery mildew and the main pests of the crop.