Why is wheat smut dangerous and how to deal with it
When growing wheat, it is not always possible to obtain the maximum yield, since it is demanding on climatic conditions and soil, as well as susceptible to many diseases.
One of the most common is smut. We will tell you why it is dangerous and how to deal with it.
The content of the article
Wheat smut: the nature of the disease
Wheat smut is a type of fungal disease that affects cereals of spring and winter varieties... The causative agents of the disease are smut fungi belonging to the basidial class. Their contact with seeds or soil leads to plant disease.
Smut is difficult to treat... Basidiomycetes have a very strong and viable mycelium.
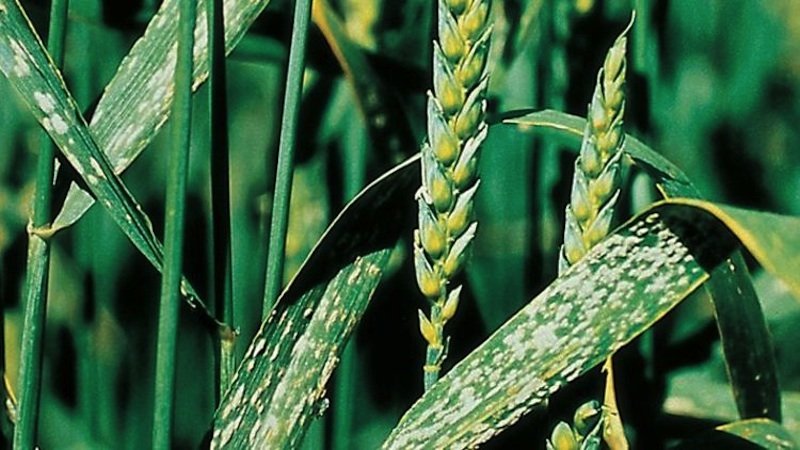

This disease causes significant harm to agriculture, leading to partial or complete loss of crops. wheat. The quality of the resulting grain decreases. Spikes infected with mycelium develop poorly, weaken, and cannot resist other diseases. They become less hardy and drought-resistant.
Many infected plants do not have time to hatch by the time of harvest. The smut is especially harmful to winter crops.
Causes of occurrence
The risk of infection increases with autumn droughts, non-compliance with planting technology wheat, deep immersion of seeds in the soil.
Reference. Planting winter wheat too late or early spring wheat creates a favorable environment for the development of the disease.
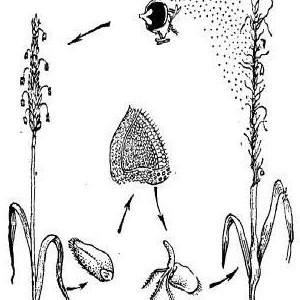 Most often healthy plants are infected from diseased plants... The infected cereal disintegrates into parts, the spores released by the wind are carried to other plants.
Most often healthy plants are infected from diseased plants... The infected cereal disintegrates into parts, the spores released by the wind are carried to other plants.
Infection is also possible when spores are in the soil.... In the spring they begin to sprout and form mycelium. The optimum temperature for spore activation is + 2 ... + 5 ° С. The developing mycelium infects the sprouts of cereals and spreads within their stem. During the flowering period of cereals, the mycelium reaches the panicle and accelerates its development. As a result, the spike turns black, and the weevils are replaced by the spores of the parasite. The infected plant produces an unusable spore mass instead of grain.
Uncontaminated containers and agricultural implements can also become a source of the spread of the disease. The causative agent is carried by animals, birds and insects.
Symptoms
Symptoms of infection appear on a panicle and ear of wheat... At a certain stage of development, the mycelium of smut fungi disintegrates into individual cells, which are covered with a thickened membrane and turn into spores.
A dusty or dark-colored mass is formed in the modified grains, stems, or even on the leaves. Clusters of spores give the affected parts of the plant a charred appearance, as if the plant is covered with soot. Therefore, the disease is called smut (photo below).
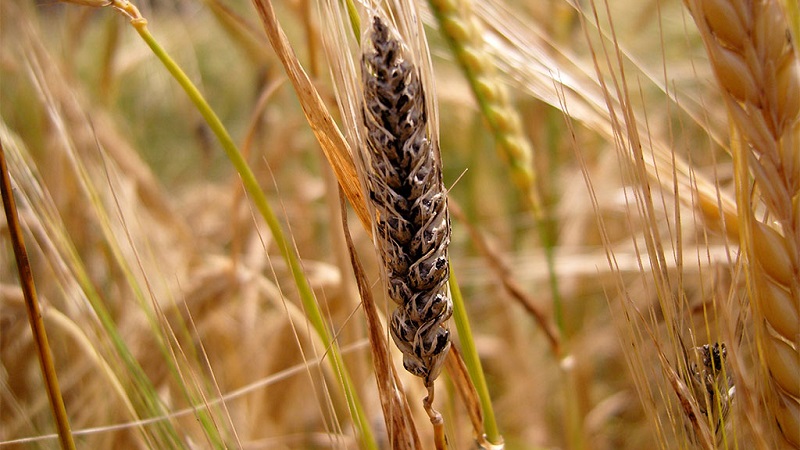

Kinds
There are several types of smutthat infects wheat. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Solid
When a culture is damaged by a hard smut, the inner part of the grain is destroyed, the outer shell does not change. The causative agent of the disease is Tilletia caries. The teliospore of this type of smut enters the external environment during harvesting or during the primary processing of grains. Contamination of healthy grain and soil occurs.
Reference. Hard smut is the most dangerous for soft wheat varieties. It manifests itself in the stage of milk ripeness of the cereal.
The main signs of hard smut:
 small, flattened ears;
small, flattened ears;- parted scales;
- swollen elongated grains;
- the plant acquires a blue-green color and an unpleasant herring smell;
- in place of the grains, a black spore mass is formed;
- ears of affected wheat lose weight and do not drop during ripening.
The disease is faster develops in dry and cold weather.
Dusty
When a head smut is damaged, the shell and the inner part of the grain are destroyed... The causative agent of the disease is Ustilago tritici. The infection affects the ears of winter and spring wheat. It begins in the growing season from the bottom of the ear. From infected seeds of one plant, the disease is transferred to another by the wind.
Signs of the disease:
 heading of culture is accelerated;
heading of culture is accelerated;- an infected plant is higher than healthy ones;
- the plant bushes weakly;
- the ear has a scorched appearance;
- the infected grain is covered with a gray coat.
Disease accelerates development at low air and soil temperatures, non-compliance with sowing dates, in case of autumn droughts. A dusty smut can destroy an entire crop.
It can be useful:
Indian
This type of disease was first reported in India in 1930.... Currently distributed in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, Nepal, USA, and Mexico. The causative agent is Tilletia indica. In an ear, from 1 to 5 spikelets are affected.
Symptoms of the disease:
 instead of grains - seed coats with a black mass of spores inside and the smell of rotting fish;
instead of grains - seed coats with a black mass of spores inside and the smell of rotting fish;- the affected grains are swollen;
- the infected plant is dwarf;
- when wheat ripens, the spikelet scales of the affected plants diverge;
- teliospores ovoid or oblong, 1-3 mm in diameter, when ripe, form a brown-black dusty mass.
Infection and development of the disease occurs with a sharp fluctuation in temperature. from + 7 ° С to + 22 ° С and high air humidity (over 65%). Spores are carried by the wind from diseased plants to healthy insects, animals and birds. The source of distribution can be non-disinfected agricultural implements, containers, storage places.
Spores remain viable in grain for up to 18 years, in soil - up to 6 years.
Dwarf
It mainly affects winter wheat. The causative agent is Tilletia controversa Kuhn. More harmful than hard smut. The seedling of the culture is initially affected.
Distinctive features appear during the earing period:
 plants bush strongly, form up to 50 stems;
plants bush strongly, form up to 50 stems;- low growth culture;
- ears are dense, do not come out of the axils of the upper leaves;
- the number of ovaries in a spikelet increases to 4-7;
- instead of caryopses, spherical smut sacs with teliospores are formed in the ear.
Spores are highly viable (up to 10 years in soil).
Stem
Stem smut caused by the fungus Urocystis tritici Koern... On the leaves and stems of the plant, convex light stripes are formed, which become lead-gray as they develop.
The stripes range in length from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The striped epidermis dries and cracks, exposing a dark mass of spores. Wheat becomes infected during germination, then the whole plant is affected.
 Features:
Features:
- stunting;
- the ear is missing or deformed;
- there are no grains in a developed ear;
- leaves and stems are twisted.
Disease Source - Infected Seeds... Spore viability is 1 year.
How to deal with the disease on plantings
If wheat is infected with smut, it is destroyed... On average, this is 15-20% of the harvest. If a lesion is noticed during the ripening period, it is better to let it die.
Teliospores cannot be treated with pesticides. This will harm the quality of not only diseased, but also healthy plants more than smut.
The fight against the disease is to prevent possible infection... Control measures:
- compliance with agrotechnology and crop rotation;
- seed approbation in order to identify contaminated grain;
- disinfection of agricultural implements and machines;
- use of wheat varieties resistant to disease;
- disinfection of seed.
Chemical seed dressing is effective for hard and dusty smut. There are several methods of etching:
 Dry... It is carried out with the help of machines with powdered toxic chemicals: "Merkuran", "TMTD", "Granozan". Since the chemicals are poorly adhered to the grain, the method is considered ineffective.
Dry... It is carried out with the help of machines with powdered toxic chemicals: "Merkuran", "TMTD", "Granozan". Since the chemicals are poorly adhered to the grain, the method is considered ineffective.- With moisture... The grain is treated with special machines with a suspension of pesticides: "Merkuran", "Granosan", "Hexachlorobenzene". This method is effective - the number of infected cereals decreases, and good germination of seeds is traced.
- Wet... Seed material is etched with formalin solution 5 days before sowing. The method consists of three stages: wetting, languishing, drying. The process is very laborious, therefore it is rarely used, either with a small amount of grain, or in the case of severe damage to the seed.
- Semi-dry... The principle is the same as in the wet method, but without drying the grain.
On mown wheat
If the wheat is mown, they begin to fight the spores that have survived in the ground... Manure and minerals are added to moist and well-heated soil. This creates conditions conducive to the death of the fungus.
Also, the soil is enriched with manganese and boron. They increase the resistance of plants to diseases.
Read also:
Using contaminated grain
It is undesirable to use wheat grains infected with smut for food... Spores contaminate the flour, it takes on the smell of spoiled herring and a dirty color. Bread made from such flour is poorly baked, smells unpleasant and has a sweet taste.
To get rid of smut, wheat is washed in a washing machine and treated three times brush apparatus. The grain thus refined is mixed with the clean grain. According to quality standards, the amount of smut grain in wheat should be no more than 5%
Geographic spread of the disease
Smut is widespread... The causative agents of this disease have the same habitat as the plants feeding them.
Hard smut is ubiquitous... Dust smut - in the European part of Russia, in some areas of Western Siberia, small foci in the Samara and Orenburg regions, in the North Caucasus and in the Transcaucasus.
Stem and dwarf smut are observed in the Stavropol Territory and Crimea.
The Indian smut has not been registered in Russia.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent smut, you should:
 use only healthy material;
use only healthy material;- not to allow sowing wheat seeds collected from fields affected by smut by more than 0.5%;
- timely dressing seed material;
- use varieties that are resistant to this disease;
- sow wheat on time.
Conclusion
Smut is a common and difficult to treat fungal disease affecting wheat. Fungal spores are highly viable. The disease leads to partial or complete loss of wheat yield, so it must be fought. Since the affected plantings cannot be treated with pesticides, special attention is paid to preventive measures.