Medium early gooseberry variety "Pink 2"
Despite the abundance of new gooseberry varieties, many gardeners choose time-tested crops. Among them is Pink 2, which is characterized by medium early ripening, resistance to common diseases and large, sweet and sour fruits. The article will tell you about the nuances of growing gooseberries Pink 2.
The content of the article
- What is this gooseberry variety
- Characteristics and description of the bushes
- Characteristics and description of fruits
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety compared to other varieties and hybrids
- Growing technology
- Features of growing this variety, depending on the region
- Pollinating varieties
- Conclusion
What is this gooseberry variety
Pink 2 - gooseberry mid-early ripening... Fruiting begins 3-4 years after planting, the berries ripen in the second decade of June. Productivity - 3-5 kg per bush, with industrial cultivation - 10-12 t / ha.
100 g of fruit contains 13.4% soluble solids, 9.4% sugar, 1.7% titratable acids, 16 mg vitamin C, 20 mg bioflavonoids.
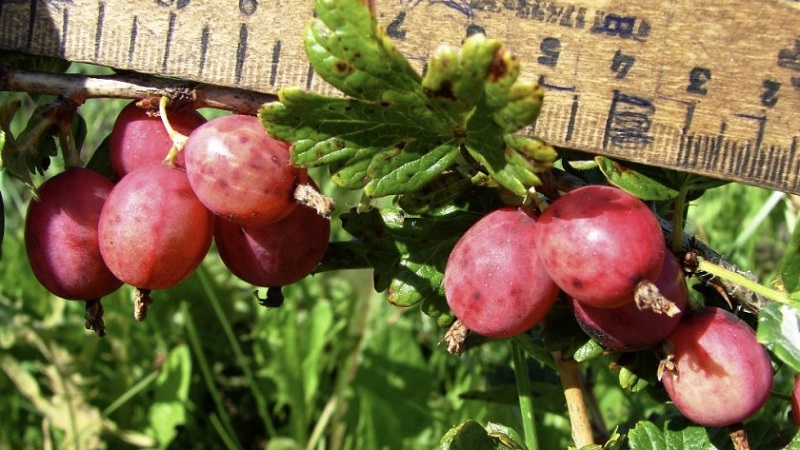

Harvested in dry and clear weather... For fresh consumption, the berries are picked at the stage of full ripeness, when they become soft and the skin turns dark red. And for processing, dense, pinkish-red fruits are suitable.
Fully ripe berries are stored in the refrigerator for a maximum of five days, and fruits plucked at the stage of technical ripeness - 10 days. The frozen crop is stored for up to six months.
Brief history of origin and distribution
Pink 2 was bred in 1963 by domestic breeders Moscow Fruit and Berry Experimental Station based on the varieties Date and Seyanets Lefora.
Characteristics and description of the bushes
Medium-sized bushes with a semi-spreading and dense crown... Young shoots are erect, of medium thickness, flexible, non-pubescent, green, lignified - thick, covered with light gray bark. Thorns are few, they are long, thin, dark-colored, located along the entire length of the shoots and directed perpendicular to the shoot or downward.
The leaf plates are large, green, have a three-lobed shape with pointed tops and a glossy, slightly wrinkled surface.
During flowering, flowers collected in a brush of 1-2 pieces appear on the bushes with light green petals with a pink border, curved to a large calyx.
Resistant to temperatures
The variety is characterized by medium frost resistance. - bushes tolerate up to -20 ... -25 ° C and winter temperature drops.
Moisture and drought resistance
Excessive watering and waterlogging of the soil lead to the development of fungal diseases and decay of the root system. Prolonged drought and heat provoke a decrease in yield and a deterioration in the quality of fruits.
Disease and pest resistance
The variety is resistant to powdery mildew, anthracnose and septoria... In case of violation of agrotechnical rules, in case of rainy or excessively hot weather, the development of fungal diseases, mosaics and attacks of pests is possible: aphids, moth butterflies.
Characteristics and description of fruits
The berries are large, weigh an average of 5-7 g (some specimens reach 10 g), round or oval, covered with a dense pinkish-red skin with a thin layer of waxy coating, which becomes dark red when fully ripe.
The pulp contains large seeds, characterized by a dessert, sweet and sour taste.
Areas of their application
The fruits of Pink 2 are consumed fresh, freezeare used for preparation of wine and various preparations: jams, preserves, confiture.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety compared to other varieties and hybrids
The main advantages of the variety:
- self-fertility;
- stable high yield;
- large-fruited;
- immunity to a number of common diseases;
- good keeping quality and transportability;
- excellent dessert taste;
- frost resistance;
- the possibility of industrial cultivation;
- universal use of fruits.
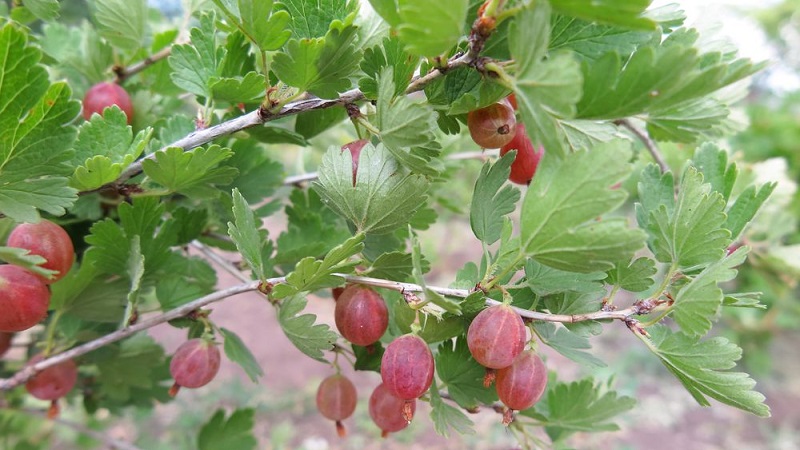

The disadvantages of Pink 2 include:
- the need for top dressing;
- complicated reproduction;
- the need for fertile soil.
Growing technology
Pink 2 has the same planting and grooming requirements as the others gooseberry varieties, the only exception is its high need for feeding.
Optimal conditions
For planting seedlings, choose a well-lit place, protected from cold wind and drafts.located on a plain or high ground. The depth of groundwater is at least 1 m, otherwise the gooseberries are planted on a fill mound up to 50 cm high and 1 m wide.
The variety grows well in loose, light, fertile soil with a weak or neutral acidity level (pH 5.5). Suitable options are clay, loamy, sandy loam and sandy soils.
reference... Lime or dolomite flour is added to the acidic soil in advance.
When buying seedlings, one- or two-year copies are chosen. with a developed root system 22-30 cm long, without signs of disease, rotting or pest damage.
It is allowed to plant gooseberries next to tomatoes, mint, garlic and dill... The best predecessors are vegetables, cereals and green manures, the worst are currants and other varieties of gooseberries.
Terms and rules of landing
Planting is carried out in the spring, at the end of March, or in the fall, from late September to mid-October.
Landing rules:
- 2-3 weeks before planting the seedlings, dig holes with a diameter of 60 cm and a depth of 50 cm in the prepared area.
- Pour nutritious soil at the bottom of each pit (excavated soil, 10 kg of manure or humus, 150 g of superphosphate, 200 g of crushed limestone, two buckets of peat, 300 g of wood ash or 40 g of potassium salt).
- Form a hill out of the soil mixture, place a seedling on it directly or at a slight slope, spread its roots along the slopes.
- Sprinkle the seedlings with soil mixture so that the root collar is 2-3 cm deep.
- Tamp and water the soil at the rate of a bucket of water for each plant.
- Mulch the soil with humus, compost or peat.
- Cut off the shoots, leaving 3-5 buds on them.
Distance between bushes should be 1-1.5 m, between rows - 2-2.5 m.
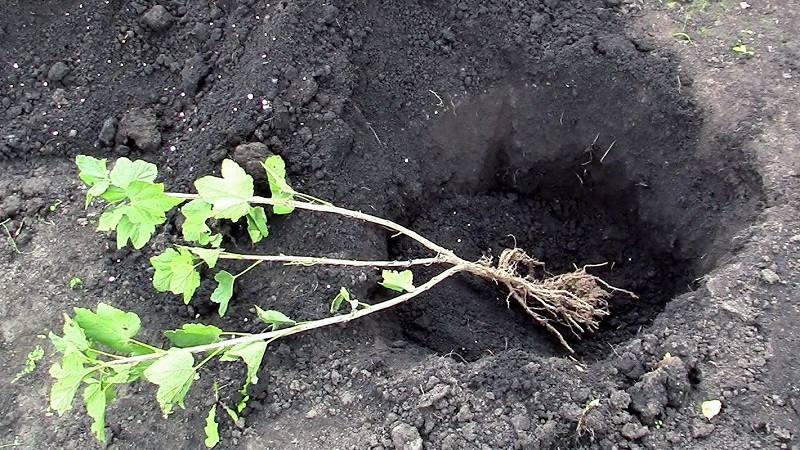

Further care
Gooseberries are watered every 10-12 days with settled, warm water under the root at the rate of 10 liters per bush.
After watering or rain, the soil is loosened - it prevents the formation of dry crust on its surface, improves the access of oxygen, nutrients and moisture to the roots. At the same time, weeding is carried out and weeds are removed, which takes useful elements, water from the soil and creates a favorable environment for the development of diseases and pests.
Top dressing is applied three times per season according to the scheme:
- spring (March) - 0.5 buckets of humus, 50 g of superphosphate, 25 g of ammonium sulfate and 25 g of potassium sulfate for each bush (for adult plants, the amount of fertilizer is doubled);
- after flowering - manure solution (1: 5) at the rate of 5-10 liters per plant;
- after 15-20 days - re-application of manure solution.
Gooseberries are pruned annually... In the spring, before the buds open, formative pruning is carried out, as a result of which 3-5 strong branches are left on the bush. The formed bush should have 16-20 shoots of different ages. In autumn, after the foliage has fallen, cut off all shoots over 7 years old.
Remove regularly all dry, damaged, poorly overwintered or growing shoots inside the bush.
Possible problems, diseases, pests
Improper crop care, such as over-watering or adverse weather conditions, can result in the defeat of the bushes by fungal diseases or mosaic. In the first case, the plants are treated with Bordeaux liquid or the HOM preparation, in the second, they are dug up and burned.
Hot and dry weather may cause pests (aphids, moth butterflies). To combat insects, insecticidal preparations are used, for example, "Actellik", "Karbofos" or "Fufanon".
Important! During fruiting, only folk remedies are allowed, for example, tobacco or soap-oil solutions. For the first, 200 g of ground tobacco leaves are dissolved in 8 liters of water, 2-3 tsp. red pepper powder, insist 2-3 hours and spray the bushes. For the second solution in 8 liters of warm water, add 200 g of grated alkaline soap and mix until smooth, and then 200 ml of vegetable oil.
Prevention of diseases and pest attacks consists in timely removal of weeds and fallen leaves, autumn hilling of bushes to a height of 10 cm, spraying plants with Bordeaux liquid, preparations "Bicol" or "Lepidocide".
Wintering
In autumn, the site is cleared of fallen leaves and other debris, the soil is dug up and superphosphate is introduced into it, the bushes are sprayed with insecticides and spud, the near-trunk circle is abundantly watered and mulched with humus or peat.
In the northern regions with frosty winters the bushes are tilted to the ground, plywood shields are installed around them, covered with dry foliage and covered with burlap.
Reproduction
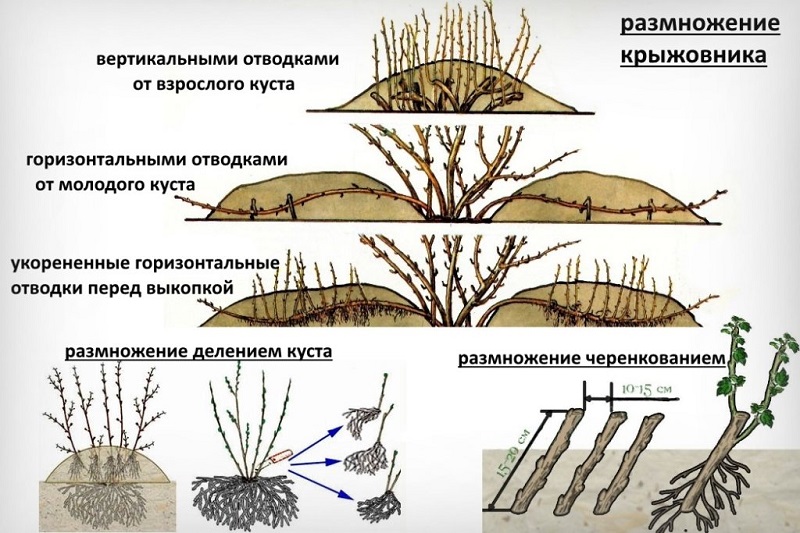
There are several ways to reproduce Pink 2.:
- Horizontal layering. Trenches are dug near the bush and, with the help of special brackets, shoots are fixed in them, growing as close to the ground as possible. Then they are covered with soil and watered. After the emergence of new shoots from the buds, they are separated from the mother plant and planted in a permanent place.
- Vertical layering. In the spring, old shoots are removed, and young ones are shortened - this stimulates the growth of new shoots. After that, the bush is spud so that the shoots form a root system, and in the fall they are separated from the main bush.
- Cuttings... In July, cut green cuttings, place them in containers with soil and put them in a greenhouse for rooting.
The variety is difficult to reproduce, especially cuttings take root badly.
Features of growing this variety, depending on the region
Regardless of the region of cultivation, gooseberry Pink 2 presents the same requirements for planting and grooming.
At the same time, in the southern regions, characterized by hotter and drier summers, the bushes are watered more often and more abundantly, and in the northern regions with frosty and long winters at the end of autumn, the bushes are covered with plywood and burlap, which is not done when the variety is grown in a milder climate.
Pollinating varieties
Pink 2 is a self-fertile varietythat does not need pollinating varieties.
Conclusion
Pink 2 is a rather rare gooseberry variety due to its difficult reproduction. It is characterized by an average degree of frost resistance, immunity to diseases, abundant yield, large size and pleasant taste of the fruit. At the same time, the variety is picky about soil fertility, needs regular fertilization and proper watering.