Growing gooseberries on a trunk
Standard plantings are gaining popularity due to a number of advantages: it is more convenient to care for them, they are less susceptible to diseases, the berries grow larger and tastier. The shrub on the trunk looks original and decorates the garden area.
When planting a standard gooseberry, it is important to consider that its cultivation requires certain knowledge, effort and time. Let's consider its main advantages and features of agricultural technology.
The content of the article
Description of gooseberries on a stem
Gooseberry is a sprawling shrub that grows over time. It makes it difficult caring for him, tillage, harvesting, contributes to the development of various diseases. The standard culture method avoids these problems.
What does it look like
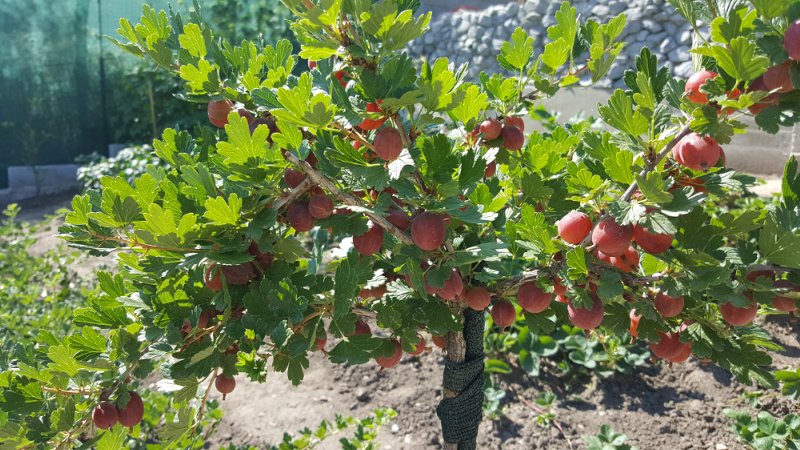

A berry culture on a trunk is a tree with a height of 0.6 to 1.5 m. The height of a plant depends on the method of cultivation. Falling branches and foliage form a cap on an even trunk.
Reference. Stamb (it. Stamm - "Trunk") - part of a tree trunk from the root collar to the first skeletal branch of the lower tier of the crown.
The gooseberry is shaped by pruning. The roots of the bush are shallow and superficial, therefore additional supports are used for stability.
Advantages and disadvantages
Gardeners leave a lot of positive reviews about gooseberries on a trunk, highlighting the advantages of this growing method:
- the bush is more compact, takes up little space on the site;
- it is easier to look after him, feed, loosening and watering;
- the crown is well ventilated and illuminated, as a result, the plant is less susceptible to various diseases;
- branches do not break under the weight of snow;
- increased productivity, fruit larger and sweeter;
- more convenient to pick berries;
- gooseberries on a trunk decorate the site.
Disadvantages of such landings:
- seedlings are more expensive than ordinary ones;
- only winter-hardy varieties are used;
- gooseberries require constant support and additional protection from frost;
- the harvest depends on one shoot;
- it is important to periodically remove root growth;
- shrub is picky about feeding.
How to grow a standard gooseberry

For breeding a standard bush, varieties are used that form few shoots and branch weakly. The most popular are Generous, Russian, Salut, Yantarny, Redball, Kolobok, Yarovaya, Ural grapes. To grow gooseberries on a stem, use 2 methods:
- the bush is formed on its own roots, using tools for trimming;
- graft on the stock.
So that the standard gooseberry does not break, a support structure is used throughout the life of the plant. For this, a wooden stake, which is impregnated against decay, or a metal profile, is suitable. They are dug into the landing pit. If the gooseberry is planted in rows, it is tied to an established trellis in the middle of the trunk and the center of the crown.
Since the cost of gooseberry seedlings is high, many gardeners form a shrub with their own hands.
By vaccination method
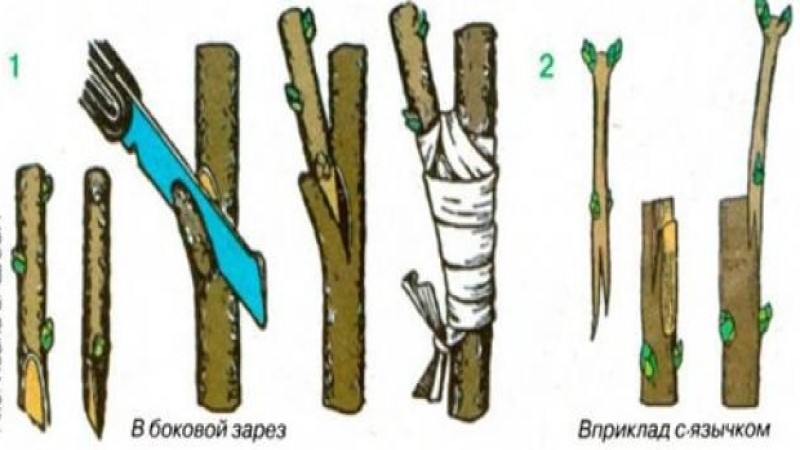
To grow a standard culture by grafting, the graft is first prepared. Cut the cuttings from the varietal bush, remove the thorns... They are stored in wet sand, sawdust or peat at a temperature of about + 3 ° C.
Gardeners recommend using golden currant seedlings as a stock (trunk).They are distinguished by a powerful root system, give little root growth, are frost-resistant and durable.
The stock is planted in advance. Forcing is carried out not by a bush, but by a vertical shoot. In addition to golden currant, yoshta (a hybrid of black currant and gooseberry) is used as a stock. It is distinguished by smooth, strong shoots and frost resistance. At the stem, 1 shoot is left. The side ones are pinched to thicken the trunk.
Reference. Annual or biennial plants are used as a stem.
Gooseberries are grown in standard (height of the grafting site - 60-100 cm) and half-stem (height - 40-60 cm) form. Vaccination is carried out in the spring, when sap flow begins. How to plant gooseberries:
- in the split - with different diameters of the scion and rootstock;
- improved copulation - when the slice sizes are the same;
- in the butt with a tongue - when the graft and stock are of different sizes;
- in the side cut - for different grades.
The grafted plants are watered and shaded. Young shoots are removed on the trunk. In the fall, the shrub is transplanted to a permanent place. A stake is installed in the planting hole, to which a bush is tied up at the grafting site. New shoots on the trunk are periodically cut off. Spring and autumn plant cut off, directing the branches in the right directions, and give the crown the required shape.
Forming by cutting
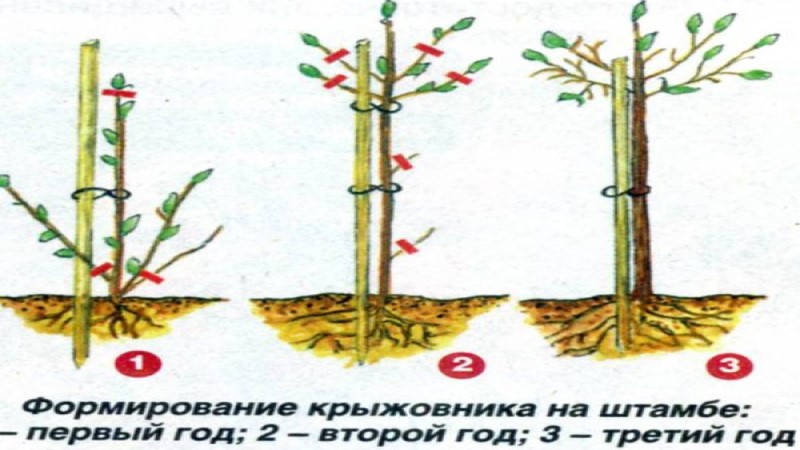

In this case, the lateral branches of the gooseberry grown on its own roots are trimmed and shortened, while maintaining the central conductor. This is an easier method available even for novice gardeners.
Reference. If the shape does not suit you, you can return to the classic bush. To do this, leave root shoots at its base.
First, gooseberries are planted in a permanent place, usually in the fall. To form, choose varieties with thick and dense shoots. After the culture is rooted, a strong upright shoot is selected and left. The rest are carved at ground level.
Then produce the "blinding" of the left shoot. To do this, remove all the kidneys from its bottom, leaving only 4-5 pieces at the top. In the first and second year of the plant's life, shoots that have developed from the buds are cut in half to create the correct shape. In subsequent years, they are not shortened, but the aged, fertile, damaged and diseased branches are removed. The growths that appear on the trunk and near it are periodically pruned.
Planting gooseberries on a trunk

Gooseberry loves air, light and space. Therefore, it is planted in a sunny place, in moist and fertile soil with a level of acidity. pH 6.0-6.8. A distance of at least 1 m is maintained between the bushes. Low-lying and swampy areas where water stagnates and places with heavy chalk or sandy soil are not suitable for the culture.
The bush gets along well next to red currants and tomatoes. It is not recommended to plant a crop next to raspberries, black currants and wheatgrass, since they have common pests.
Favorable time for planting
Autumn is considered a favorable time for planting gooseberries on a trunk. The bush is planted in early spring, but there is a risk of its death, since during the summer heat the soil becomes dry and the roots do not have time to take root.
Landing rules
Step-by-step landing algorithm:
- The site is dug up, removing weeds and stones. Dig a landing hole. It should be 2 times larger than the roots of the plant. The excavated soil is mixed with rotted manure or compost in equal proportions.
- The roots of the plant are shortened slightly so that new young roots are formed at the cut point. It is advisable to dip them into the root formation stimulant solution.
- The branches that thicken the trunk are cut off, the rest are shortened. Do not touch the top of the gooseberry.
- A support system (stake or metal profile) is driven into the planting hole, a seedling is placed in the center, the roots are straightened. Pour everything with soil mixture and tamp it.
- The plant is well watered and cover the soil with mulch.
- The gooseberries are tied to a support system in the middle of the stem and crown.
To increase the yield, quality and taste of berries, it is recommended to plant several varieties on the site.
Caring for a standard gooseberry
Stamp landings require more careful attention to themselves.
Watering
Gooseberries are drought-resistant crops, but regular watering, especially during flowering, ensures a good harvest. It is carried out at least 1 time per week, when the plant blooms, the rest of the time - 1 time in 2 weeks. Watering is important for young plants in hot, dry weather. In this case, it is carried out more often than on ordinary days, as the soil dries out. The rate of water consumption per 1 bush is 50 liters.
Loosening and mulching the soil
To protect the roots from overheating in the heat, retain moisture in the soil, reduce the growth of weeds, and provide the culture with nutrients, the soil is periodically loosened and mulched. Sawdust, peat, grass cuttings and straw are used as mulch.
Fertilizers and feeding
During planting, organic fertilizers are applied to the soil in the form of rotted manure or compost. In the spring, organic remedies are also used to provide the gooseberries with nutrients. To do this, the soil around the bush is mulched with rotted manure, but so that it does not fall on the stem.
Council. If the plant develops slowly or is weak, re-feeding is carried out in the summer.
The shrub needs potassium and nitrogen. 100-200 g of nitrogen and 15 g of potassium per 1 m² are introduced annually. If the soil is acidic, dolomite complexes are used, which normalize the balance of magnesium and calcium.
Pruning
To form the correct shape of the standard bush, it is cut off. At the same time, powerful shoots are removed that are inconvenient or ugly located. Remove old and damaged branches. Depending on the method of growing gooseberries on a trunk, pruning varies.
If the gooseberry is grown by grafting, at the end of the first or second season (it depends on the growth of the bush) it is formed from the central branch and 4-6... The stock is cut above the bud by ¼ of the seasonal growth. The lateral branches are shortened, giving the plant the shape of a sphere. Subsequently, 4 branches are left, which are shortened by 20 cm every year. Old, weak and problematic shoots are also removed. When pruning, shoots are retained at the age of 1 to 3 years, older branches are removed. Thus, in 5 years, a gooseberry of the required shape is formed, which bears fruit from 7 to 10 years.
When a bush is formed on its own roots, 1 shoot is chosen after rooting. The rest of the growth is cut at ground level. On the shoot, remove all the lower buds, leaving only the upper 4-5 pieces. In subsequent periods, the side branches are shortened, leaving 4 branches on them. As a result, a spherical shape is formed. As the culture grows, old and damaged branches are cut off, shoots around are removed.
Support
To prevent the gooseberry from breaking, a support system is used, which is installed from the wind side. It can be a wooden stake or a metal profile. A wooden support is cleaned of bark, treated with impregnation so that it does not rot, and painted. Gooseberries are tied to a peg at crown level and in the middle of the stem.
Preparing for winter
Gooseberry is a winter-hardy and frost-hardy crop. However, if the winter in the region is harsh and with little snow, it is better to plant it under the protection of buildings. In the cold season, it is recommended to increase the layer of mulch around the trunk, spud it and cover it with spruce branches.

Conclusion
The gooseberry on the trunk takes up less space, it is more convenient to look after and harvest it, the plant decorates the site. Self-cultivation of a standard crop requires some effort. If there is no time for this, ready-made seedlings are bought in special nurseries.