What grape care is required in June and how to properly carry it out
Fertilizing, tying vines, spraying against diseases and pests, pruning, pinching are just some of the activities that are important to regularly carry out when growing vines with juicy sweet fruits. We will tell you what kind of grape care to carry out in June in order to get a rich harvest.
The content of the article
June grape care

At the beginning of summer, grape bushes actively increase their green mass and become more weighty.... Therefore, the overgrown vines are tied to supports, stepchildren and excess ovaries are removed in order to prevent the shoots from breaking off.
Advice!Pinch the top clusters on the vines: they are less developed and do not grow as large as the rest.
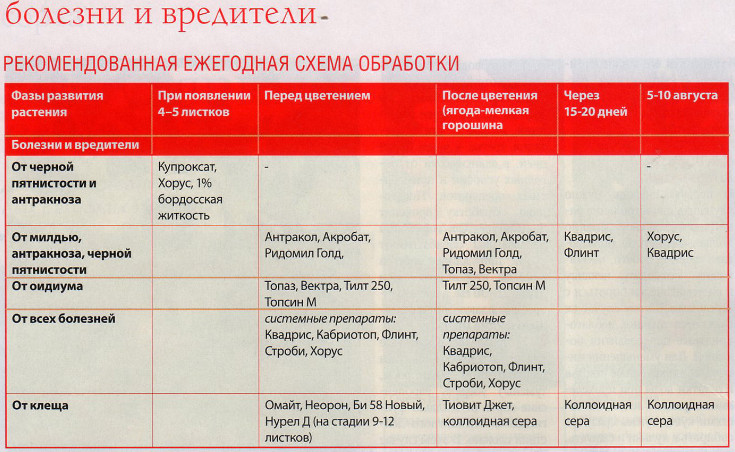
When the berries grow to the size of a pea, the bushes are sprayed with fungicides (for example, Ridomil Gold or Topaz) to prevent and treat purple spot, powdery mildew, fruit and gray rot, powdery mildew.
In June, foliar feeding (spraying) with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, preparations like "Ovyaz" and other similar means... Such procedures contribute to the active formation of ovaries.
Watering in early summer is carried out as the soil dries out. Young seedlings are especially in need of timely moisture. Usually 1-2 plentiful waterings per month are enough.
Features:
In summer, it is important to pinch the vines on time, otherwise the bunches that have set will not have time to ripen.
The stepchildren that form in the leaf axils are periodically removed. If this is not done, the bush will spend energy on the growth of new shoots, and not on the formation of existing stems and the ripening of berries.
Attention!A daily inspection of the vineyard will allow you to recognize a developing disease or pests in time.
Summer pruning grapes as such do not. In June, pinching, pinching and embossing are carried out, and excess vines and leaves shading the ovaries are periodically removed. These measures allow avoiding thickening of bushes, uneven lighting and insufficient ventilation.
The main goals of work in the vineyard in June are to protect plantings from diseases and pests, to tie up vines and remove excess shoots.
June care stages
Let's talk about stages of crop care in June for more details.
Pruning shoots

At the end of the month, the fruit-bearing vines are pruned so that more nutrients come to the formed berries and they ripen faster. To do this, the ends of the shoots are pinched or cut off after the antennae, leaving 5 leaves after the second bunch.
Trim the tops of those vines that have grown to 2.5 m in length. If this is not done, the vine will stretch further and form new clusters.
As a result, the grapes will ripen longer, the fruits will be less sweet. Young shoots growing from the replacement knot do not pinch.
Removing stepchildren
From June to the end of August, all stepchildren that appear in the leaf axils are regularly plucked so that the bush does not waste energy on building up unnecessary greenery. Stepson is a lateral process that appears in the leaf axil in the main part of the shoot.
Advice!When removing the stepson, leave a stump 1.5–2 cm high in its place. Then a new shoot will not appear at this place.
If pinching is not carried out, the bushes become too thick, and not enough sunlight gets on the bunch.As a result, the berries become sour. The thickening of the vineyard leads to the appearance of diseases and the spread of pests.
Watering
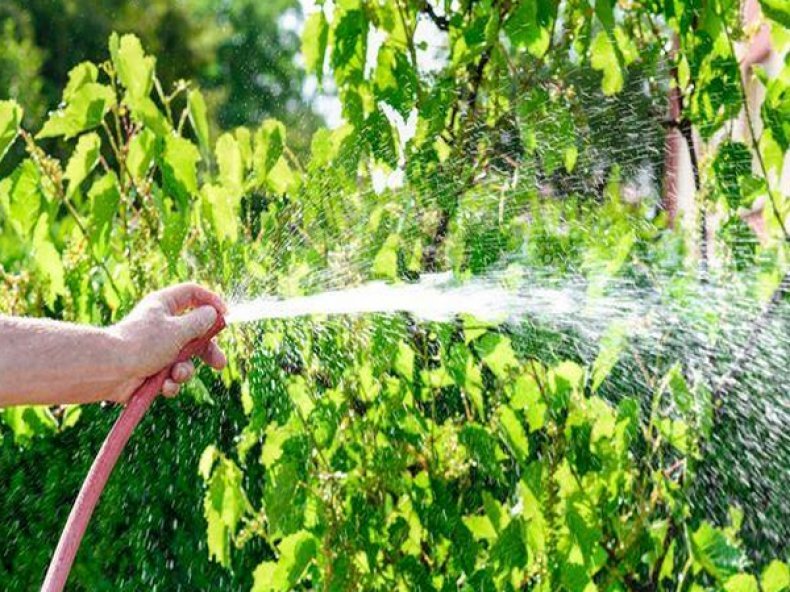

Adult grape bushes with a powerful root system practically do not need watering. If the summer is dry, 1-2 abundant watering is enough.
Young seedlings do not have a strong enough root system to extract water at depth. Therefore, they are watered about once a week at the rate of 10 liters per plant. After irrigation or rain, the soil is loosened, destroying the dense top layer. Along the way, they pull out the weeds that take food from the grapes.
Vaccinations
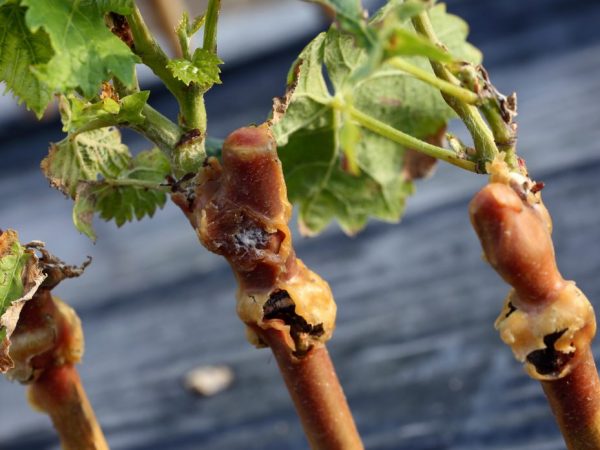

Some grape varieties are susceptible to the development of diseases and are not frost-resistant. Grafting of this sort on a more stable relative helps to correct the situation.
Reference! With the help of grafting, several varieties are grown on one bush, which is convenient if the plot is small and there is no way to break a large vineyard.
Grape cuttings are planted in several ways. In June and July, they are grafted with green cuttings on a green shoot. Cuttings of the desired variety are cut immediately before the procedure. The tip of the scion is sharpened and inserted into the rootstock split.
Immediately after the procedure, the stock is watered and hilled. If after 12-14 days new shoots have not appeared on the grafted cuttings, the upper part of the rootstock is cut off together with the grafting and the procedure is repeated.
Secrets of a successful vaccination:
- for the stock choose a frost-resistant hybrid resistant to oidium, mildew and phylloxera;
- cutting cuttings and splitting the scion is done with a sharp disinfected tool;
- the rootstock vine is trimmed perpendicular to the vine growth line.
Top dressing
Fertilization convenient to combine with watering. Superphosphate, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium sulfate are added to the water intended for grape bushes. The exact dosage is calculated in accordance with the instructions for the preparation.
Garter

Distinguish between dry and green garter vines. A dry garter is an attachment to trellis last year's vines. It is carried out in spring or early June, until fresh shoots have grown.
The green garter is the attachment of new green vines to the support. It is carried out several times during the season (each time the shoots grow 20-30 cm).
Rationing of bunches
Rationing of bunches consists in removing unnecessary inflorescences. In grape varieties with small sleeves, the inflorescences of the 1st order are removed, in the rest - the inflorescences of the 3rd and 4th orders. The procedure is carried out to improve the quality of the harvest and unload the grapevine.
It is interesting:
How to properly care for grapes in July: what to do, tips for novice winegrowers
Katarovka
Catarovka is held in June and August. This is an agrotechnical technique, which consists in pruning the surface roots on the underground part of the vine. If in the first years of the growth of the bush you do not pay attention to this procedure, the surface roots will die when the soil freezes, and in the summer the bush will suffer from a lack of moisture.
Important! Trimming the roots of the upper tier allows for good development of deep calcaneal and intermediate roots.
Remove the roots in late June and August in the morning. To do this, a hole is made around the base of the bush with a depth of about 20 cm and the upper roots are cut with a pruner or a sharp knife without leaving hemp. To protect against infections, the sections are disinfected with a 3% solution of copper sulfate or 1% boric acid. The hole is covered with earth.
Protection against diseases and pests
A properly selected grape protection scheme allows you to successfully control the development of diseases and the reproduction of pests. Processing carried out in several stages:
- The first spraying is carried out in the spring, when the shoots of early varieties reach a length of 10 cm. Copper-containing and sulfur-containing contact fungicides (for example, "Kumir" and "Cumulus") are used for treatment.They will protect the vineyard from anthracnose, phomopsis, mildew, oidium and ticks. Processing is carried out twice with an interval of 2 weeks.
- After another 2 weeks, spraying with "Kumir" and "Cumulus" is again carried out, but "Aktara" is already added to protect the grapes from felt and leaf mites.
- The third stage of protection is processing before flowering. This time, combined drugs are used for a complex of diseases.
- The next spraying is carried out after the end of flowering, but no later than 2 weeks after the previous treatment. Use insecticides against pests (for example, "Borey").
- The next treatment is carried out after another 2 weeks. This time it is good to spray in 2 stages to protect the formed clusters from diseases and pests. First, spray with a mixture of fungicide and insecticide (for example, "Topaz" + "Borey"), and the next day - a copper-containing fungicide ("Kumir" and others).
Further spraying is carried out as necessary at intervals of 2 weeks.
Features of summer care depending on the region
Grapes are a southern plant demanding heat and light. However, the achievements of modern breeding make it possible to grow it not only in the Krasnodar Territory, but also practically throughout Russia, including the middle lane, the Urals and even Siberia.
In central Russia, in particular in the Moscow region and the Leningrad region, the June grape care does not differ from that described above. The vines are pinched, tied up, watered, and protected from diseases and pests.
When grown in the Urals and Siberia, special attention is paid to the rationing of ovaries, since the short and not always hot summer does not allow a large number of brushes to mature.
Tips from experienced winegrowers
Tips from experienced winegrowers will help novice gardeners avoid mistakes when growing grape bushes:
- Before starting pruning, think over in advance not only the order of actions, but also the shape of the future bush.
- When growing grapes in regions with harsh winters, cover the vines to protect them from freezing during the colder months. In this case, keep the stem of the bush minimal.
- Remove vines older than 2 years, as they will no longer bear fruit.
- When pruning fruit-bearing vines, leave at least 8 eyes on each of them, as some of them are empty.
Conclusion
Competent vineyard care in June is a guarantee of a harvest of sweet and large berries. Timely pruning, pinching and normalization of bunches allows you to remove excess greens and ovaries, and treatment with fungicides and insecticides protects plantings from the development of diseases and pests.