Frost-resistant high-yielding pear variety "Cathedral"
The early-fruiting, middle-summer variety of pears Cathedral pleases gardeners with fragrant fruits of the correct shape. Their pulp is sweet, oily, fine-grained, contains 8.5% sugar and only 0.3% acid. Pears do not differ in keeping quality and are suitable for fresh consumption and preparation of dried fruits, jam, compotes and marmalade. In this article, we have collected complete information about the Cathedral pear variety: description, characteristics, ripening times, planting features and subtleties of care.
The content of the article
The history of origin and description of the cathedral pear variety
Pear Cathedral is a mid-summer variety, bred by engineers of the Moscow Agricultural Academy named after K. A. Timiryazeva " by crossing the Forest Beauty variety with a hybrid of the same Forest Beauty and Duchess.
Originators - S. T. Chizhov and S. P. Potapov. State trials began in 1990, and in 2001 the variety was included in the State Register of the Russian Federation. The pear has received permission to grow in the Central Region.
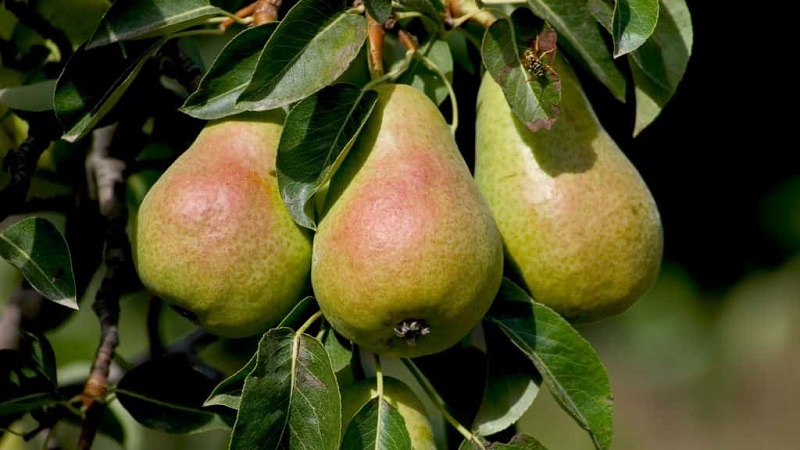

Variety characteristics
The table shows the distinctive characteristics of the variety:
| Indicators | Specifications |
| Wood | Medium height, 3-5 m. Crohn of regular conical shape. The branches are straight, sparsely located, the ends look up. |
| Escapes | Straight, rounded, red-brown, with slight pubescence. Buds are broadly conical, large, pubescent. |
| Leaves | Medium to large in size, green in color, oval, slightly pointed, smooth, glossy. The leaf plate is concave, curved upward, along the edge there are small notches. |
| The beginning and type of fruiting | The first fruits appear 3-4 years after planting. Fruiting on simple ringlets and annual shoots. |
| Fruit ripening | Second decade of August. |
| Bloom | April - May. The flowers are large, cupped, white, with oval petals. |
| Peduncle | Medium, curved |
| Fruit shape | Correct, pear-shaped, lumpy surface. |
| Seed chambers | Closed type, small. The sub-cup tube is long, funnel-shaped. Seeds are small and medium, ovoid, dark brown in color. |
| Pulp | White, delicate, juicy, medium density, fine-grained. |
| Skin | Smooth, thin, oily, glossy. The color is green-yellow at the moment of removable ripeness, light yellow in the consumer state. The coat color is weak, blurred, in the form of a red blush. There are many subcutaneous points, but they are almost invisible, gray or green. |
| Weight | 110-120 g |
| Taste | Sweet and sour. 4 points on a five-point scale. |
| Sugar,% | 8,5 |
| Acid,% | 0,3 |
| Dry matter,% | 16 |
| Scent | Middle |
| Appointment | Canteen - for fresh consumption, processing into jam, dried fruits, marshmallows and compotes. |
| Yield | 85 kg / ha, the maximum rate is 136 kg / sq. m. from one tree - 35-40 kg. |
| Marketability,% | 95 |
| Keeping quality | 10-12 days |
| Transportation | Average |
| Sustainability | For severe frosts (up to -30 ° C), scab, sooty fungus. |
Pollinators
Cathedral pear is self-fertile, sets fruit well without "helpers"... However, gardeners recommend planting it next to suitable pollinating varieties to increase yields and fruit quality. The varieties Lada, Chizhovskaya, Rogneda and Detskaya are ideal for this pear.

Advantages and disadvantages
Benefits of the variety:
- winter hardiness;
- scab immunity;
- early maturity;
- pleasant taste and aroma;
- juicy pulp;
- stable fruiting;
- high productivity.
disadvantages:
- fruits of small and medium size;
- short shelf life;
- low level of transportability.
Planting seedlings
Saplings are planted in spring and autumn.... In regions with a warm climate, autumn planting is practiced - in the last days of September - early October. This planting has an indisputable advantage: a sufficient amount of moisture is collected in the soil, which stimulates root formation and increases the survival rate of seedlings.
Trees planted in autumn tolerate temperature changes well and are resistant to insects and diseases.
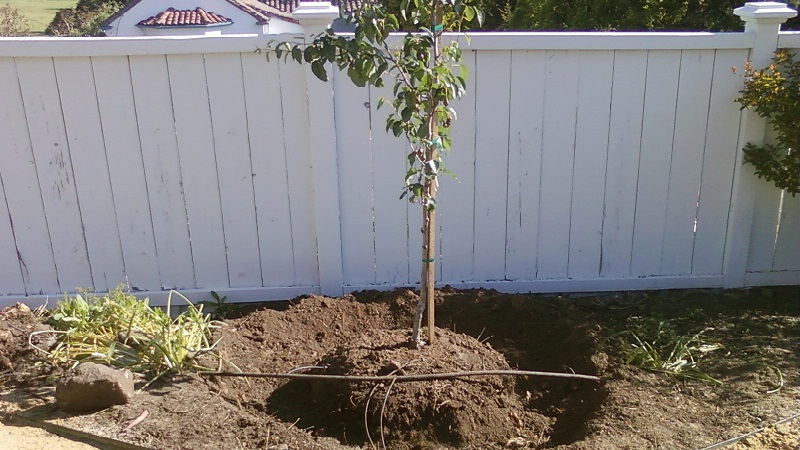

In the central regions of Russia, spring planting is performed - late April - early May... The root system manages to take root in a new place before the onset of the first frost, which ensures successful wintering for the seedlings.
Reference.It is recommended to plant a pear of the Kafedralnaya variety immediately in a permanent place, since the plant cannot tolerate transplants.
The culture is demanding on the composition of the soil and grows and develops best on breathable, nutritious sandy loam chernozem. Avoid areas with a high groundwater table - accumulated water freezes in winter and harms the plant. If there is no other way out, the seedlings are planted on an artificially created hill.
Pear loves warmth and sunshine, therefore, it feels best in the southern part of the garden. With a lack of lighting, the branches stretch towards the light and often break under the weight of the fruit and their own weight. Therefore, for this culture, planting in spacious areas without shading, but with protection from drafts, is preferable.
The optimal age for quality planting material is 2-3 years... There should be no damage on the branches. The bark is smooth and elastic. Rhizome - developed, flawless, with a large number of root processes.
About other varieties of pear:
Planting instructions:
- The pit is prepared in advance... With the planned spring planting, it is dug up in September - early October, with the autumn planting - two weeks before the scheduled date.
- Pit diameter and depth depend on the development of the rhizome. Standard sizes: diameter - 0.8 m, depth - 1 m.
- The topsoil is discarded to the side when digging, and then mixed with 20 liters of humus, 20 liters of peat and 10 liters of coarse sand.
- The soil is mixed with 3 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate and 200 g of superphosphate and poured onto the bottom. The soil, fertilized with organic matter, is poured on top, and 20 liters of water are poured.
- Two weeks after watering the pit start landing. 30 cm recede from the center of the pit and a support for the seedling is dug in so that after planting it protrudes 0.5 m above the ground.
- Collect earth around the support in the form of a hill.
- The leaves of the seedling are cut off and remove damaged roots.
- The rhizome is dipped in a solution of "Heteroauxin" for 20-30 minutes, then placed on a hill. The roots are carefully spread and covered with the remaining nutrient soil. The root collar should remain 5-7 cm above the soil. The soil is watered with water for better shrinkage.
After planting, the seedling is tied to a support with soft ropeswithout crushing the bark, and shake it periodically so that the earth fills the voids between the roots. A shaft with a diameter of 0.3 m is formed around the tree so that the water does not spread during watering.

Subtleties of care
Agricultural technology of the cathedral pear variety is standard and provides moderate watering, whitewashing, top dressing if necessary, prevention of fungal diseases.
Irrigation intensity
Mature trees tolerate drought and do not need additional watering, but young trees are watered regularly. Water consumption per pear is 20-30 liters. Watering frequency is once a week in two approaches, morning and evening. Water is poured in carefully so as not to erode the soil around the roots. The ideal way to water a pear is by sprinkling.
During fruiting, watering is increased to preserve the harvest... After harvesting the fruits, watering is stopped. The exception is drought at the end of August.
After each watering, the soil is loosenedto prevent the appearance of a dense earth crust, which prevents air from penetrating to the rhizome.
Council. Mulch the tree trunk with straw, peat, or sawdust. Mulch retains moisture in the soil and inhibits the growth of weeds.
Fertilizing the soil
The frequency of fertilizing depends on the fertility of the soil and the appearance of the tree.... Pears planted in well-fertilized soil grow faster and produce a rich harvest. They do not need to be fed annually. The poor sandy soil is fertilized with organic matter and minerals every year, after the snow melts, in summer and autumn.
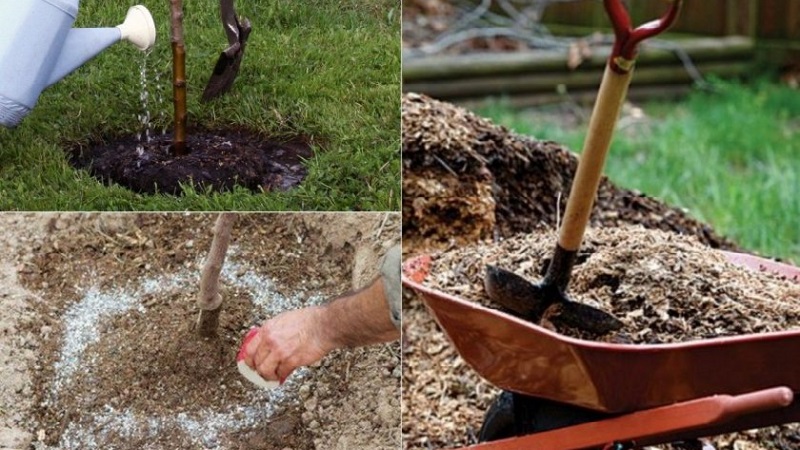

The table shows the seasonal fertilization scheme:
| Season | Fertilizer and dosage | Appointment |
| Spring | Before flowering:
After flowering: chicken manure infusion 1:15. Consumption - 25 liters for each tree after watering. |
Acceleration growth of foliage and shoots, the formation of a healthy ovary. |
| Summer | In mid-June: chicken manure infusion 1:15. Consumption - 25 liters for each tree after watering.
Mineral dressing for digging:
|
Strengthening immunity, accelerating fruiting. |
| Fall | Potassium phosphate dressing:
|
Preparation for wintering. |
Pruning
Pruning is performed before the start of sap flow - in April.
The branches of a young tree are pruned with pruning shears, starting from the second year of development, observing the rules:
- Healthy branches are left, weak ones are removed.
- The branches are cut into a ring without leaving hemp.
- In one approach, no more than 14-15 branches are cut.
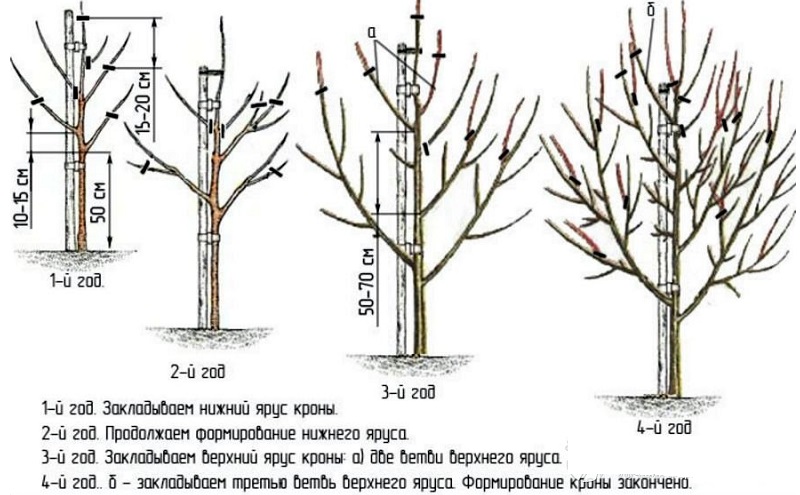
Mature trees are sanitized every year: cut off dry branches and thin out the crown, remove weak shoots and tops.
Council. In the first year of flowering, remove 80% of the flowers from the seedling. This procedure saves the strength of the tree and contributes to its better development in the future.
Wintering
For successful wintering, the tree is watered abundantly before the onset of the first frostso that the root system has time to be saturated with moisture. Then the trunk circle is mulched with straw or sawdust with a layer of 25-30 cm.
Mature trees winter successfully without shelter., but seedlings and young trees 2-3 years old can freeze in severe frost. Therefore, in late October - early November, the trunks are wrapped in cardboard or spruce branches. The branches are tied with a rope and covered with an awning or dense agrofiber. This will protect them from wind damage.
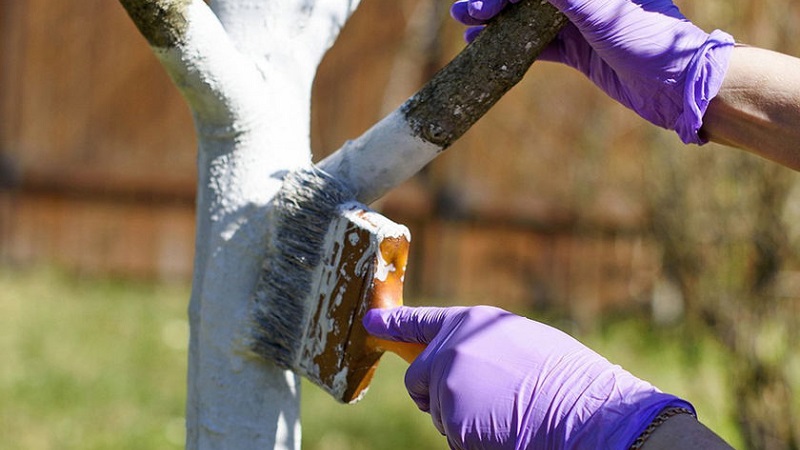
Whitewash
Whitewashing with slaked lime protects the bark from the bright spring sun and insects... 1 kg of clay and 2 kg of lime are dissolved in 10 liters of water. The composition is applied to the trunk, moving from the ground to the lower branches.

Disease and pest control
Pear Cathedral is not afraid of scab and sooty fungus, with proper care it rarely suffers from fungal diseases... Without proper care, trees weaken and become susceptible to fungi.
The table shows the main diseases of the pear and treatment tactics:
| Disease | Signs | Treatment | Prevention |
| Rust | Leaves with orange spots dry up and fall off. | Before and after flowering - 1% Bordeaux liquid solution.
"Speed" (2 ml per 10 l of water) - when foliage appears, during flowering and after. |
Cleaning and burning of dry foliage, digging the trunk circle and introducing copper sulfate. |
| Fruit rot (moniliosis) |
Brown spots on fruits and growths with fungal spores inside. The pulp of the fruit is loose, unpleasant in taste. | Wood treatment with 1% Bordeaux liquid, "HOM" in spring and autumn.
Whitewashing with lime mortar: 1 kg of powder per 10 liters. |
Timely removal of dry and diseased branches, infected fruits. |
| Stem, rot (cystoporosis) | Dark red color of bark, many dry branches. | Treatment with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid, "Nitrofen" (300 g per 10 l) until the kidneys swell.
During the budding period - a solution of copper oxychloride (900 g per 10 l). Consumption - 3 liters per 1 tree. After flowering - 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid. Twice at intervals of two weeks. |
Removal of the affected bark, treatment of wounds with copper sulfate and garden varnish.
Autumn whitewashing of the trunk and skeletal branches. |
| Powdery mildew | White bloom on shoots and foliage, deformation and fall of flower ovaries. | Before budding and after flowering, spraying trees with a solution of "Fundazol" or "Sulfite". | Cleaning and burning of fallen leaves. |
Read also:
Overview of pear varieties Autumn Yakovleva
A selection of the best varieties of winter-hardy pears for Siberia
The table describes the main pests of pears and methods of dealing with them.:
| Pest | Signs | Fight | Prevention |
| Aphid green apple tree |
Foliage curling and drying of the upper shoots. | Two-time treatment of trees in early spring and summer with preparations "Nitrofen", "Karbofos", "Kemifos", "Decis", "Cyanox".
|
Whitewashing and removal of old bark, deep digging of the trunk circle, weed removal. |
| Leaf roll | Cobweb-covered leaves twisted into a tube. | Before budding - "Detox", "Zolon", "Tagore" (10 ml per 10 liters of water). Consumption - 2-5 liters per tree, taking into account age. | Removal of affected leaves and clutches of the pest from the bark. |
| Gall mite | The pest feeds on the sap of the bark, the tree dries up, the leaves wither and fall off. | Double treatment (in spring and summer) with "Fufanon", a solution of colloidal sulfur (5-10 g per 10 liters of water).
|
Removal of affected areas. |
| Pear sucker |
The pest's food source is intercellular juice. Buds and leaves shrivel and fall off. | Before the appearance of foliage - "Nitrofen" (200 g per 10 liters of water).
|
Autumn digging of soil in the near-trunk circle, removal of old bark and diseased branches. |
Harvesting and storage
Pear Cathedral is a fast-growing variety. The first crop is harvested already in the third year after planting.... The fruits ripen in early August. Unfortunately, they are not stored for a long time - only 10-12 days. Therefore, pears are consumed immediately or allowed for processing. Jam, marshmallow, marmalade, compotes and dried fruits are prepared from the fruits.
Conclusion
Pear Cathedral is a proven and beloved early-growing medium-ripening variety. The first crop is harvested three years after planting. The fruits have a thin skin and a juicy, sweet, fine-grained pulp. Pears are stored for no more than 12 days, so they are eaten fresh or quickly processed into jam, compotes, dried fruits.
The plant is demanding on the composition and fertility of the soil. Trees grow best on breathable, nutritious sandy loam chernozem. Adults tolerate drought, but young trees require regular watering and sprinkling once a week. Top dressing is applied as needed, observing the condition of the pear. Prevention helps prevent the spread of fungi and insects: dry foliage is removed and burned, the trunk circle is dug up, and sanitary pruning of branches is performed.